Rockwell Automation 8520 9/Series CNC Integration Maintenance Manual Documentation Set User Manual
Page 663
Section 13A
Connecting 8520 Digital Drive Systems
13A-29
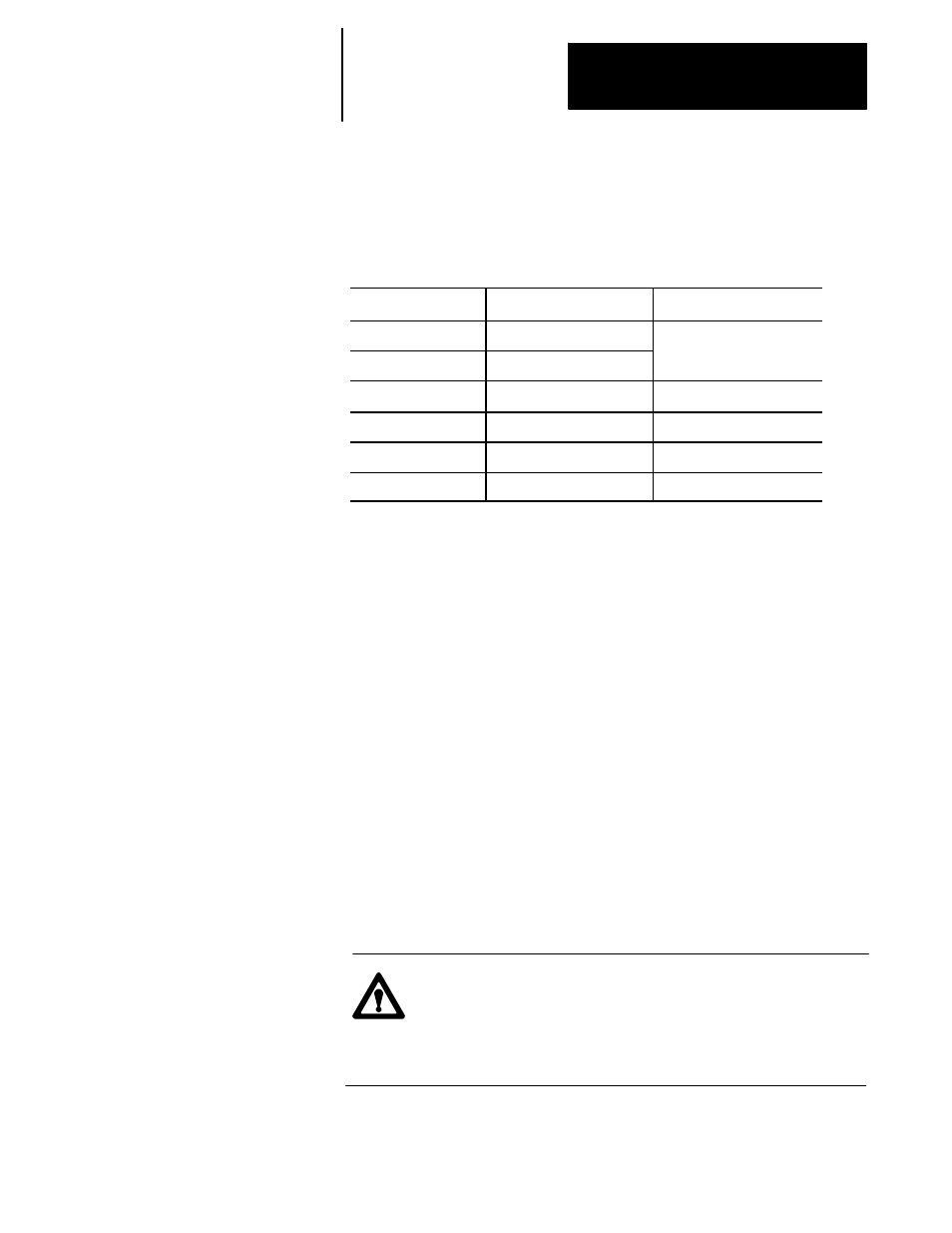
Table 13A.Q lists the servo encoder specifications.
Table 13A.Q
Servo Encoder Specifications
Absolute Encoder
Incremental Encoder
Number of Pulse
8192 pulse/rev
6000 pulse/rev
Number of Multi-turning
±
99999 turns
Resolution
8192
´
4 = 32768 counts/rev
6000
´
4 = 24000 counts/rev
Supply Voltage
+5V (+10%, -1%)
+5V (+10%, -1%)
Battery Backup Voltage
2.9V to 4.5V
N/A
Weight
500 g
500 g
Incremental Encoders
Incremental encoders provide coarse axis position feedback to the servo
module. These encoders also provide U, V, and W motor phase signals for
use in motor commutation until the first marker is detected. After the first
marker is detected, the servo module determines incremental axis position
from the A, B, and C signals which are output by the encoder.
After initial power-up, the control must determine motor phasing by
finding the encoder marker. Until this marker is found, phasing is
estimated using the U, V, and W phase signals. This limits motor power to
approximately 85% of maximum.
After the first marker is detected, the exact electrical position is known.
Since precise commutation is now possible, full power is possible.
An axis homing cycle is required to establish axis position after the motor
is phased. Once axis position is established, axis position feedback is
transmitted back to the servo module in an A quad B format with marker.
This feedback transmission takes place on an incremental basis.
ATTENTION: Do not adjust encoder alignment. Commutation
requires the encoder marker to be aligned with the windings of
the servo motor. This alignment process is done during the
mounting of the incremental or absolute encoder to the servo
motor.
