6 working modes, 1 normal working mode, 2 exception working mode – Freescale Semiconductor StarCore SC140 User Manual
Page 217: Working modes -37, Normal working mode -37, Exception working mode -37
Working Modes
SC140 DSP Core Reference Manual
5-37
5.6 Working Modes
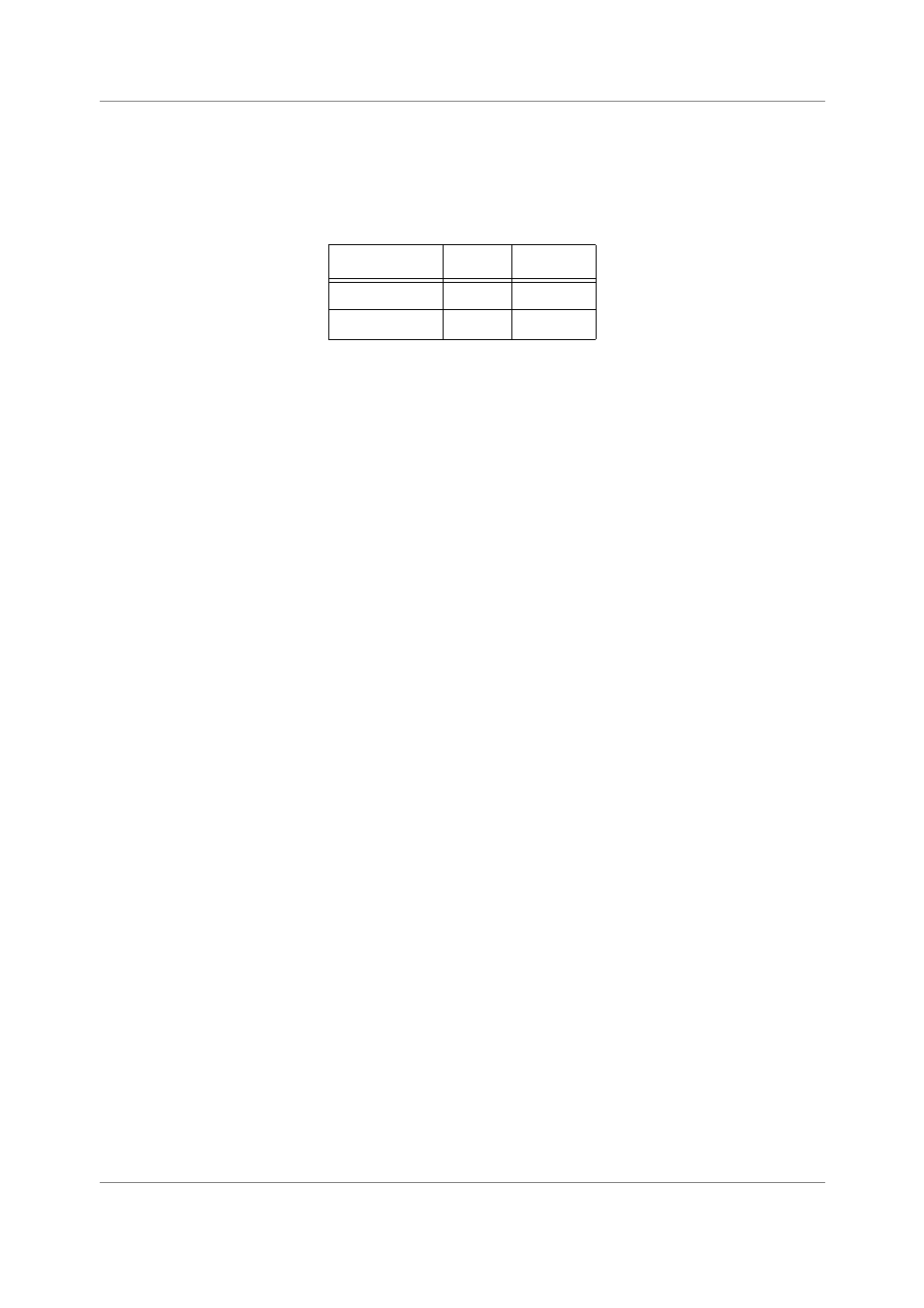
The working mode is determined by the EXP bit in theStatus Register (SR), as shown in the table below:
Table 5-15. Working Modes
The SC140 can operate in one of two working modes.
Normal mode -
Typically intended for task-related services. Works with NSP as the stack pointer.
Exception mode - Typically intended for RTOS kernels, exception routines and peripheral device
drivers. Works with the ESP as the stack pointer.
5.6.1 Normal Working Mode
This mode uses the Normal Stack Pointer (NSP). This mode is intended for application tasks that were
each allocated a distinct stack area. It could also be used for RTOS services that are tightly related to a
specific task, and hence would work more efficiently if they could reference the NSP with SP. Example for
such tasks are memory allocation and management tasks, or RTOS messaging services that need
observability into the task data structures.
The core stays in this mode unless:
•
An exception is encountered, as described in
•
A hardware reset occurs, as described in
Section 5.7.4, “Reset Processing State.”
•
An RTE-like instruction (RTE/D) is issued,.
5.6.2 Exception Working Mode
This mode uses the Exception Stack Pointer (ESP). It is intended for the RTOS kernel, interrupt service
routines, peripheral device drivers, etc. Also, application code for single stack systems runs in this mode.
The SC140 core can enter the exception working mode in any of the following ways:
•
An external hardware interrupt request is issued to the core, for example by an off-chip device or
an on-chip peripheral.
•
A software exception request (TRAP) is issued by the program itself.
•
An internal exception such as an illegal opcode, illegal execution set, or DALU overflow occurs.
•
A debug exception request is issued by the EOnCE.
This is the default state of the core after exiting the reset state. Refer to
for a detailed description of the different exception types, and of the way an exception is
serviced.
Working Mode
EXP bit
Active SP
Normal
0
NSP
Exception
1
ESP
