Figure 97 – Brocade TurboIron 24X Series Configuration Guide User Manual
Page 645
Brocade TurboIron 24X Series Configuration Guide
611
53-1003053-01
Overview of OSPF
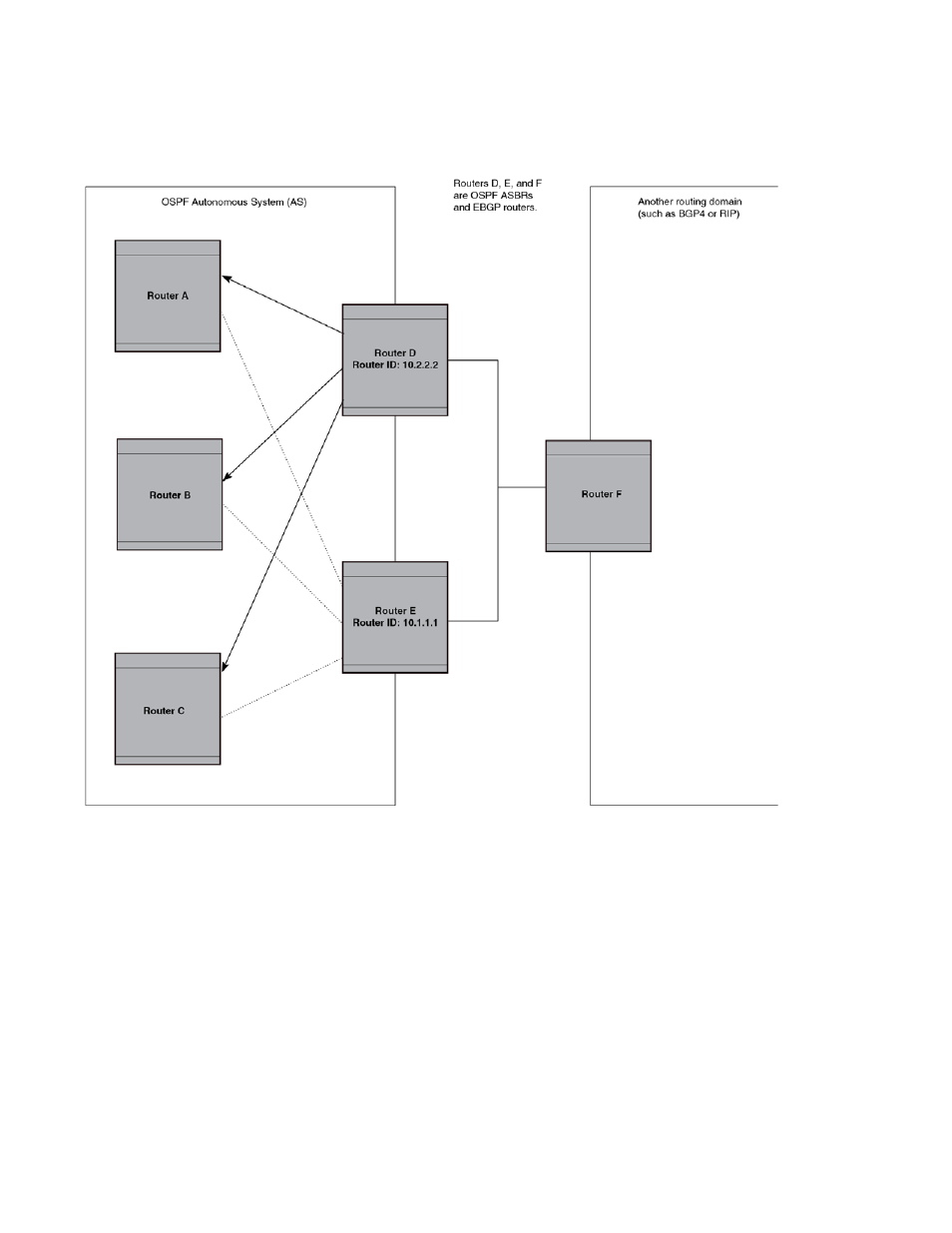
FIGURE 97
AS External LSA reduction
Notice that both Router D and Router E have a route to the other routing domain through Router F.
In earlier, if Routers D and E have equal-cost routes to Router F, then both Router D and Router E
flood AS External LSAs to Routers A, B, and C advertising the route to Router F. Since both routers
are flooding equivalent routes, Routers A, B, and C receive multiple routes with the same cost to
the same destination (Router F). For Routers A, B, and C, either route to Router F (through Router D
or through Router E) is equally good.
OSPF eliminates the duplicate AS External LSAs. When two or more Layer 3 Switches configured as
ASBRs have equal-cost routes to the same next-hop router in an external routing domain, the ASBR
with the highest router ID floods the AS External LSAs for the external domain into the OSPF AS,
while the other ASBRs flush the equivalent AS External LSAs from their databases. As a result, the
overall volume of route advertisement traffic within the AS is reduced and the Layer 3 Switches
that flush the duplicate AS External LSAs have more memory for other OSPF data. In
since Router D has a higher router ID than Router E, Router D floods the AS External LSAs for
Router F to Routers A, B, and C. Router E flushes the equivalent AS External LSAs from its
database.
