6 modifier control register (mctl), Modifier control register (mctl) -37, Modifier control register (mctl) format -37 – Freescale Semiconductor StarCore SC140 User Manual
Page 69: Address modifier (am) bits -37, Register is not used since both rn and b
Address Generation Unit
SC140 DSP Core Reference Manual
2-37
2.3.2.6 Modifier Control Register (MCTL)
The MCTL register is a 32-bit read/write register. This control register is used to program the address
mode (AM) for each of the eight low address registers (R0–R7). The addressing mode of the high address
register file (R8–R15) cannot be programmed and functions in linear addressing mode only. The format of
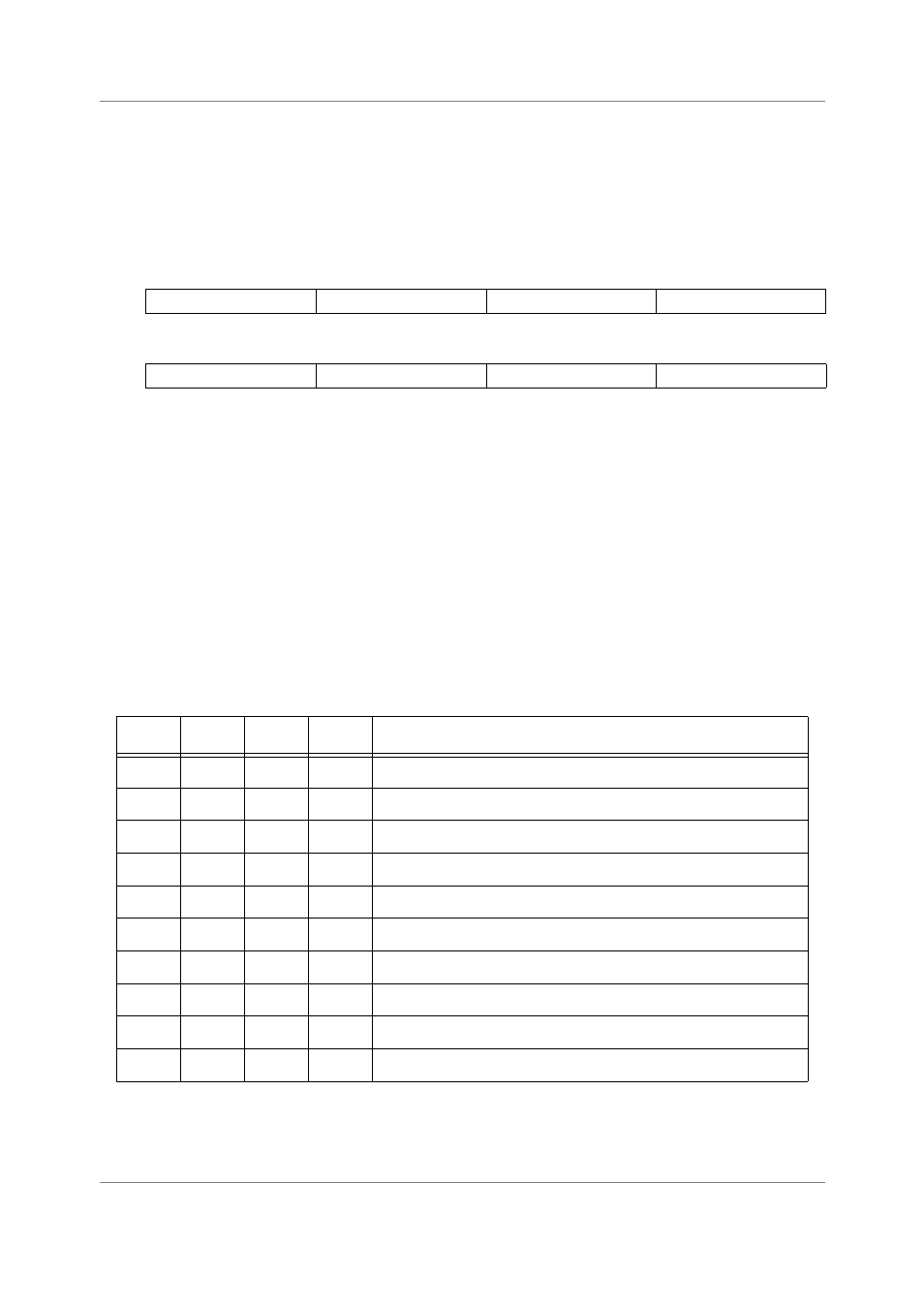
MCTL is shown in Figure 2-14.
Figure 2-14. Modifier Control Register (MCTL) Format
The AM bits (AM3, AM2, AM1, AM0) associated with each address register (R0-R7) reflect the address
modifier mode of this address register as shown in Table 2-17. Each of the Rn registers can use M0, M1,
M2, or M3 as their associated modulo register either in modulo addressing mode, or in multiple
wrap-around modulo addressing mode. When activating the modulo addressing mode, the corresponding
B register is used to define the lower boundary value (B0 with R0, and so on). The linear or the
reverse-carry addressing modes can also be used, freeing the B register to be used as an additional linear
address register.
The high bank of the address register file (R8–R15) can only be used in linear addressing mode. Each Rn
(n = 8:15) is available only if the corresponding B
n
-8
register is not used since both Rn and B
n
-8
are mapped
to the same physical register.
MCTL is initialized to zero at reset, setting a default linear mode for all Rn registers. All other AM field
combinations are reserved and should not be used.
Bit 31
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
Bit 16
R7 AM[3:0]
R6 AM[3:0]
R5 AM[3:0]
R4 AM[3:0]
Bit 15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
Bit 0
R3 AM[3:0]
R2 AM[3:0]
R1 AM[3:0]
R0 AM[3:0]
Table 2-17. Address Modifier (AM) Bits
AM3
AM2
AM1
AM0
Address Modifier Modes
0
0
0
0
Linear addressing
0
0
0
1
Reverse-carry addressing
1
0
0
0
M0 used—Modulo addressing
1
0
0
1
M1 used—Modulo addressing
1
0
1
0
M2 used—Modulo addressing
1
0
1
1
M3 used—Modulo addressing
1
1
0
0
M0 used—Multiple wrap-around modulo addressing
1
1
0
1
M1 used—Multiple wrap-around modulo addressing
1
1
1
0
M2 used—Multiple wrap-around modulo addressing
1
1
1
1
M3 used—Multiple wrap-around modulo addressing
