Fig. 23.1 – Westermo RedFox Series User Manual
Page 516
Westermo OS Management Guide
Version 4.17.0-0
192.168.0.0/24
192.168.1.0/24
192.168.2.0/24
192.168.3.0/24
DHCP pools:
A: 192.168.0.100−150/24, gw 192.168.0.1
B: 192.168.1.100−150/24, gw 192.168.1.1
C: 192.168.2.100−150/24, gw 192.168.2.1
D: 192.168.3.100−150/24, gw 192.168.3.1
.1
.1
.1
.1
.2
192.168.100.1
Server
DHCP
Router
PC1
PC2
PC3
PC4
PC5
PC6
DHCP
Relay
Agent
(RA1)
DHCP
Relay
Agent
(RA2)
DHCP
Relay
Agent
(RA3)
Intranet/Internet
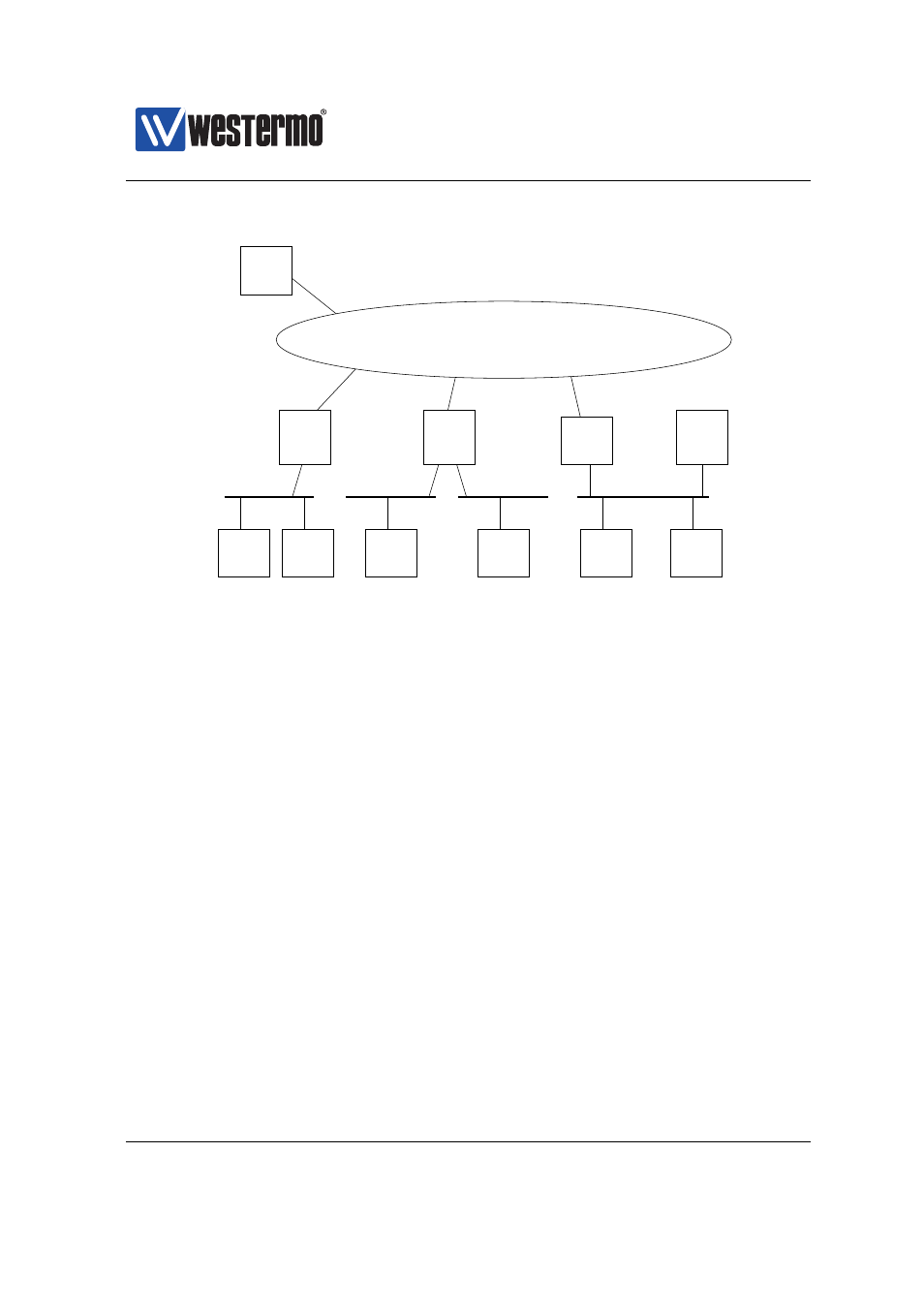
Figure 23.1: Sample topology where DHCP relay agents serve local DHCP clients,
and forwards DHCP requests to/from a central DHCP server.
❼ DHCP Servers: The relay agent must also know where to forward the DHCP
requests from the local PCs, i.e., the relay agent must be configured with IP
address of the DHCP server (here 192.168.100.1). As of WeOS v4.17.0, the
relay agent can be configured with up to two DHCP servers. When config-
uring two DHCP servers, the DHCP relay will forward the DHCP requests to
both servers, thereby providing redundancy.
DHCP servers listen to UDP port 67 by default. It is possible configure the
WeOS relay agent to forward packets to a different port on the server, see
also
and
❼ Address pools: The DHCP server will in turn be configured with appropriate
address pools (here denoted A-D), from which it can hand out addresses to
the local PCs.
When a DHCP relay agent receives a DHCP request from a PC, it will add its
local IP address into the giaddr field of the DHCP message when forwarding
it to the server (e.g., RA1 will set giaddr to 192.168.0.1) when forwarding
requests from PC1 to the DHCP server). Based on the giaddr, the DHCP
server can distinguish which pool to hand out address from (here ”A”).
516
➞ 2015 Westermo Teleindustri AB
