Delta DVP-ES2 User Manual
Page 627
5 . S e q u e n t i a l F u n c t i o n C h a r t
Actions of Step Points:
STL program is composed of many step points, and each step point represents a single task in the
STL control process. To perform a sequential control result, every step point needs to do 3 actions.
1.
Drive output coils
2.
Designate the transition condition
3. Designate
which
step will take over the control from the current step
Example:
SET
Y1
Y0
SET
S20
Y20
SET
S30
S10
S
X0
S20
S
X1
SET
Y1
Y0
SET
S20
Y20
SET
S30
S10
S
X0
S20
S
X1
When X0 = ON,
S20 = ON,
S10 = OFF
.
Explanation:
When S10 = ON, Y0 and Y1 will be ON. When X0 = ON, S20 will be ON and Y20 will be ON. When
S10 = OFF, Y0 will be OFF but Y1 will still be ON (SET instruction is applied on Y1, so Y1 will be ON
and latched.)
STL Transition:
When step point Sn
is ON, its following output circuit will be activated. When Sn = OFF, its following
output circuit will be OFF. The interval between the activation of the step point and its following
output circuit is one scan cycle.
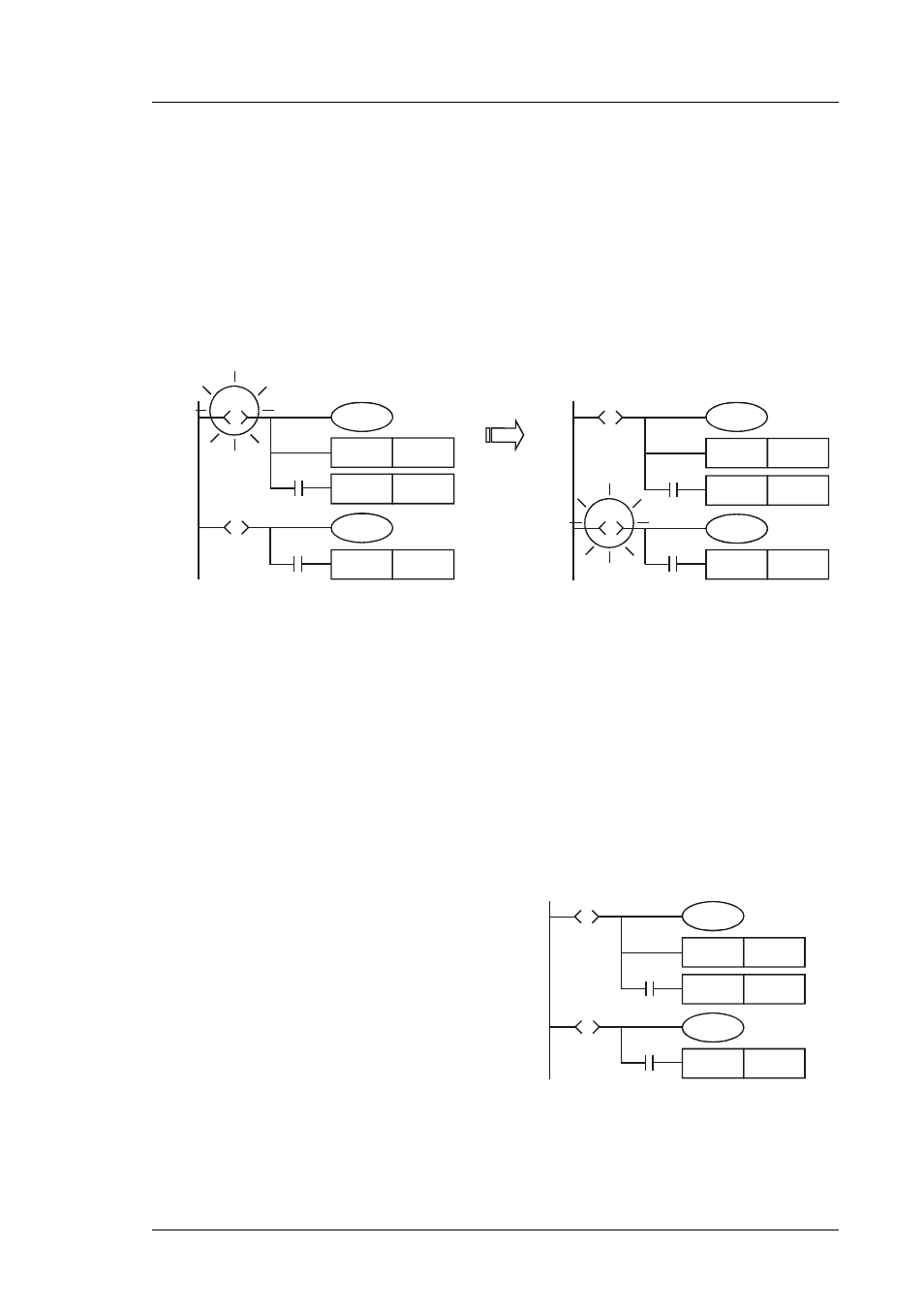
Repeated Usage of Output Coil:
4.
Output coils of the same number could be used
in different step points.
5.
See the diagram opposite. There can be the
same output device (Y0) among different steps
(sequences). Y0 remains ON when S10
transfers to S20.
6.
Y0 will be OFF due to the transition from S10 to
S20. However when S20 is ON, Y0 will be ON
again. Therefore in this case, Y0 remains ON
when S10 transfers to S20.
7.
For general ladder diagrams, repeated usages
SET
Y1
Y0
SET
S20
SET
S30
S10
S
X0
S20
S
X1
Y0
5 - 5
