2 sc140 dual stack memory use, Sc140 dual stack memory use -33, Sc140 memory use with dual stack pointers -33 – Freescale Semiconductor StarCore SC140 User Manual
Page 213
Stack Support
SC140 DSP Core Reference Manual
5-33
Memory space is required for interrupts because any task may be active when an interrupt occurs. The ISR
pushes registers on the current stack and may also allocate local variables on the current stack. Since it is
not known which task is being executed when an interrupt occurs, each task stack must be increased by the
maximum ISR memory use. In both situations, the memory is used only once, but it is allocated in more
than one location. RTOS functions return without switching tasks. In addition, RTOS calls are not
preemptable, although they are interruptible. Interrupts have the same behavior as RTOS functions in that
they return without switching tasks.
5.5.2 SC140 Dual Stack Memory Use
The solution to excessive stack memory use is to separate tasks from the RTOS and interrupts. This is done
by using the user/normal and exception working modes. The programming model has two stack pointers:
NSP and ESP. The NSP is used by tasks when the core is in the user or normal working modes. The ESP is
used in the exception working mode by the RTOS and interrupts. Since the RTOS and interrupts have their
own stack pointer, memory for the RTOS and interrupts can be allocated separately. Thus, the RTOS and
interrupt code can be modified independently of the tasks.
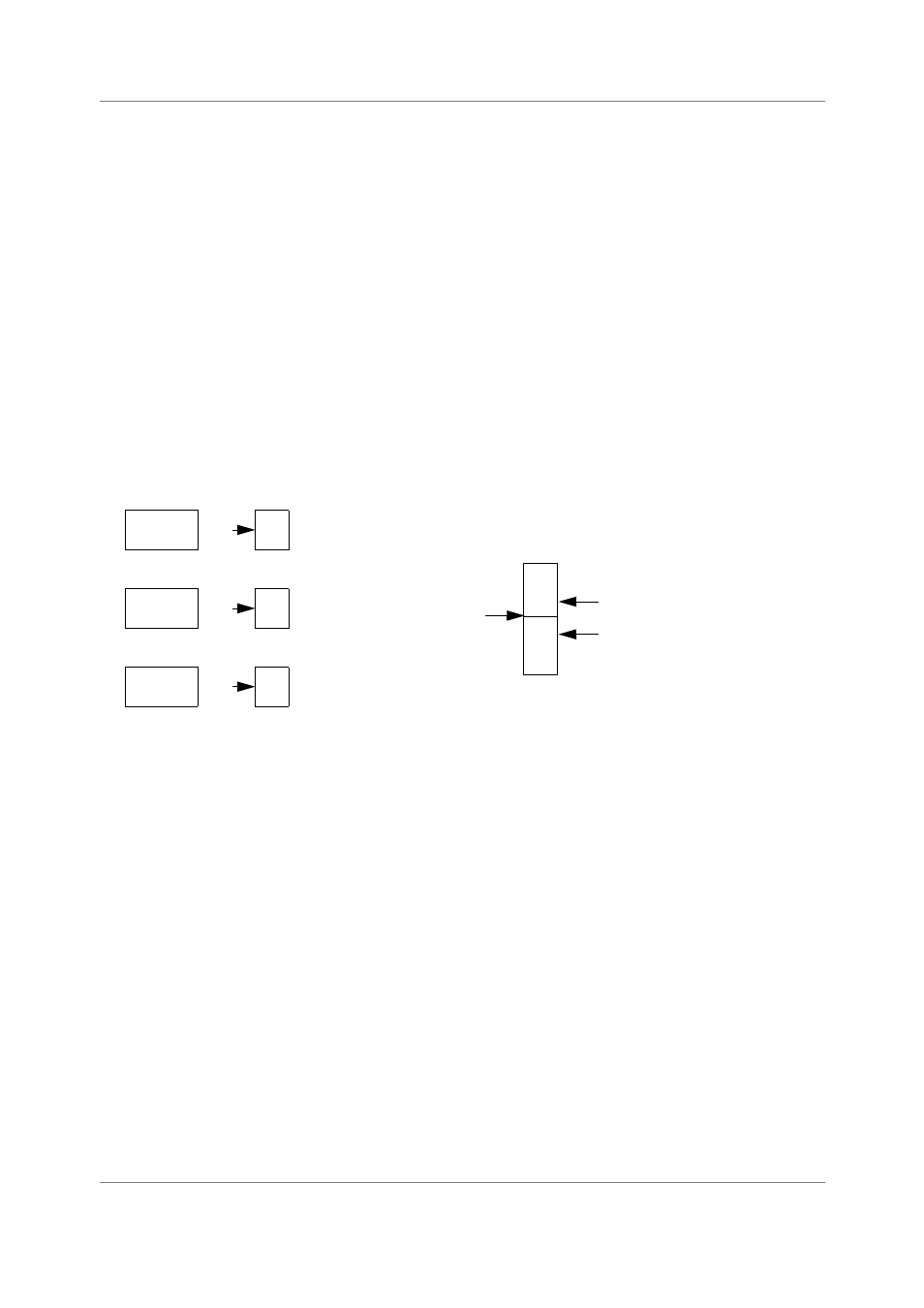
Figure 5-7 shows the stack structure.
Figure 5-7. SC140 Memory Use with Dual Stack Pointers
The core uses the exception working mode whenever it is processing an exception. When an exception
occurs, the core switches to the ESP, saves the PC and SR, and uses the exception stack later for saving
registers and allocating local variables and subroutine calls.
RTOS calls are performed by executing a TRAP instructions, which generates a software interrupt. Since
the processor is now in exception working mode, all stack memory use is on the exception stack.
As the core enters the exception working mode, the RTOS usually needs to save the current context by
storing registers other than the SR and PC in the normal stack. For this purpose, specialized push and pop
instructions (PUSHN/POPN) are provided that always access the normal stack, regardless of the mode.
Task
Ta
s
k
Task
Ta
s
k
Task
Ta
s
k
NSP
NSP
NSP
St
a
c
k
St
a
c
k
St
a
c
k
ESP
Space allocated for interrupts
Space allocated for RTOS calls
Except
ion
St
a
c
k
