Figure 66, Configuring mstp – Brocade Multi-Service IronWare Switching Configuration Guide (Supporting R05.6.00) User Manual
Page 386
356
Multi-Service IronWare Switching Configuration Guide
53-1003036-02
802.1s Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol
12
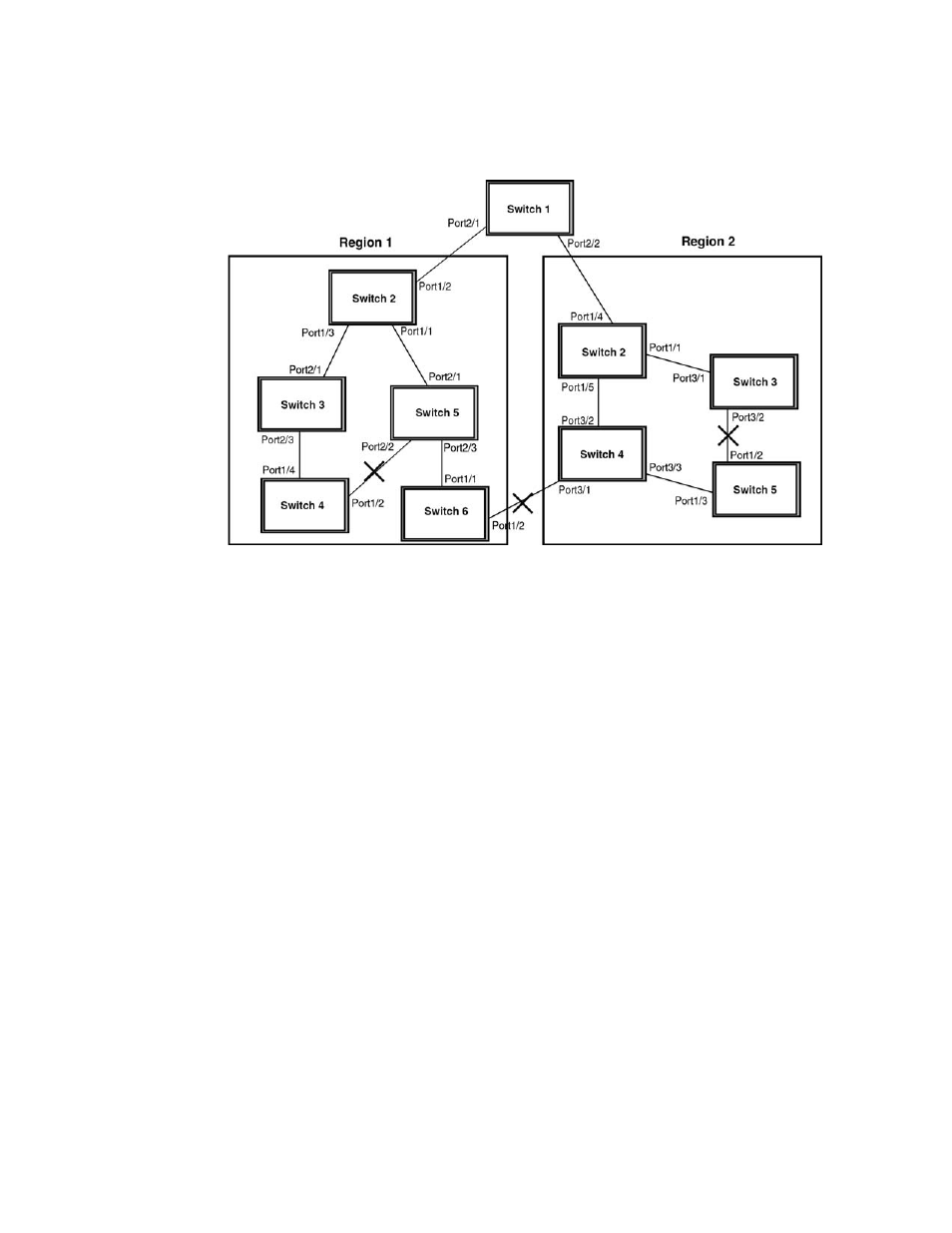
FIGURE 66
MSTP configured network
The following definitions describe the STP instances that define an MSTP configuration:
Common Spanning (CST) – MSTP runs a single instance of spanning tree, called the Common
Spanning Tree (CST), across all the bridges in a network. This instance treats each region as a
single bridge. It all other ways, it operates exactly like Rapid Spanning Tree (RSTP).
Internal Spanning Tree (IST) – Instances of spanning tree that operate within a defined region
are called ISTs (Internal Spanning Tree).
Common and Internal Spanning Trees (CIST) – This is the default MSTP instance 0. It contains
all of the ISTs and all bridges that are not formally configured into a region. This instance
interoperates with bridges running legacy STP and RSTP implementations.
Multiple Spanning Tree Instance (MSTI) – The MSTI is identified by an MST identifier (MSTid)
value between 1 and 4094. This defines an individual instance of an IST. One or more VLANs
can be assigned to an MSTI. A VLAN cannot be assigned to multiple MSTIs.
MSTP Region – These are clusters of bridges that run multiple instances of the MSTP protocol.
Multiple bridges detect that they are in the same region by exchanging their configuration
(instance to VLAN mapping), name, and revision-level. Therefore, if you need to have two
bridges in the same region, the two bridges must have identical configurations, names, and
revision-levels.
Configuring MSTP
To configure a device for MSTP for 1 or more VLANs that have the same Layer 2 topology, you could
configure the name and the revision on each device that is being configured for MSTP. This name is
unique to each device. You must then create an MSTP Instance and assign an ID. VLANs are then
assigned to MSTP instances. These instances must be configured on all devices that interoperate
with the same VLAN assignments. Port cost, priority and global parameters can then be configured
for individual ports and instances. In addition, operational edge ports and point-to-point links can
be created and MSTP can be disabled on individual ports.
