6 registers, 1 register designation methods – Yaskawa MP920 User's Manual Design User Manual
Page 103
3.6 Registers
3-29
3
3.6
Registers
This section explains the types of register used by MP920 user programs and how these registers
are used.
3.6.1
Register Designation Methods
Registers can be designated by direct designation of the register number or by symbolic des-
ignation. These two types of register designation can be used together in the same user pro-
gram. When symbolic designation is used, the correspondence between the symbols and the
register numbers is defined in the symbol table that is described later.
Table 3.12 shows the register designation methods.
Table 3.12 Register Designation Methods
Designation Type
Description
Direct Register
Number Designation
Bit registers:
MB00100A
Integer registers:
MW00100
Double-length integer registers: ML00100
Real # registers:
MF00100
Address registers:
MA00100
: For subscripts, add the subscript i or j after the register number.
Symbol Designation
Bit registers:
RESET-A.
Integer registers:
STIME-H.
Double-length integer registers: POS-REF.
Real # registers:
IN-DEF.
Address registers:
PID-DATA.
↓
Address registers are designated using up to 8 alphanumeric characters.
: For subscripts, add a period (.) and then the subscript i or j after the sym-
bol.
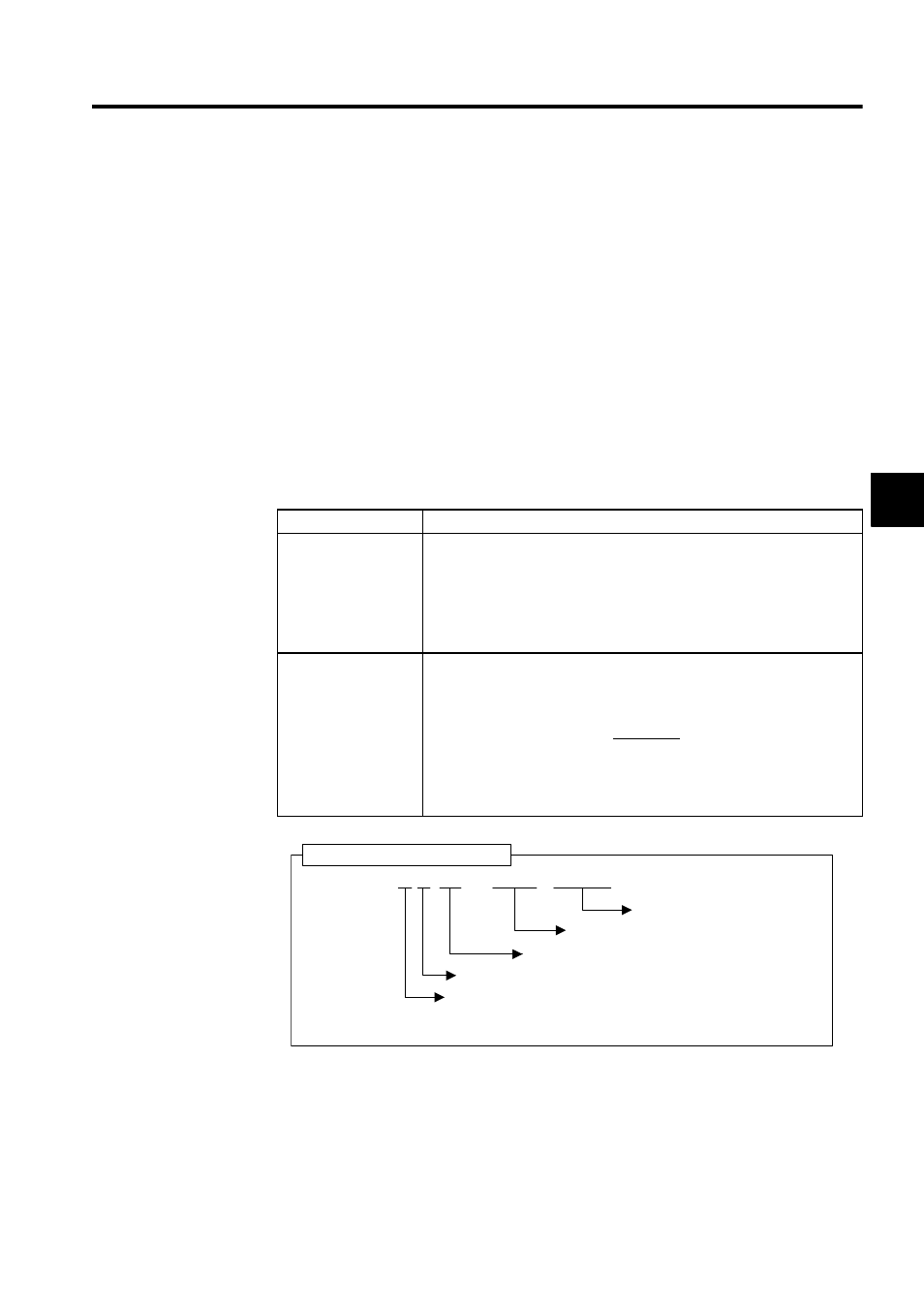
Direct Register Number Designation
Register number: V T
No.
[Bit No.]
[Subscript]
Can designate the subscript i or j.
When T = B (bit) (hexadecimal, 0 to F)
Register No. for V (decimal or hexadecimal)
Data type of V (T: B, W, L, F, A)
Type of register
Drawing: (V: S, M, I, O, C, #, D)
Function: (V: S, M, I, O, C, #, D, X, Y, Z, A)
