Delta DVP-ES2 User Manual
Page 26
D V P - E S 2 / E X 2 / S S 2 / S A2 / S X 2 / S E O p e r a t i o n M a n u a l - P r o g r a m m i n g
1-18
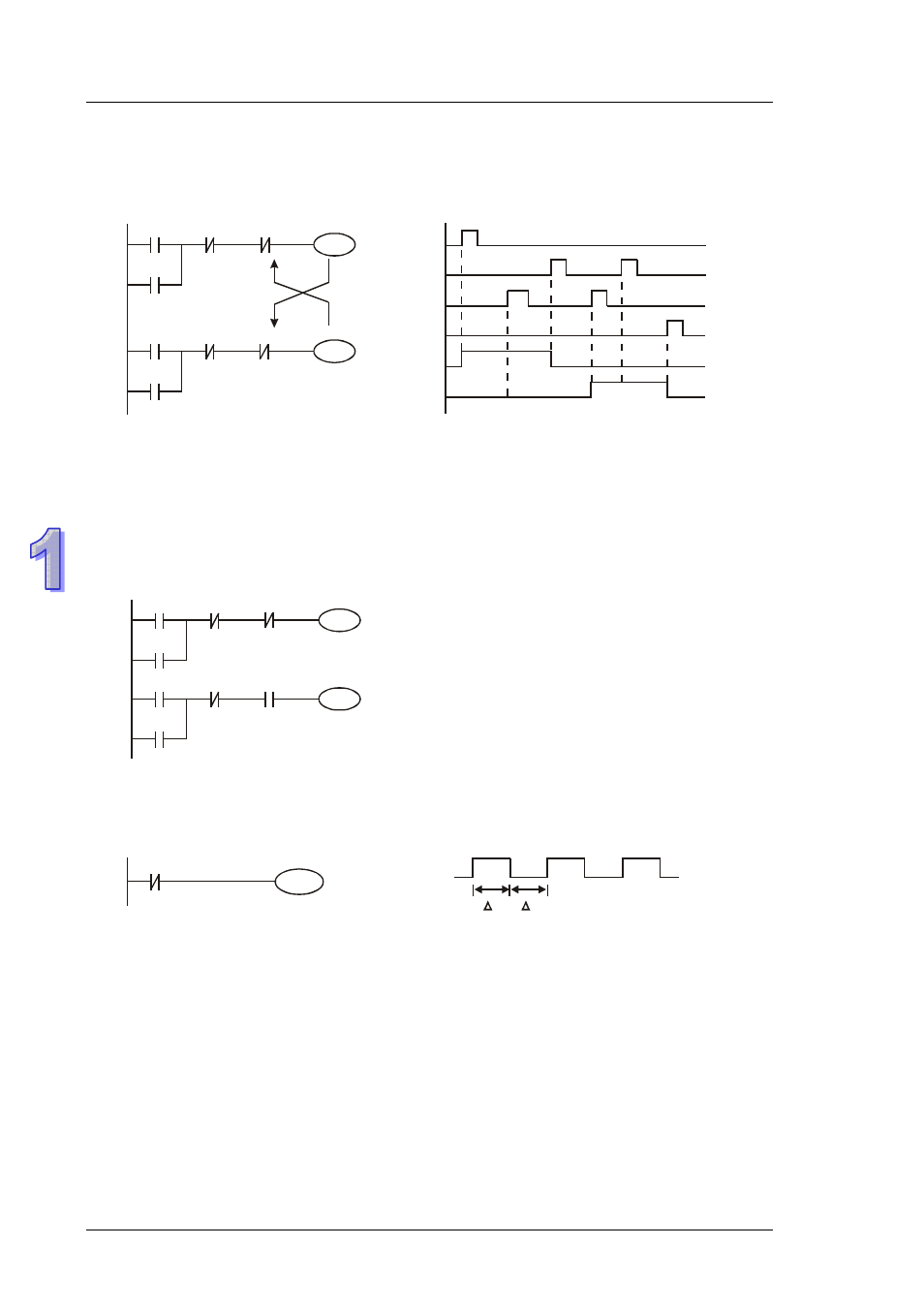
Example 6- Interlock control
X3
Y1
X1
Y1
X4
Y2
X2
Y2
Y1
Y2
X1
X3
X2
X4
Y1
Y2
NC contact Y1 is connected to Y2 output circuit and NC contact Y2 is connected Y1 output circuit.
If Y1 is ON, Y2 will definitely be OFF and vice versa. This forms an Interlock circuit which prevents
both outputs to be ON at the same time. Even if both X1 and X2 are ON, in this case only Y1 will
be enabled.
Example 7 - Sequential Control
X3
Y1
X1
Y1
X4
Y2
X2
Y2
Y1
Y2
Connect NC contact Y2 to Y1 output circuit and
NO contact Y1 to Y2 output circuit. Y1 becomes
one of the conditions to turn on Y2. In addition, Y1
will be OFF when Y2 is ON, which forms an
sequential control process.
Example 8 - Oscillating Circuit
An oscillating circuit with cycle ΔT+ΔT
Y1
Y1
Y1
T
T
In the first scan, Y1 turns on. In the second scan, Y1 turns off due to the reversed state of contact
Y1. Y1 output status changes in every scan and forms an oscillating circuit with output cycleΔ
T(ON)+ΔT(OFF)
