Figure 82: diffserv domain example – Allied Telesis AT-S62 User Manual
Page 274
Chapter 15: Quality of Service
274
Section II: Advanced Operations
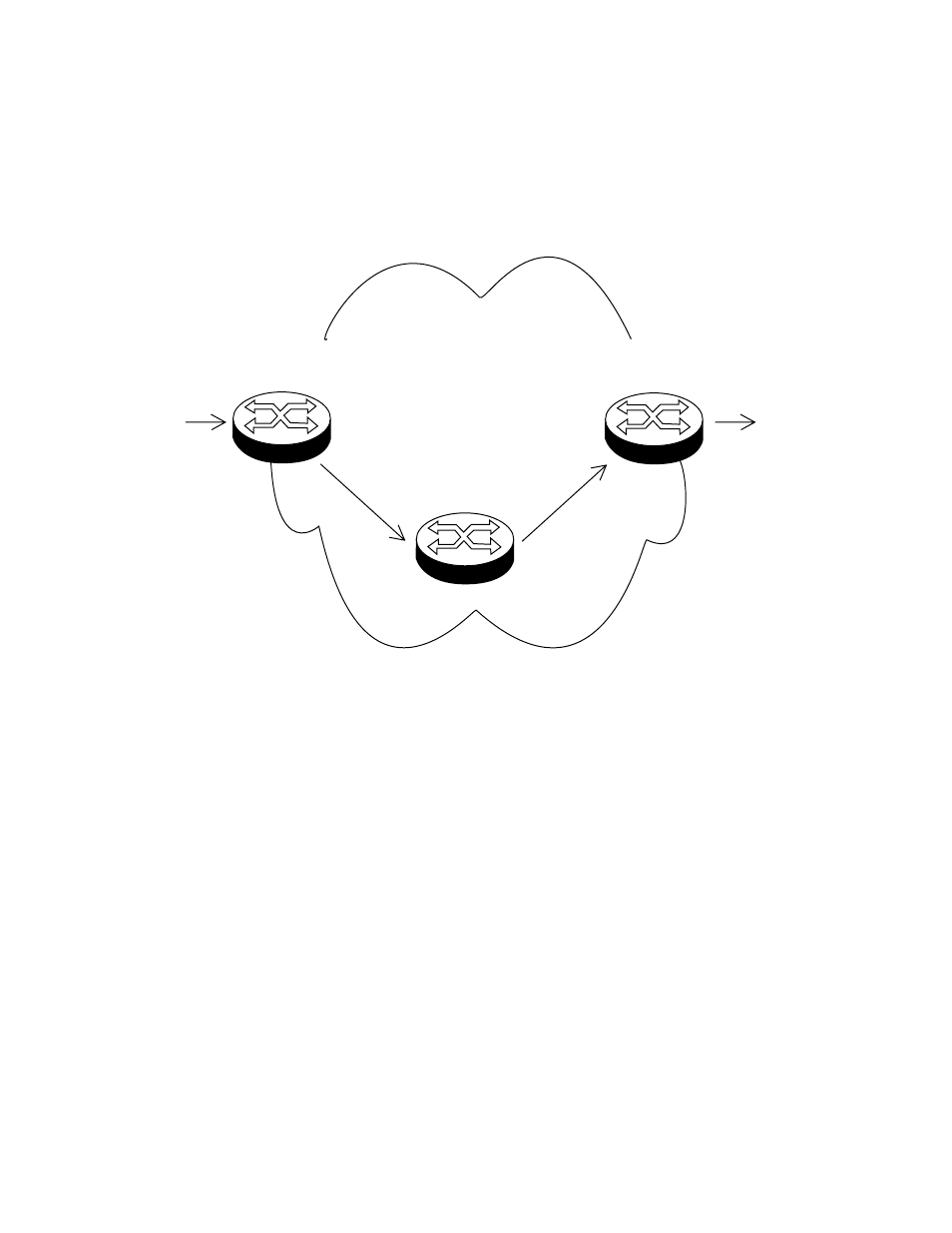
A simple example of this process is shown in Figure 82, for limiting the
amount of bandwidth used by traffic from a particular IP address. In the
domain shown, this bandwidth limit is supplied by the class of service
represented by a DSCP value of 40. In the next DiffServ domain, this
traffic is assigned to the class of service represented by a DSCP value of
3.
Figure 82. DiffServ Domain Example
To use the QoS tool set to configure a DiffServ domain:
1. As packets come into the domain at edge switches, replace their
DSCP value, if required.
Classify the packets according to the required characteristics. For
available options, see Chapter 13, “Classifiers” on page 233.
Assign the classifiers to flow groups and the flow groups to traffic
classes, with a different traffic class for each DiffServ code point
grouping within the DiffServ domain.
Give each traffic class the priority and/or bandwidth limiting controls
that are required for that type of packet within this part of the domain.
Assign a DSCP value to each traffic class, to be written into the TOS
field of the packet header.
2. On switches and routers within the DiffServ domain, classify packets
according to the DSCP values that were assigned to traffic classes on
the edge switches.
Non-DiffServ
traffic
Classify by source IP address
Mark with DSCP=40
Limit bandwidth
DiffServ Domain
Classify by DSCP=40
Limit bandwidth
Classify by DSCP=40
Limit bandwidth
Re-mark to DSCP=3
Next DiffServ
domain
