Shunt resistor selection chart – Rockwell Automation 8520 9/Series CNC Integration Maintenance Manual Documentation Set User Manual
Page 654
Section 13A
Connecting 8520 Digital Drive Systems
13A-20
Where:
- J = total motor and axis inertia measured at motor shaft, summed for
all motors connected to the servo amplifier [Kg cm s
2
]
- N = maximum motor speed [rpm]
- T = desired deceleration time from maximum motor speed to stop
[sec.]
Important: These equations are for approximating shunt resistor
requirements. They can produce worst case data that is unrealistic for most
applications. For example, in most machine tool applications it is unlikely
that all axes will ever be traveling simultaneously at their maximum speed.
Factor the type of duty expected for your machine into these equations.
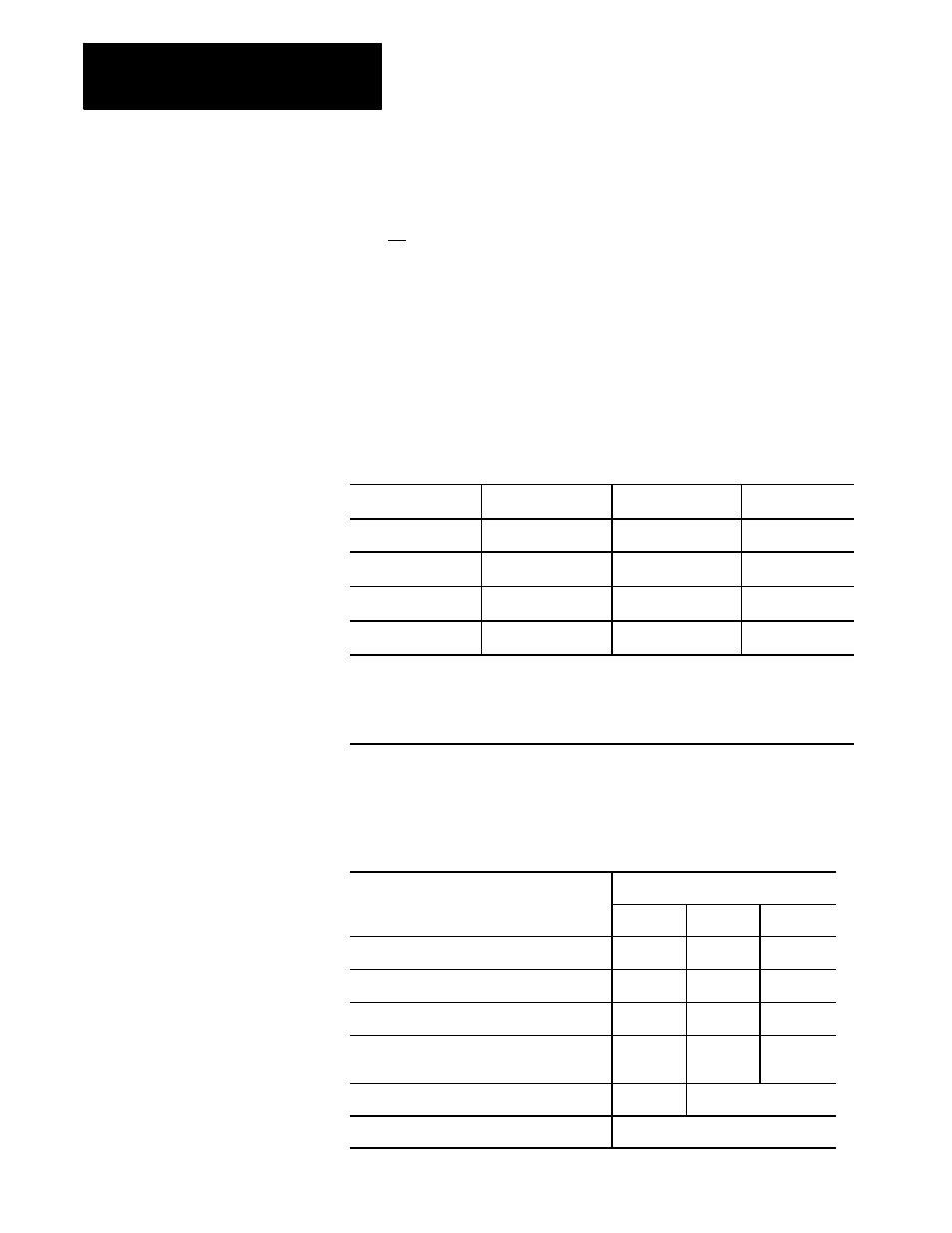
Shunt Resistor Selection Chart
P
< 1100
1100
£
P
< 1800
1800
£
P
W
< 180
Shunt Option #1
Shunt Option #2
1
180
£
W
< 540
Shunt Option #2
Shunt Option #2
1
540
£
W
< 810
Shunt Option #3
Shunt Option #3
1
810
£
W
2
2
2
1
Not possible with current configuration. Move one or more motors to another servo amplifier, or reduce
inertia, or reduce motor speed.
2
Not possible with current configuration. Move one or more motors to another servo amplifier, or reduce
inertia, or reduce motor speed, or increase time from maximum speed to stop.
Table 13A.M lists the internal/external shunt resistor, contactor, and fuse
specifications.
Table 13A.M
Internal/External Shunt Specifications
Specifications
Shunt Options
Option #1
Option #2
Option #3
Shunt Location
Internal
External
External
Shunt Resistance
16 ohms
10 ohms
10 ohms
Shunt Continuous Rating
196 watts
600 watts
900 watts
Shunt Duty Cycle Limit (determined by servo
amplifier jumper settings)
2 sec
5 sec
5 sec
Shunt Fuse Rating
15A/600V non-time delay
Shunt Contactor Size
15A/600V or greater
