3 multiplication, 4 division, 5 unsigned arithmetic – Freescale Semiconductor StarCore SC140 User Manual
Page 52: Multiplication -20, Division -20, Unsigned arithmetic -20, Fractional and integer multiplication -20, Cation operation is given in, Section 2.2.2.3, “multiplication, 1 unsigned multiplication
2-20
SC140 DSP Core Reference Manual
DALU
2.2.2.3 Multiplication
Most of the operations are performed identically in fractional and integer arithmetic. However, the
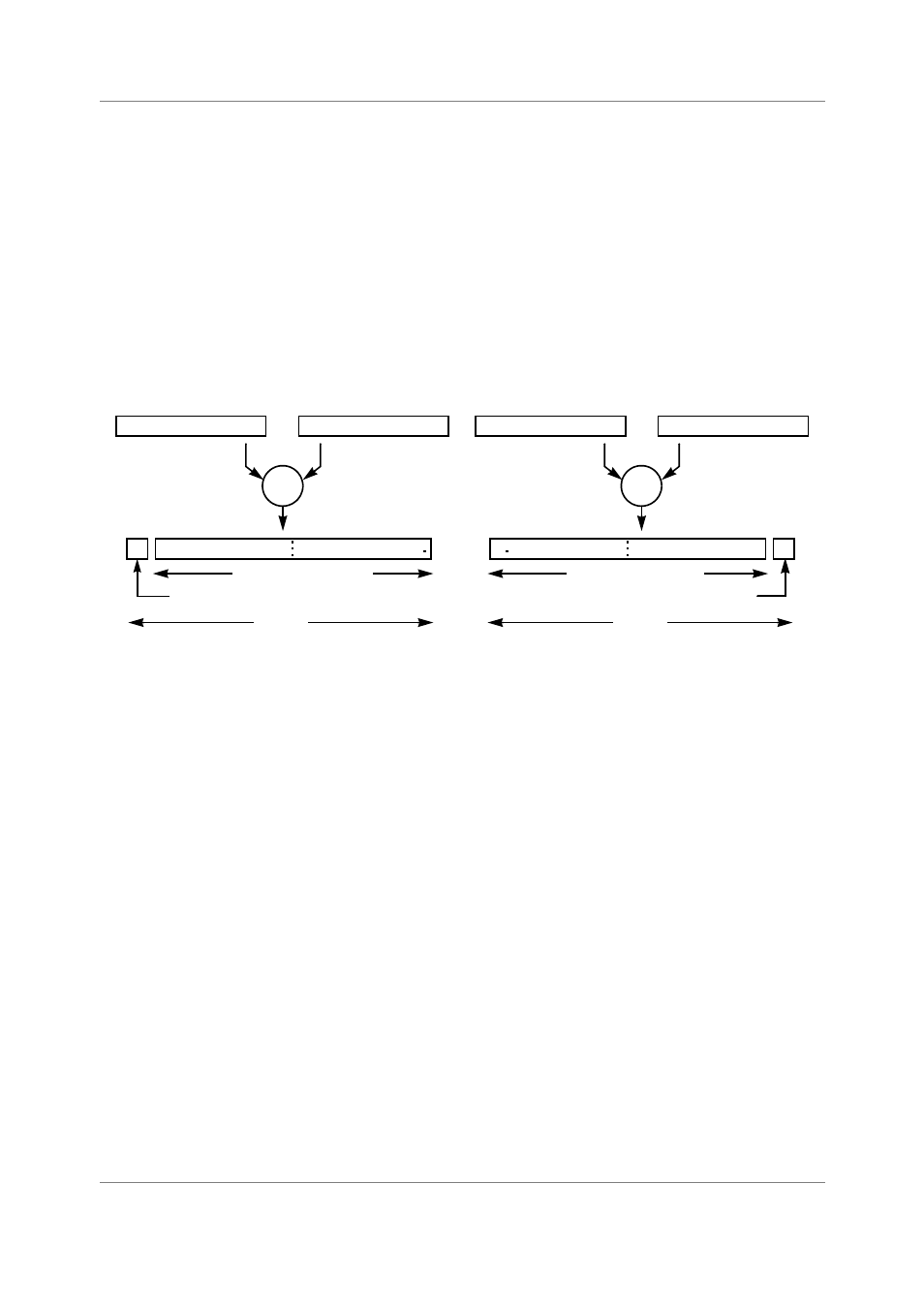
multiplication operation is not the same for integer and fractional arithmetic. As illustrated in Figure 2-4,
fractional and integer multiplication differ by a 1-bit shift. Any binary multiplication of two N-bit signed
numbers gives a signed result that is 2N-1 bits in length. This 2N-1 bit result must then be correctly placed
into a field of 2N-bits to correctly fit into the on-chip registers. For correct fractional multiplication, an
extra 0-bit is placed at the LSB to give a 2N-bit result. For correct integer multiplication, an extra sign bit
is placed at the MSB to give a 2N-bit result.
The MPY, MAC, MPYR, and MACR instructions perform fractional multiplication and fractional
multiply-accumulation. The IMPY and the IMAC instructions perform integer multiplication.
2.2.2.4 Division
Fractional division of both positive and signed values is supported using the DIV instruction. The dividend
(numerator) is a 32-bit fraction and the divisor (denominator) is a 16-bit fraction. For a detailed description
of the DIV instruction, see
Appendix A, “SC140 DSP Core Instruction Set.”
2.2.2.5 Unsigned Arithmetic
Unsigned arithmetic can be performed on the SC140 core architecture. Most of the unsigned arithmetic
instructions are performed the same as the signed instructions. However, some operations require special
hardware and are implemented as separate instructions.
2.2.2.5.1 Unsigned Multiplication
Unsigned multiplication (MPYUU, MACUU) and mixed unsigned-signed multiplication (MPYSU,
MACSU) are used to support double precision, as described in
Section 2.2.2.8, “Multi-Precision
These instructions can be used for unsigned arithmetic multiplication.
Figure 2-4. Fractional and Integer Multiplication
S
S
S
2N – 1 product
2N bits
S
S
0
2N – 1 product
2N bits
Integer
Fractional
Signed Multiplication: N x N --> 2N – 1 Bits
X
sign extension
zero fill
X
Signed Multiplier
Signed Multiplier
S
HP
LP
S
HP
LP
