Westermo RedFox Series User Manual
Page 349
Westermo OS Management Guide
Version 4.17.0-0
Switch
RSTP
Switch
RSTP
Switch
RSTP
Switch
RSTP
Switch
RSTP
Switch
RSTP
Switch
RSTP
Switch
RSTP
Switch
RSTP
Switch
RSTP
Host
Host
Host
Host
Host
Host
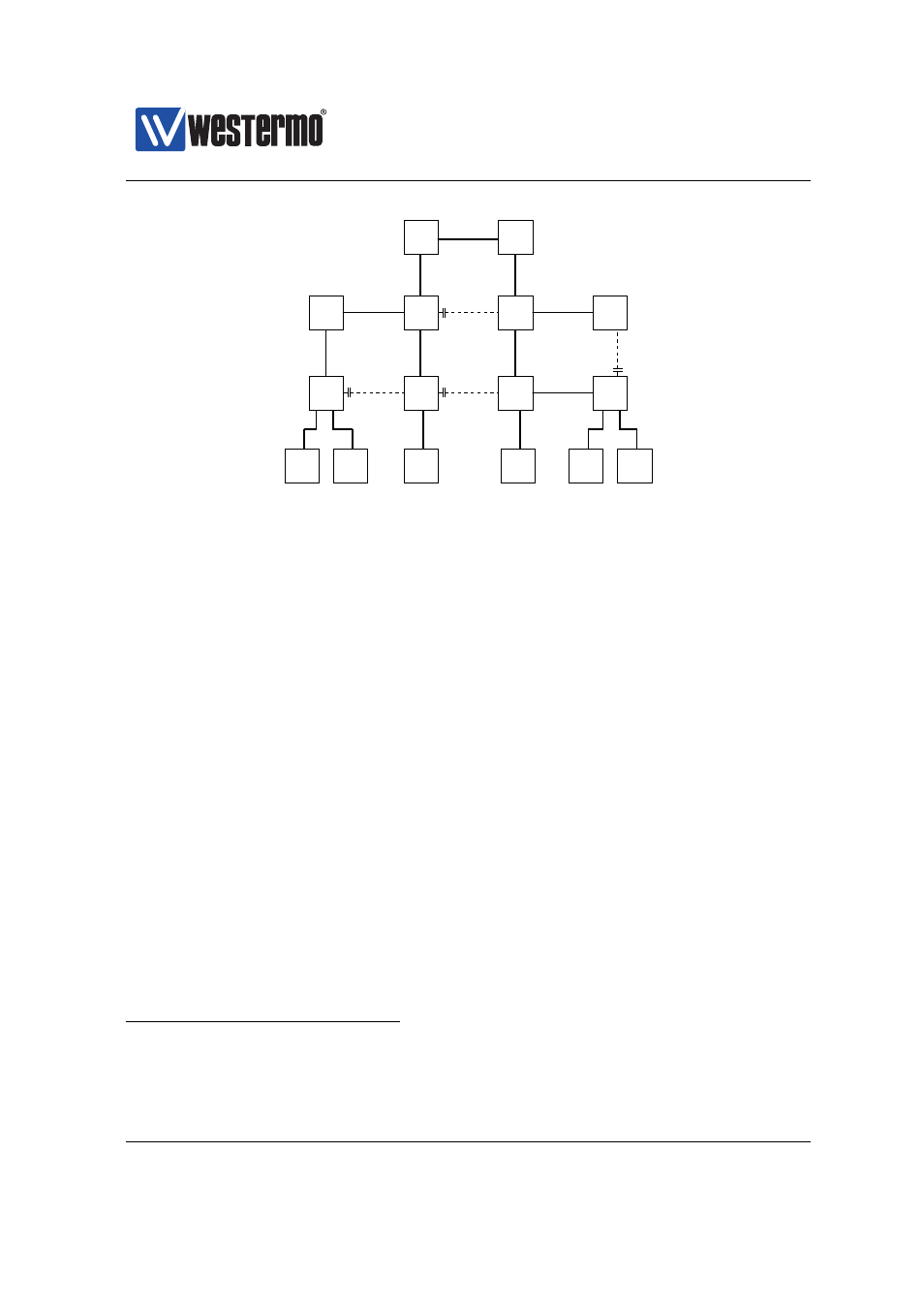
Figure 16.1: Example of RSTP creating a spanning tree. Dashed links have logi-
cally been ”cut off” from the active topology by RSTP, eliminating the loops.
plug-and-play protocol - bridges can use RSTP/STP to form a tree without need
for any configuration. However, the protocol provides a set of parameters which
the operator can use to fine-tune the network setup. Below is a list of those
parameters of specific interest for the WeOS RSTP/STP implementation:
❼ Bridge priority: Used for root bridge and designated bridge election. See
❼ Port/Path cost: Each port is assigned a ”cost”. This is used by each bridge to
find the least cost path to the root bridge as part of the tree establishment.
See
❼ Max age/Hello time: Used to detect that a STP/RSTP neighbour is down. The
max age also puts a protocol limit to the size of the network
❼ Forward Delay: Used when operating in STP mode (i.e., not RSTP). Defines
the time period by which the protocol can be sure that STP information on a
topology change has propagated from one side of the network to the other.
The STP convergence time is limited by twice the forwarding delay (plus the
time it takes to detect the topology change).
❼ Admin Edge: Ports where only end nodes connect are referred to as edge
ports. If a port is only used for connecting hosts (i.e., no risk for loops), it
1
In RSTP the Message Age field in the Hello Messages effectively acts as a hop count, counting
the distance from the Root. If the Message Age exceeds the Max Age the packet is dropped. Thus,
the setting of the Max Age parameter restricts the size of the RSTP LAN.
➞ 2015 Westermo Teleindustri AB
349
