Sections 30.1.2, Fig. 30.1, 2 common vrrp parameters – Westermo RedFox Series User Manual
Page 663
Westermo OS Management Guide
Version 4.17.0-0
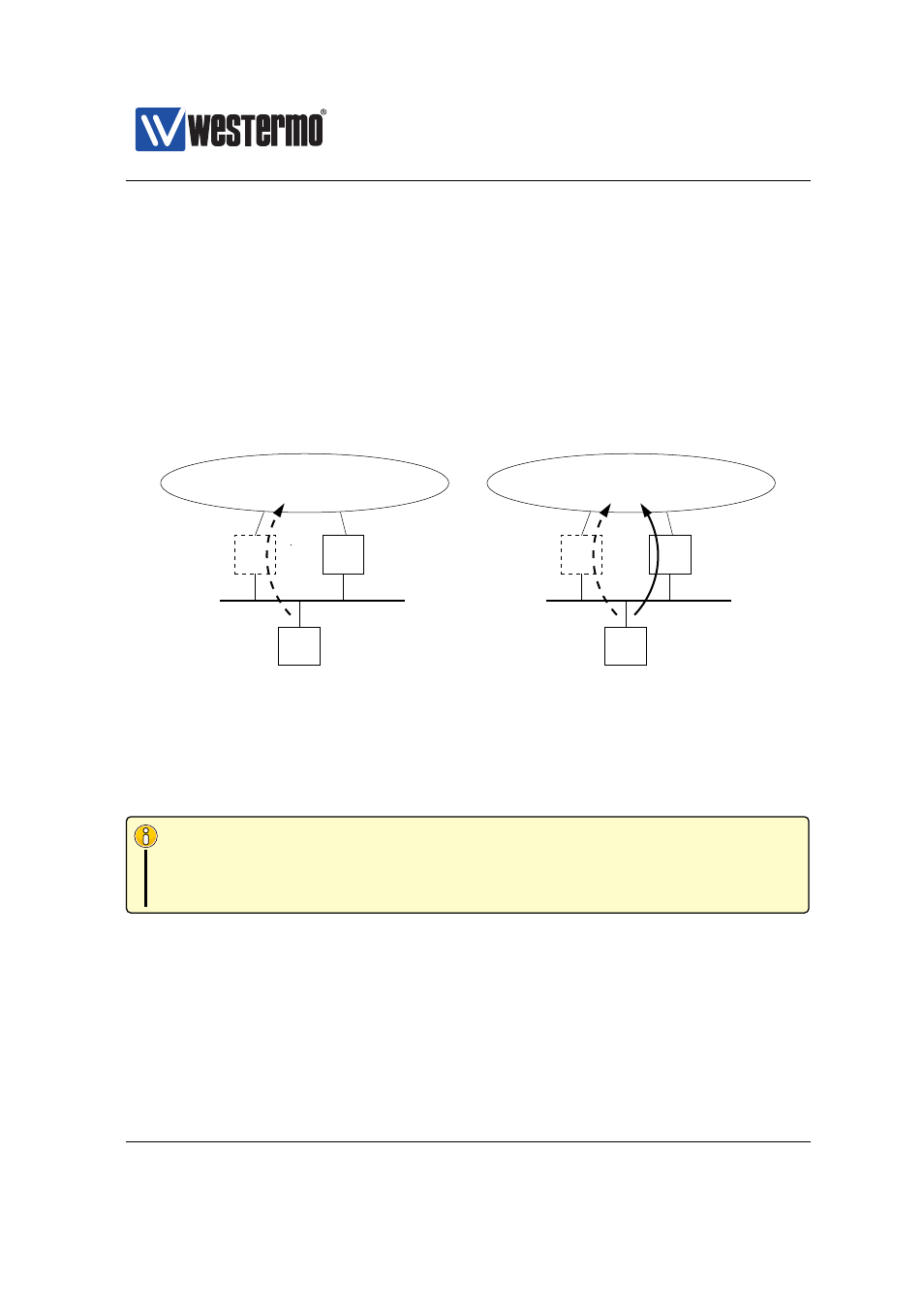
192.168.1.1. If R1 fails, the host will lose Internet connectivity even though
a redundant path (R2) happens to exists.
❼ VRRP enables routers to share a virtual IP (VIP) address. The router with the
highest priority acts as master for the VIP address, while the other routers
are backups in case the master fails.
b illustrates the use of VRRP.
R1 and R2 are both responsible for the VIP address (192.168.1.3), with R1
as master since it has higher priority (150>100). If R1 goes down, R2 will
become master of the VIP address and communication can automatically
resume. Note that the default gateway of the host is configured to the VIP
address.
192.168.1.3
Virtual IP:
Priority 150
(Master)
192.168.1.3
Virtual IP:
Priority 100
(Backup)
Default GW:
192.168.1.1
(i.e., "R1")
.1
R2
.2
H
.1
R2
.2
.78
H
192.168.1.0/24
192.168.1.0/24
.78
a)
b)
Default GW:
192.168.1.3
(i.e., "VIP")
Internet
(or Corporate Intranet)
Internet
(or Corporate Intranet)
R1
R1
Figure 30.1: Illustrating the need for VRRP to support redundancy: a) Host (H)
loses connectivity when Router 1 (R1) fails. b) Host (H) can continue to commu-
nicate even though Router 1 (R1) fails, since VRRP enables Router 2 (R2) to take
over.
Note
VRRP enables a host to have redundant routers. For redundancy ”router to
router”, dynamic routing protocols such as OSPF (
) can be used.
30.1.2
Common VRRP parameters
Some common VRRP parameters are listed below:
1. VRRP instance: WeOS allows you to configure up to 16 VRRP instances per
unit. Each instance will operate on a (VLAN) interface (e.g., vlan1) and be
➞ 2015 Westermo Teleindustri AB
663
