Preparing to print separations – Adobe InDesign User Manual
Page 721
Preparing to print separations
Host-based separations
In-RIP separations
Creating separations
Prepare your document for color separations
Outputting spot colors
View the process color equivalents of a spot color
Print an object on all color plates
Printing gradients as separations
Printing a composite
Preview color separations
For detailed information and instructions, click the links below.
Creating separations
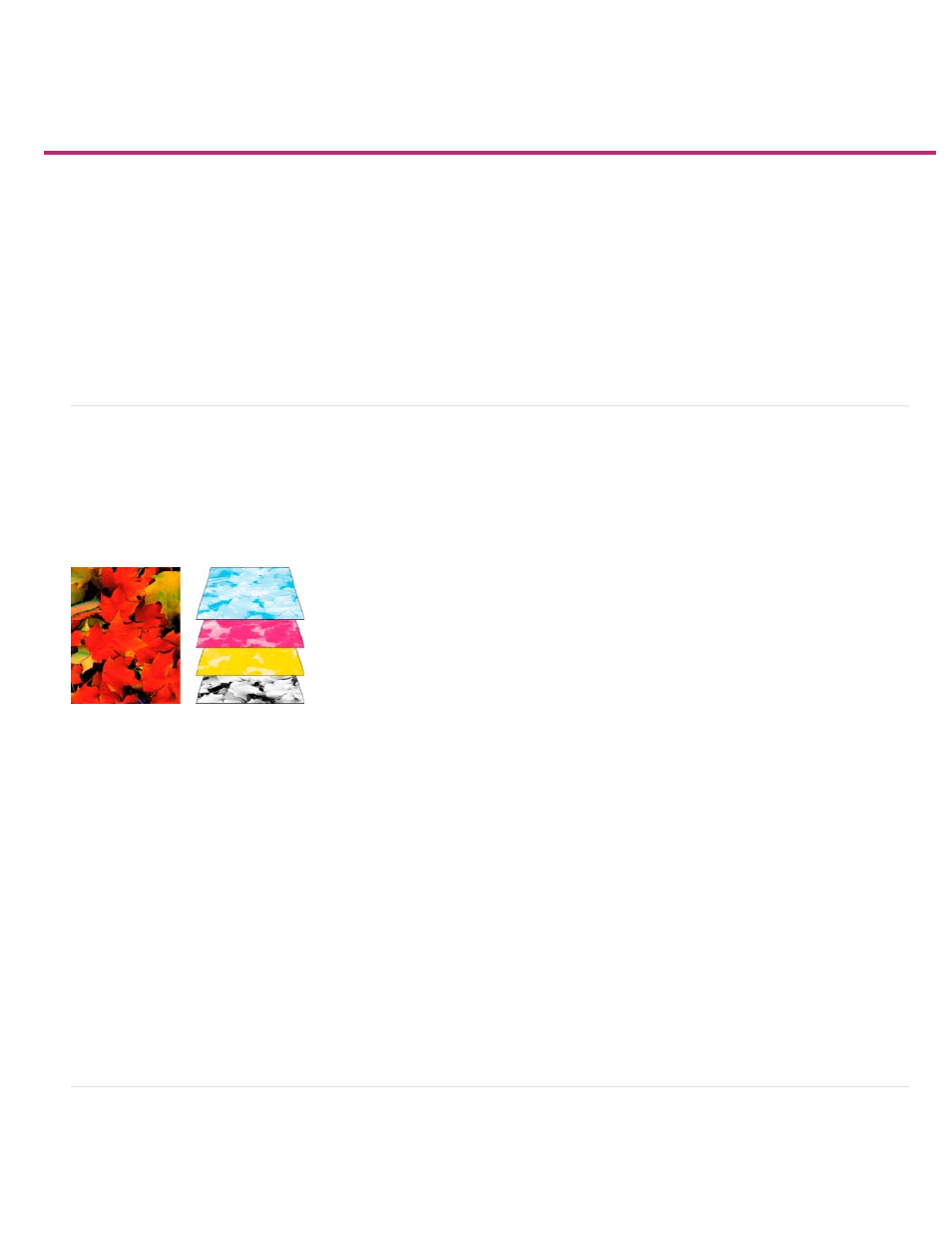
To reproduce color and continuous-tone images, printers usually separate artwork into four plates—one plate for each of the cyan (C), yellow (Y),
magenta (M), and black (K) portions of the image. When inked with the appropriate color and printed in register with one another, these colors
combine to reproduce the original artwork. The process of dividing the image into two or more colors is called color separating, and the films from
which the plates are created are called the separations.
Composite (left) and separations (right)
Separation workflows
Adobe InDesign CS4 supports two common PostScript workflows; the main difference is where separations are created—at the host computer (the
system using InDesign and the printer driver), or at the output device’s RIP (raster image processor). Another alternative is a PDF workflow.
In the traditional host-based, preseparated workflow, InDesign creates PostScript information for each of the
separations required for the document, and sends that information to the output device.
In the newer RIP-based workflow, a new generation of PostScript RIPs performs color separations, trapping, and even color
management at the RIP, leaving the host computer free to perform other tasks. This approach takes less time for InDesign to generate the file,
and minimizes the amount of data transmitted for any given print job. For example, instead of sending PostScript information for four or more
pages to print host-based color separations, InDesign sends the PostScript information for a single composite PostScript file for processing in the
RIP.
Prepare your document for color separations
1. Correct any color problems in your artwork.
716
