Index registers (i, j, k) – Maple Systems MAPware-7000 User Manual
Page 298
298
MAPware-7000 Programming Manual
1010-1040, Rev. 02
I/O Configuration
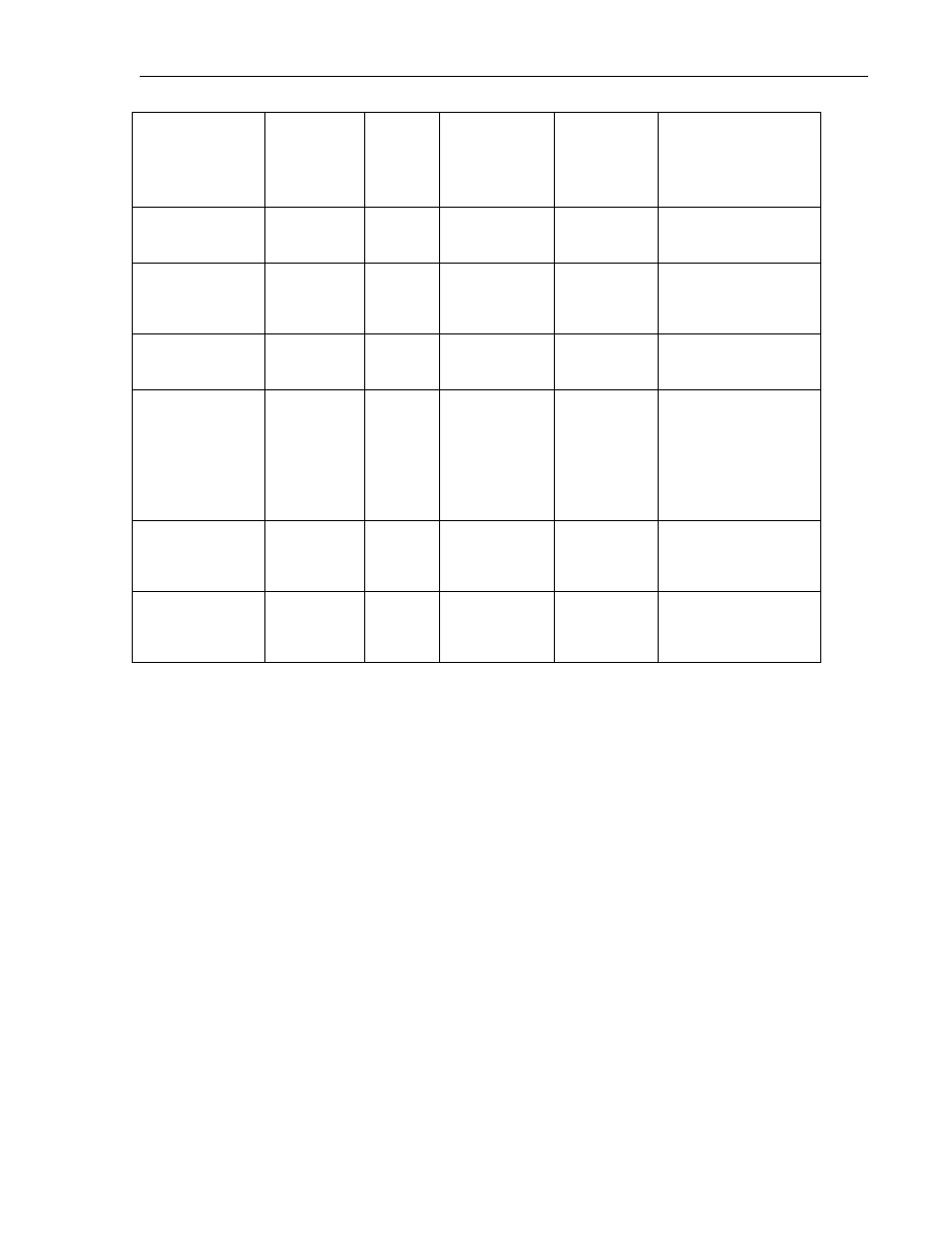
Registers
MW0000 or
MW0000_00
0-3100, 0-
15
Bit or Register
(2 bytes)
Read/Write
IO registers for base
expansion modules Note:
IO Coils and IO Registers
share same memory
System Coils
S00000
0-99
Bit Only
Read/Write
Status and control bits
for HMC
System Registers
SW0000 or
SW0000_00
0-255,
0-15
Bit or Register
(2 bytes)
Read/Write
Status and control
registers for HMC
Internal Coils
B00000
0-4095
Bit Only
Read/Write
General Purpose Internal
Coils
Internal Registers
BW0000
0-255
Register Only
(2 bytes)
Read/Write
General Purpose Internal
Registers
Note: Internal Coils and
Internal Registers share
same memory
Data Registers
D00000 or
D00000_00
0-4095, 0-
15
Bit or Register
(1, 2 or 4 bytes)
Read/Write
General Purpose
Registers
Retentive Registers
R00000
0-1399
2
Register Only
(1, 2 or 4 bytes)
Read/Write
Non-volatile memory
registers
1 – The HMC7030 supports C.0000-C.0099
2 – The HMC7030 supports R0-R299
Note: Memory areas are accessible in the Tag Database under Node Name: [Operator Panel] None (-)
Generally speaking, the entire memory area of the HMC can be used for any purpose. However,
the memory is split into several classifications so that they can be used for special purposes.
Index Registers (I, J, K)
The HMC7000 Series has three 16-bit index registers (I, J, and K) that perform a specific purpose.
As the name implies, these registers are used to ‘index’ or act as pointers to multiple registers.
This method is called ‘indirect addressing’ because the HMC7000 does not read/write to the
specified address directly. Instead, the target address is determined indirectly by referencing
the base address and the value read from the index register.
For example, if the MOV WORD instruction is used in a Ladder Logic Block, you can assign an
index register to one of the operands:
