Forced switch – Brocade Multi-Service IronWare Switching Configuration Guide (Supporting R05.6.00) User Manual
Page 554
524
Multi-Service IronWare Switching Configuration Guide
53-1003036-02
Forced switch
15
Forced switch
Forced switch (FS) is an operator-initiated mechanism that moves the blocking role of the RPL to a
different ring link followed by unblocking the RPL, even if one or more failed links exist in the ring.
The node configured to initiate an FS blocks the port and sends out a R-APS (FS) to inform other
nodes to unblock any blocked ports (including failed ones) as long as no other local request with
higher priority exists. The RPL owner unblocks the RPL and flushes the FDB.
Any node accepting a R-APS (FS) message stops transmitting R-APS messages.
Multiple FS instances can be configured in the topology even when the topology is in the same
segment where an FS is being cleared by no command. When an operator clears an FS on the
same node where an FS is configured, this node keeps the port in the blocking state, sends out a
R-APS (NR) to adjacent nodes, and starts the guard timer. Other nodes that receive the R-APS (NR)
forward the message. When the RPL owner receives this message, the RPL owner starts the WTB
timer. When the WTB timer expires, the RPL owner sends out a R-APS (NR, RB), blocks the RPL, and
flushes the FDB. Other nodes in the topology that receive the R-APS (NR, RB) unblock any
non-failed port and flush the FDB.
An FS request can be accepted no matter what state the topology is in. Since the local FS and
R-APS (FS) are higher priority than SF; an SF occur i ng later than FS will not trigger the SF process.
In addition, because the local FS and R-APS (FS) are higher priority than SF, when a node receives
a R-APS (FS) without any local higher priority event, it will unblock any blocked port. The node with
the failed link also unblocks the blocked port; but because the link has failed, the topology is
broken into segments.
Since the local FS and R-APS (FS) are higher priority than a local SF clear when the link failure is
removed without any local higher priority event, the nodes with the recovering link do not trigger SF
recovery.
After the operator clears the FS condition on the node, the node starts the guard timer and sends
out a R-APS (NR). When the RPL owner receives a R-APS(NR), it stops the WTB timer and starts the
guard timer. The RPL owner blocks the RPL and sends out a R-APS (NR, RB). Any node receiving a
R-APS (NR, RB) unblocks the non-failed blocked port. If the guard timer is still running on the node
with previous FS, this node ignores R-APS messages until the guard timer expires. The topology is
again broken into segments. After this node processes the R-APS (NR, RB), however, it unblocks the
blocked node; and the topology is in a loop free state and in one segment.
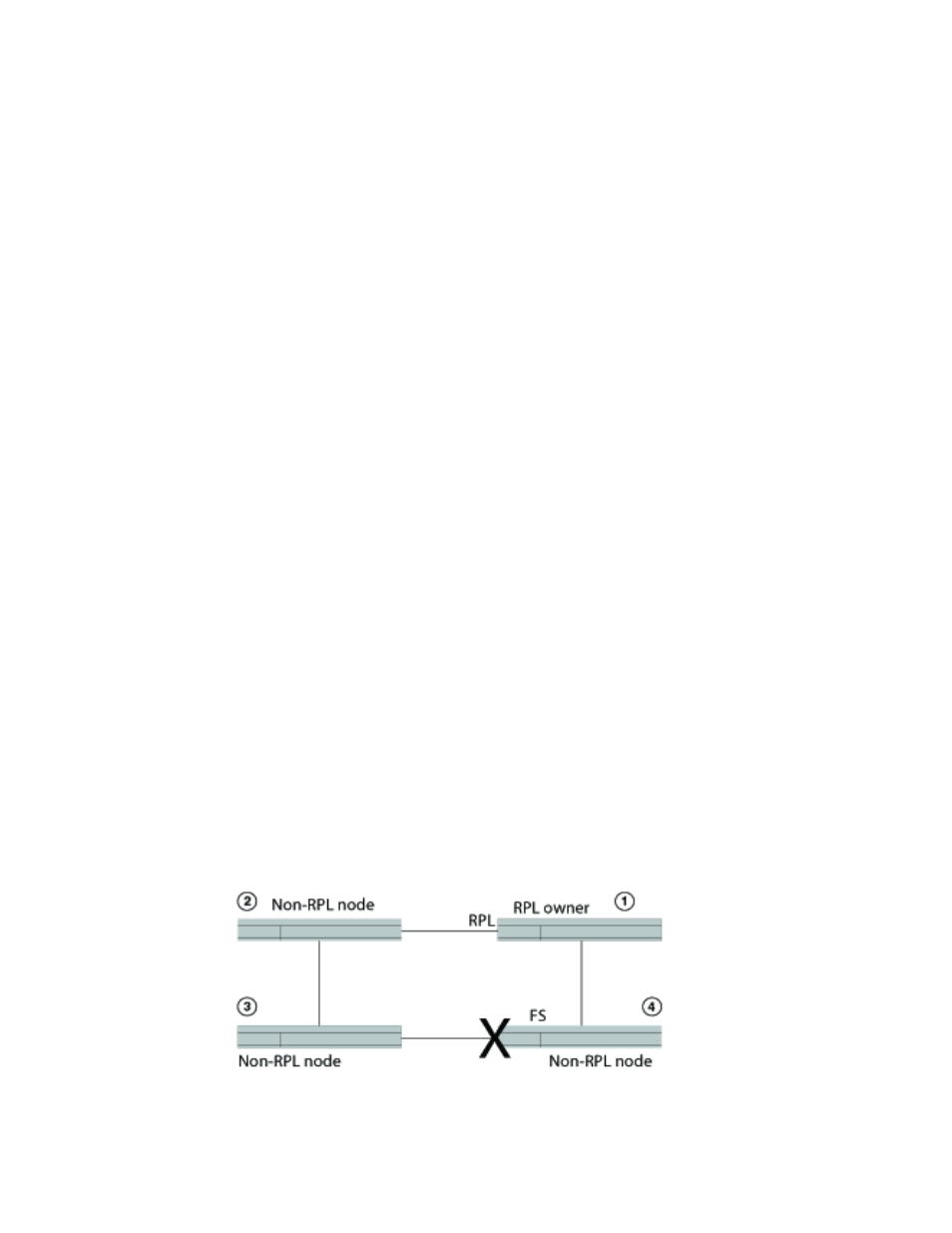
shows a port failure on ERN 4.
FIGURE 140
Single forced switch scenario
