Delta DVP-ES2 User Manual
Page 575
3 . I n s t r u c t i o n S e t
3 - 4 5 9
Program Example 3:
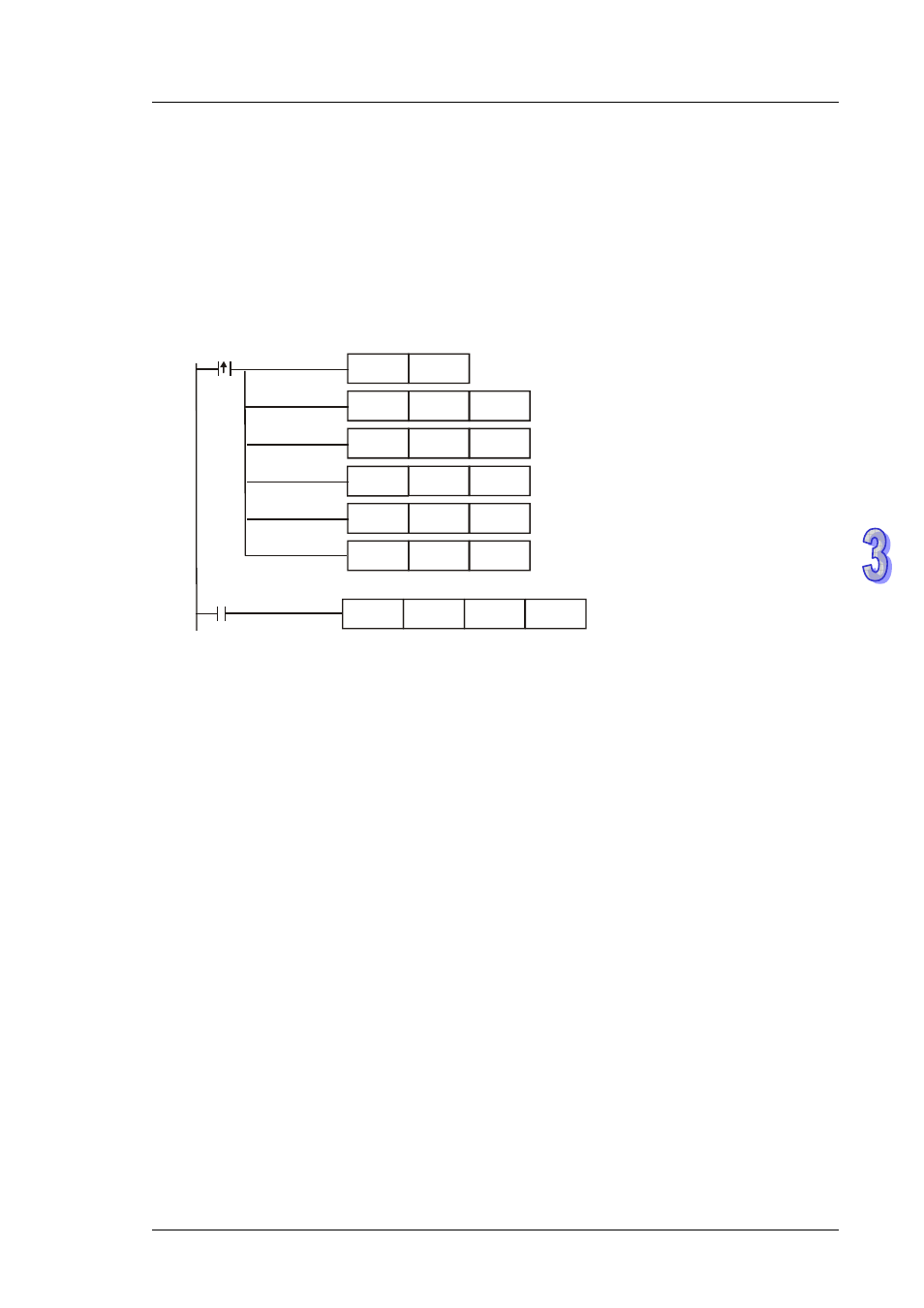
1.
Assume the source value S
1
, D100 = F500, max. source value D0 = F3000, min. source value
D2 = F200, max. destination value D4 = F500, and min. destination value D6 = F30. When X0
= ON, M1162 is set up to adopt floating point operation. DSCLP instruction executes and the
result of proportional calculation will be stored in D10.
2.
Equation: D10 = [(F500 – F200) × (F500 – F30)] ÷ (F3000 – F200) + F30 = F80.35. Round off
the result into an integer, D10 = F80.
X0
DSCLP
D100
D0
D10
X0
DMOVR
DMOVR
F3000
F200
F500
F500
F30
D0
D2
D4
D6
DMOVR
DMOVR
DMOVR
D100
SET
M1162
Points to note:
1. Range
of
S
1
for 16-bit instruction: max. source value
≥ S
1
≥ min. source value; -32,768 ~
32,767. If the value exceeds the bounds, the bound value will be used for calculation.
2.
Range of integer S
1
for 32-bit instruction: max. source value
≥ S
1
≥ min. source value;
-2,147,483,648 ~ 2,147,483,647. If the value exceeds the bounds, the bound value will be
used for calculation.
3.
Range of floating point S
1
for 32-bit instruction: max. source value
≥ S
1
≥ min. source value;
adopting the range of 32-bit floating point. If the value exceeds the bounds, the bound value
will be used for calculation.
4.
When adopting the slope equation, please note that the Max. source value must be larger than
the min. source value. However the max. destination value does not need to be larger than the
min. destination value.
