How mct works, Mct benefits – Brocade Multi-Service IronWare Switching Configuration Guide (Supporting R05.6.00) User Manual
Page 622
592
Multi-Service IronWare Switching Configuration Guide
53-1003036-02
About Multi-Chassis Trunk (MCT)
18
In an MCT scenario, all links are active and can be load shared to increase bandwidth. In addition,
traffic restoration can be achieved in milliseconds after an MCT link failure or MCT switch failure.
MCT is designed to increase network resilience and performance.
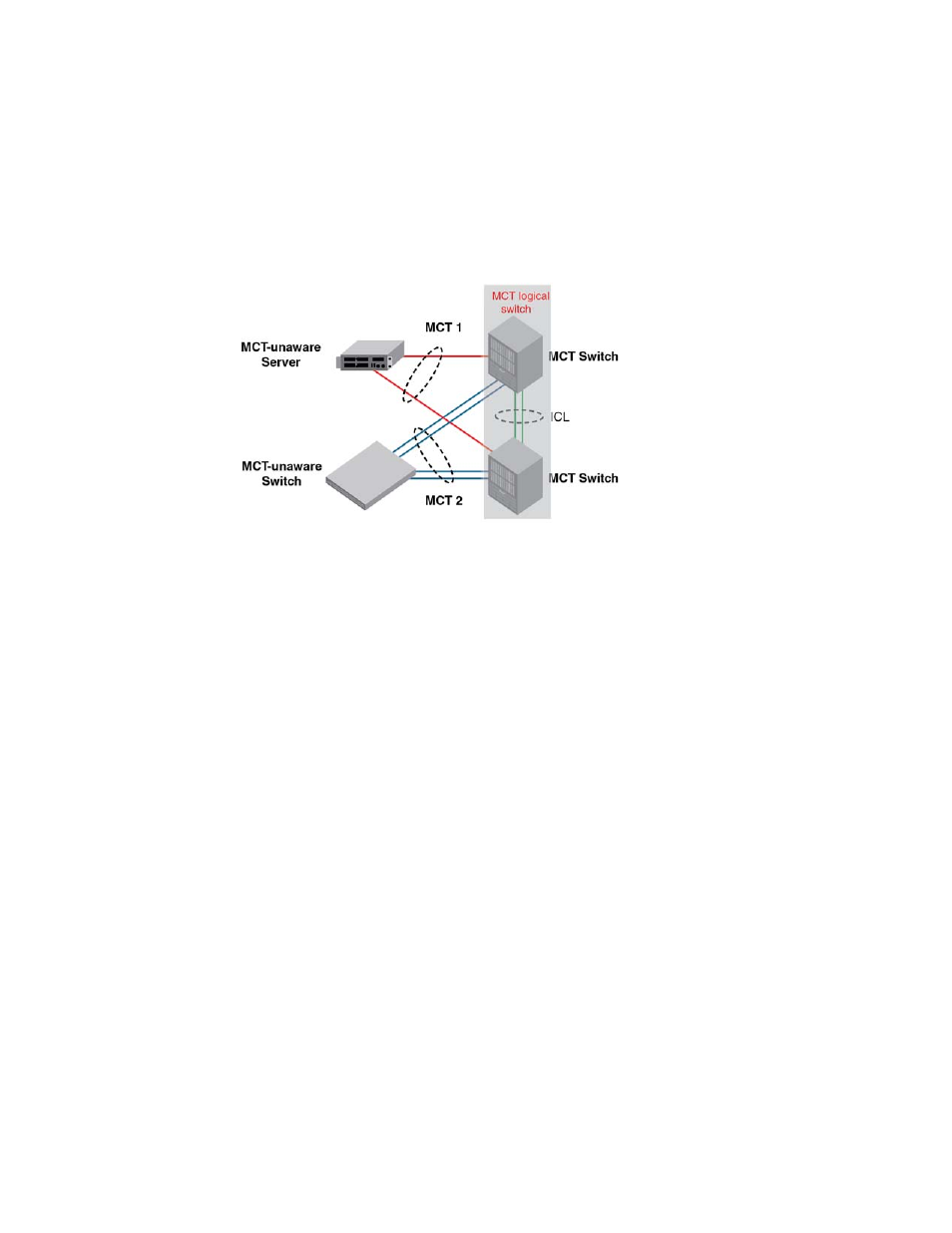
FIGURE 171
Chassis trunk example
MCT Benefits
MCT provides the following benefits:
•
Provides link-level and switch-level redundancy.
•
Provides increased capacity because it utilizes all links (including redundant ones) for traffic
transport. This contrasts with the use of the Spanning Tree Protocol, which does not use
redundant links for transporting traffic.
•
Provides traffic restoration in tens of milliseconds in case of link or switch failures.
•
Allows servers and switches to have redundant connections to two switches and to fully utilize
all links (including redundant ones) for traffic transport.
•
Allows servers and switches to use standard link aggregation (802.3ad) to connect to
redundant switches.
•
MCT is easily deployed while enhancing existing multilayer switching without fundamentally
changing the architecture.
How MCT works
The MCT is made up of the following:
•
Sub-second failover in the event of a link, module, switch fabric, control plane, or node failure
•
Layer 2 and Layer 3 forwarding (when using fast path forwarding) at the first hop regardless of
VRRP-E state.
•
Flow based load balancing rather than VLANs sharing across network links
•
Ability to provide the resiliency regardless of the traffic type layer 3, layer 2 or non-IP (legacy
protocols).
