Protocol-based vlans – Brocade Multi-Service IronWare Switching Configuration Guide (Supporting R05.6.00) User Manual
Page 196
166
Multi-Service IronWare Switching Configuration Guide
53-1003036-02
VLANs
7
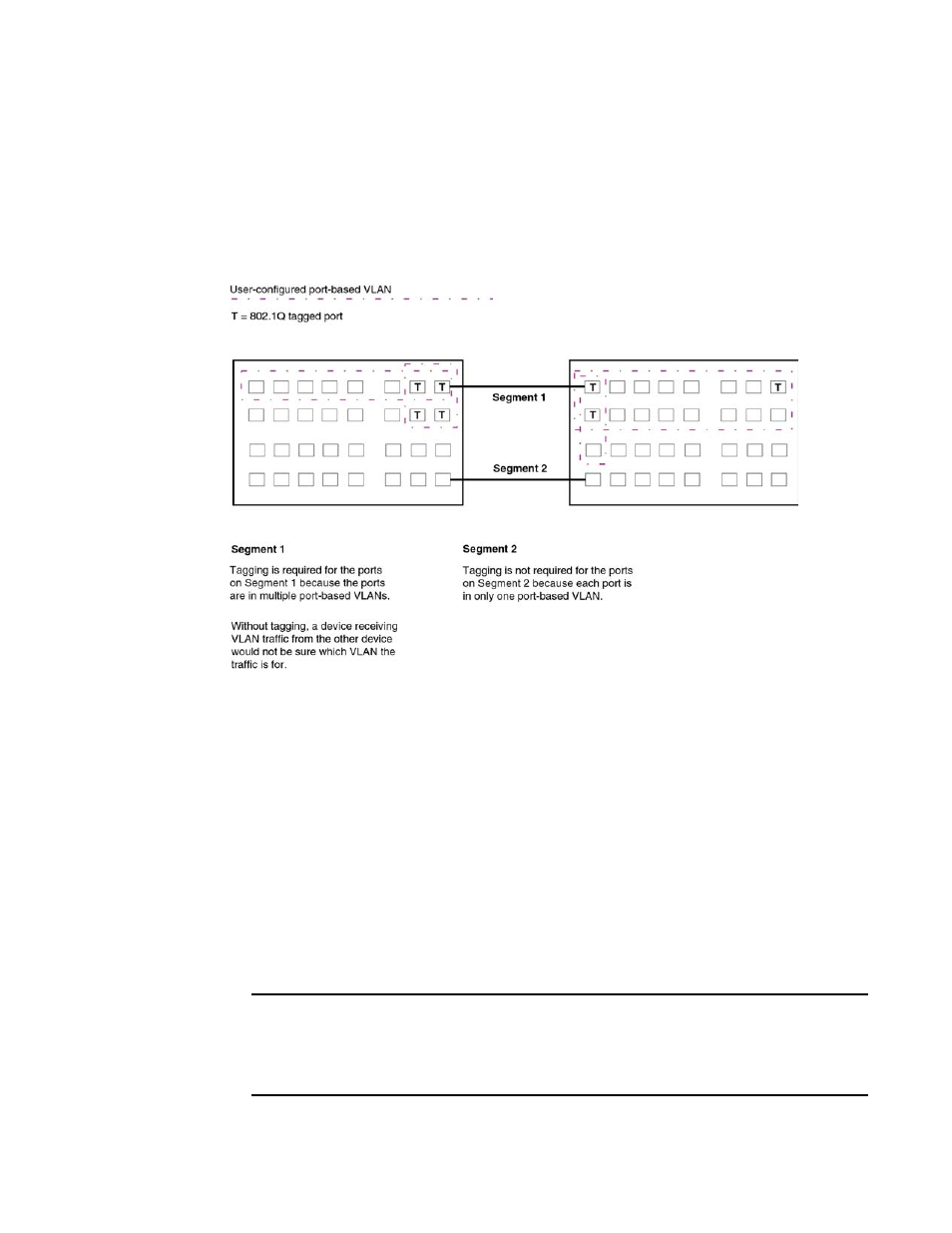
If you configure a VLAN that spans multiple devices, you need to use tagging only if a port
connecting one of the devices to the other is a member of more than one port-based VLAN. If a port
connecting one device to the other is a member of only a single port-based VLAN, tagging is not
required.
shows an example of two devices that have the same Layer 2 port-based VLANs
configured across them. Notice that only one of the VLANs requires tagging.
FIGURE 9
VLANs configured across multiple devices
Protocol-based VLANs
Interfaces that belong to a port-based VLAN can further be divided into Layer 3 broadcast domains
by using protocol-based VLANs. Protocol-based VLANs accept broadcasts of a specified protocol
type. For example, an IP subnet VLAN accepts broadcasts for the specified IP subnets only. This
feature enables you to limit the amount of broadcast traffic to end-stations, servers, and routers.
In a Brocade device, you can configure the following protocol-based VLANs within a port-based
VLAN:
•
AppleTalk - The device sends AppleTalk broadcasts to all ports within the AppleTalk protocol
VLAN.
•
IP - The device sends IP broadcasts to all ports within the IP protocol VLAN.
•
IPX - The device sends IPX broadcasts to all ports within the IPX protocol VLAN.
•
IPv6 - The device sends IPv6 broadcasts to all ports within the IPv6 protocol VLAN.
NOTE
You can configure a protocol-based VLAN as a broadcast domain for IPv6 traffic. When the
Brocade device receives an IPv6 multicast packet (a packet with 06 in the version field and
0xFF as the beginning of the destination address), the Brocade device forwards the packet to
all other ports in the VLAN except to the port that received the packet.
