7 fuzzy syntax – Delta DVP-ES2 User Manual
Page 20
D V P - E S 2 / E X 2 / S S 2 / S A2 / S X 2 / S E O p e r a t i o n M a n u a l - P r o g r a m m i n g
1-12
1.7 Fuzzy
Syntax
Generally, the ladder diagram programming is conducted according to the “up to down and left to
right” principle. However, some programming methods not following this principle still perform the
same control results. Here are some examples explaining this kind of “fuzzy syntax.”
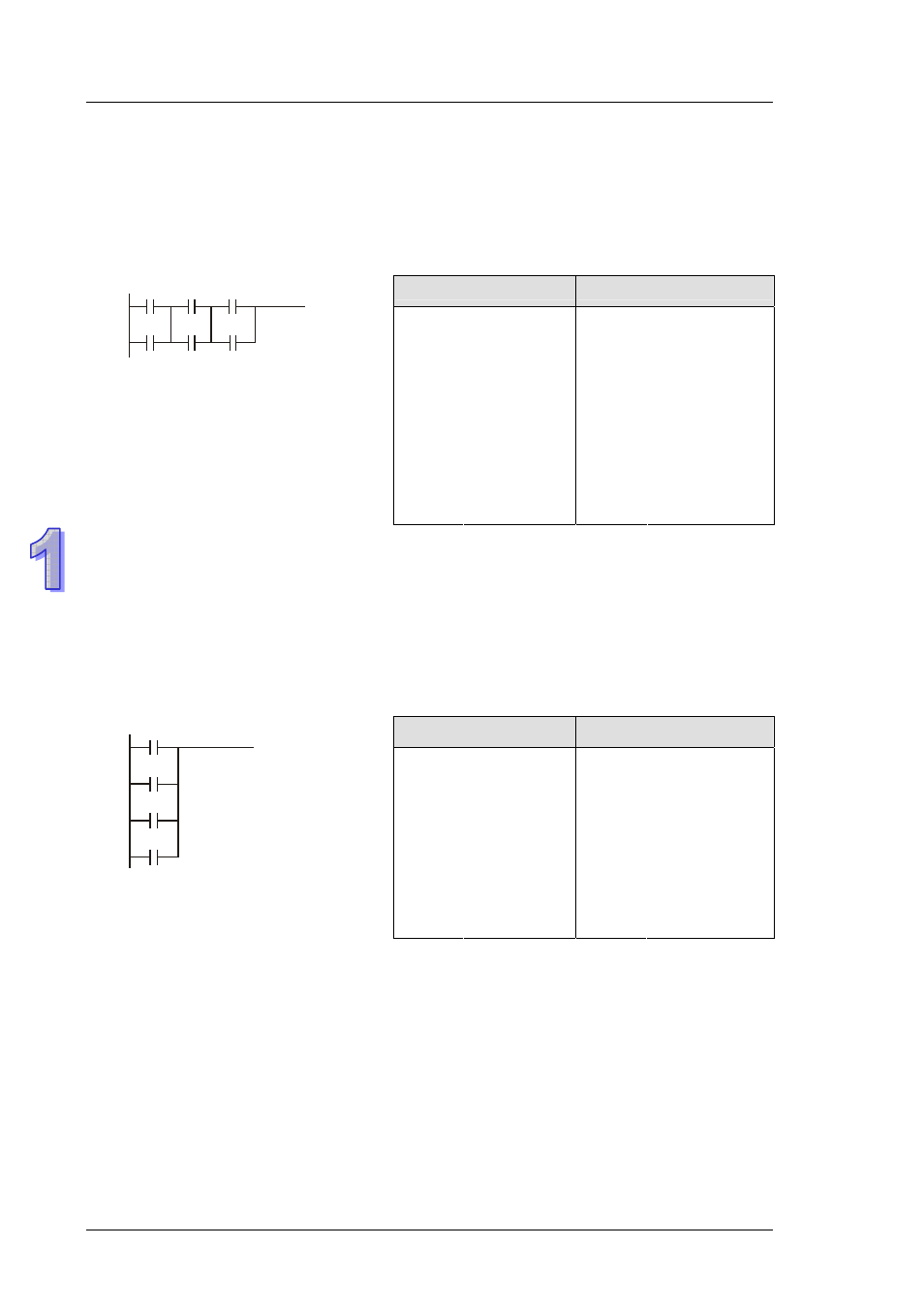
Example 1:
Better method
OK method
LD X0
LD X0
OR X1
OR X1
LD X2
LD X2
OR X3
OR X3
ANB
LD X4
LD X4
OR X5
OR X5
ANB
X0
X2
X4
X5
X3
X1
ANB
ANB
The two instruction programs can be converted into the same ladder diagram. The difference
between Better and OK method is the ANB operation conducted by MPU. ANB instruction cannot
be used continuously for more than 8 times. If more than 8 ANB instructions are used continuously,
program error will occur. Therefore, apply ANB instruction after a block is made is the better
method to prevent the possible errors. In addition, it’s also the more logical and clearer
programming method for general users.
Example 2:
Good method
Bad method
LD X0
LD X0
OR X1
LD X1
OR X2
LD X2
OR X3
LD X3
ORB
ORB
X0
X1
X2
X3
ORB
The difference between Good and Bad method is very clear. With longer program code, the
required MPU operation memory increases in the Bad method. To sum up, following the general
principle and applying good / better method when editing programs prevents possible errors and
improves program execution speed as well.
Common Programming Errors
PLC processes the diagram program from up to down and left to right. When editing ladder
diagram users should adopt this principle as well otherwise an error would be detected by WPLSoft
when compiling user program. Common program errors are listed below:
