Multiple spanning tree instance (msti), Figure 171: vlan fragmentation with stp or rstp – Allied Telesis AT-S62 User Manual
Page 509
AT-S62 Management Software Menus Interface User’s Guide
Section IV: Spanning Tree Protocols
509
Multiple
Spanning Tree
Instance (MSTI)
The individual spanning trees in MSTP are referred to as Multiple
Spanning Tree Instances (MSTIs). A MSTI can span any number of
switches. An AT-8500 Series switch can support up to 16 MSTIs at a time.
To create a MSTI, you first assign it a number, referred to as the MSTI ID.
The range is 1 to 15. (The switch comes with a default MSTI with an MSTI
ID of 0. This default spanning tree instance is discussed later in “Common
and Internal Spanning Tree (CIST)” on page 516.)
Once you have selected an MSTI ID, you need to define its scope by
assigning one or more VLANs to it. An instance can contain any number of
VLANs, but a VLAN can belong to only one MSTI at a time.
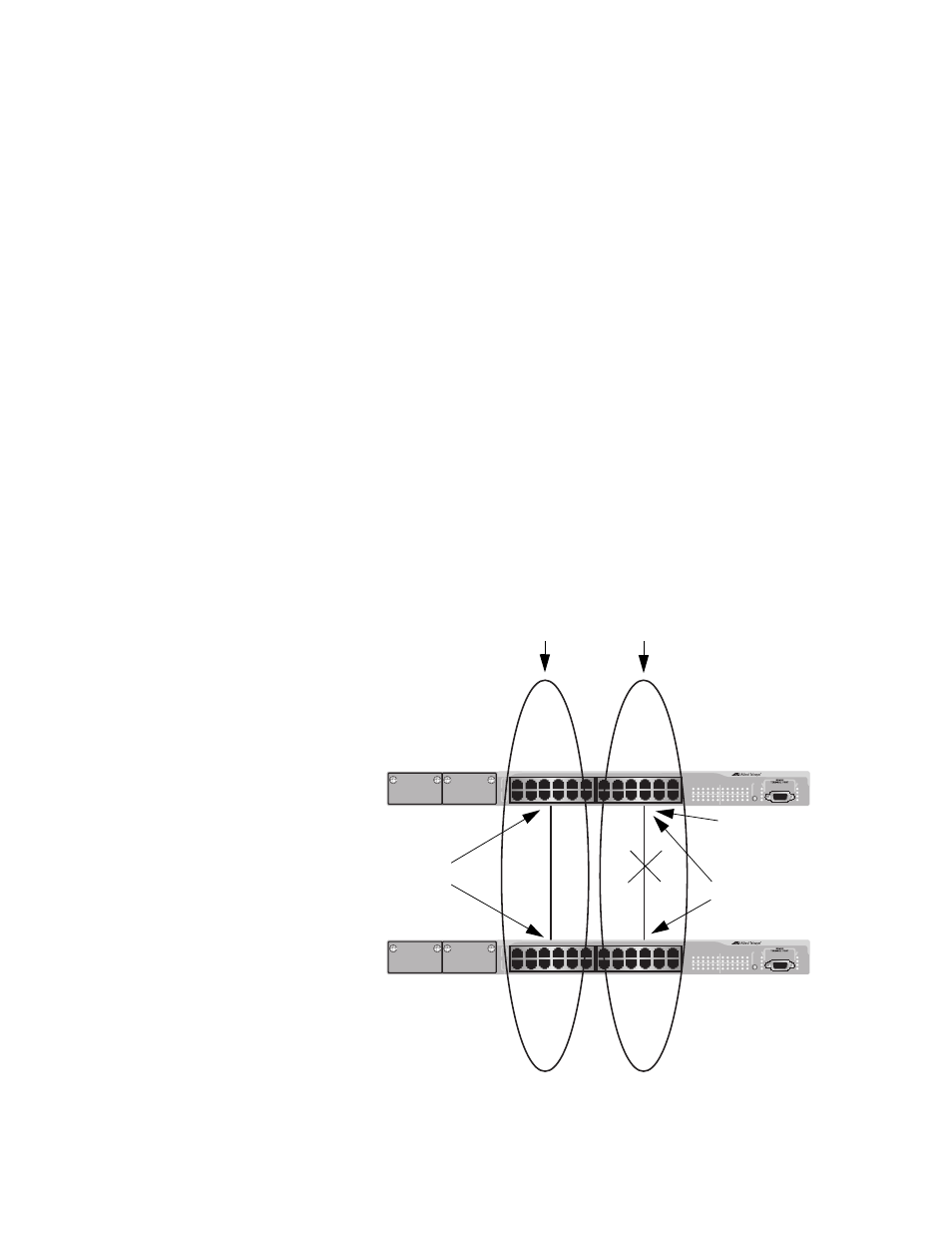
Here are a couple of examples. Figure 171 illustrates two AT-8524M
switches, each containing the two VLANs Sales and Production. The two
parts of each VLAN are connected with a direct link using untagged ports
on both switches.
If the switches were running STP or RSTP, one of the links would be
blocked because the links constitute a physical loop. Which link would be
blocked would depend on the STP or RSTP bridge settings. In the
example, the link between the two parts of the Production VLAN is
blocked, resulting in a loss of communications between the two parts of
the Production VLAN.
Figure 171. VLAN Fragmentation with STP or RSTP
LINK
MODE
LINK
MODE
FAULT
RPS
MASTER
PWR
MODE
STATUS
AT-8524M
Fast Ethernet Switch
LINK
MODE
LINK
MODE
FAULT
RPS
MASTER
PWR
MODE
STATUS
AT-8524M
Fast Ethernet Switch
Sales
VLAN
Production
VLAN
Untagged
Ports
Untagged
Ports
Blocked
Port
