Delta DVP-ES2 User Manual
Page 136
D V P - E S 2 / S A 2 / S S 2 / S A2 / S X 2 / S E O p e r a t i o n M a n u a l - P r o g r a m m i n g
3 - 2 0
3.
Transmit K1M0, K2M0, K3M0 to 16-bit registers. Only the valid bit data will be transmitted
and the upper bits in the 16-bit register will all be filled with 0. The same rule applies when
sending K1M0, K2M0, K3M0, K4M0, K5M0, K6M0, K7M0 to 32-bit registers.
4.
When the Kn value is specified as K1~K3 (K4~K7) for a 16-bit (32-bit) operation, the empty
upper bits of the target register will be filled with “0.” Therefore, the operation result in this
case is positive since the MSB(Most significant bit) is 0.
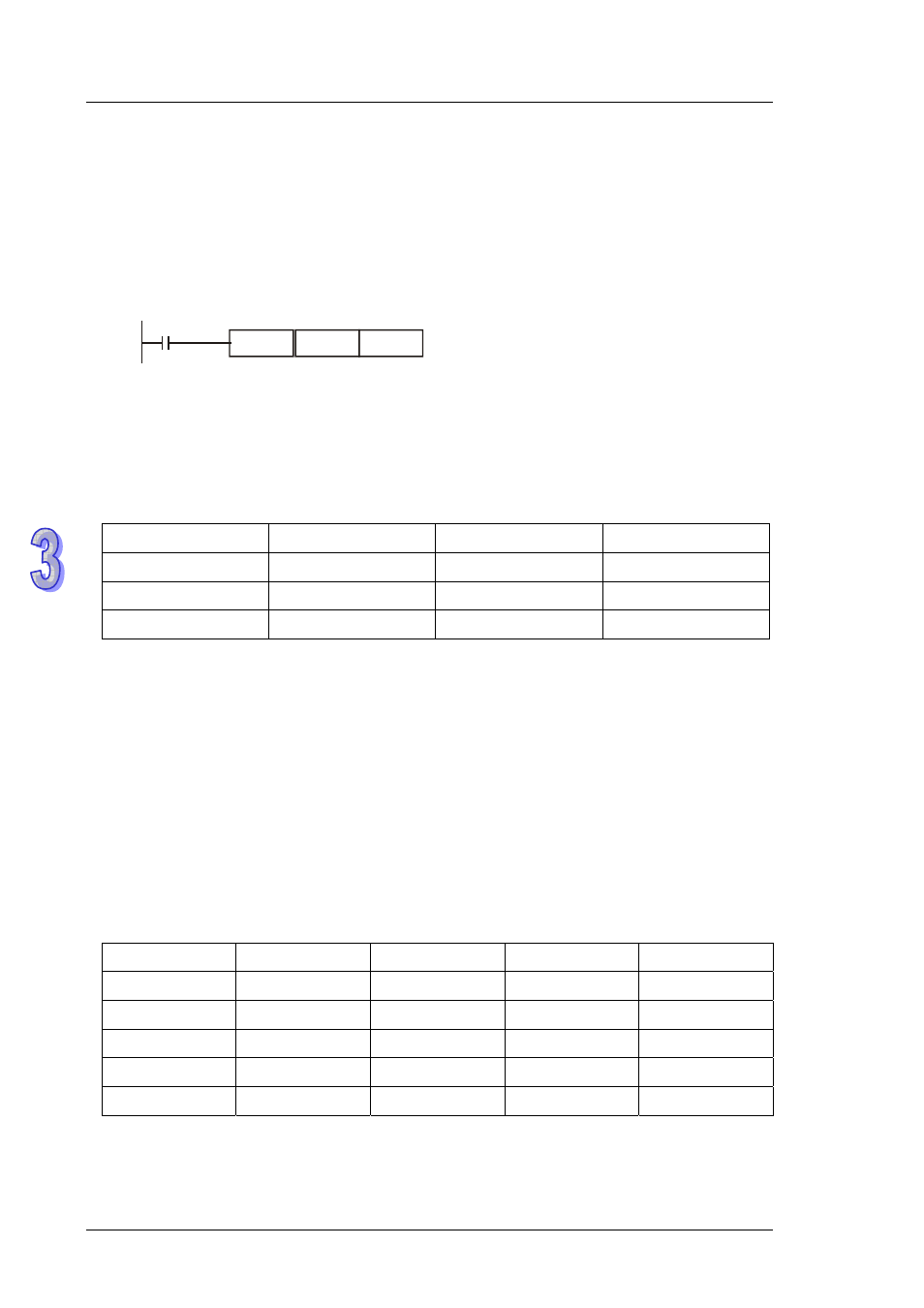
M0
K2X0
D0
BIN
The BCD value combined by X0 to X7 will be
converted to D0 as BIN value.
Assign Continuous Bit Numbers
As already explained, bit devices can be grouped into 4 bit units. The “n” in Kn defines the number
of groups of 4 bits to be combined for data operation. For data register D, consecutive D refers to
D0, D1, D2, D3, D4…; For bit devices with Kn, consecutive No. refers to:
K1X0 K1X4 K1X10
K1X14…
K2Y0 K2Y10
K2Y20
Y2X30…
K3M0 K3M12
K3M24
K3M36…
K4S0 K4S16
K4S32
K4S48…
Note: To avoid errors, please do not skip over the continuous numbers. In additoin, when K4Y0 is
used in 32-bit operation, the upper 16-bit is defined as 0. Therefore, it is recommended to use
K8Y0 in 32bit operation.
Floating Point Operation
The operations in DVP-PLC are conducted in BIN integers. When the integer performs division,
e.g. 40 ÷ 3 = 13, the remainder will be 1. When the integer performs square root operations, the
decimal point will be left out. To obtain the operation result with decimal point, please use floating
point instructions.
Application instructions revelant to floating point:
FLT DECMP
DEZCP
DMOVR
DRAD
DDEG DEBCD DEBIN DEADD DESUB
DEMUL DEDIV DEXP DLN
DLOG
DESQR DPOW INT
DSIN
DCOS
DTAN DASIN DACOS
DATAN
DADDR
DSUBR DMULR DDIVR
