Grass Valley NV9000-SE v.5.0 User Manual
Page 72
54
Routers
‘Router Controls’ table
When the DHP option is enabled, the NV9000 software in the system controller addresses the
DHP software as if it were the router itself. DHP then communicates with the NV8500 router.
DHP makes decisions about routing paths through the DHP core and sends appropriate take
commands to the router.
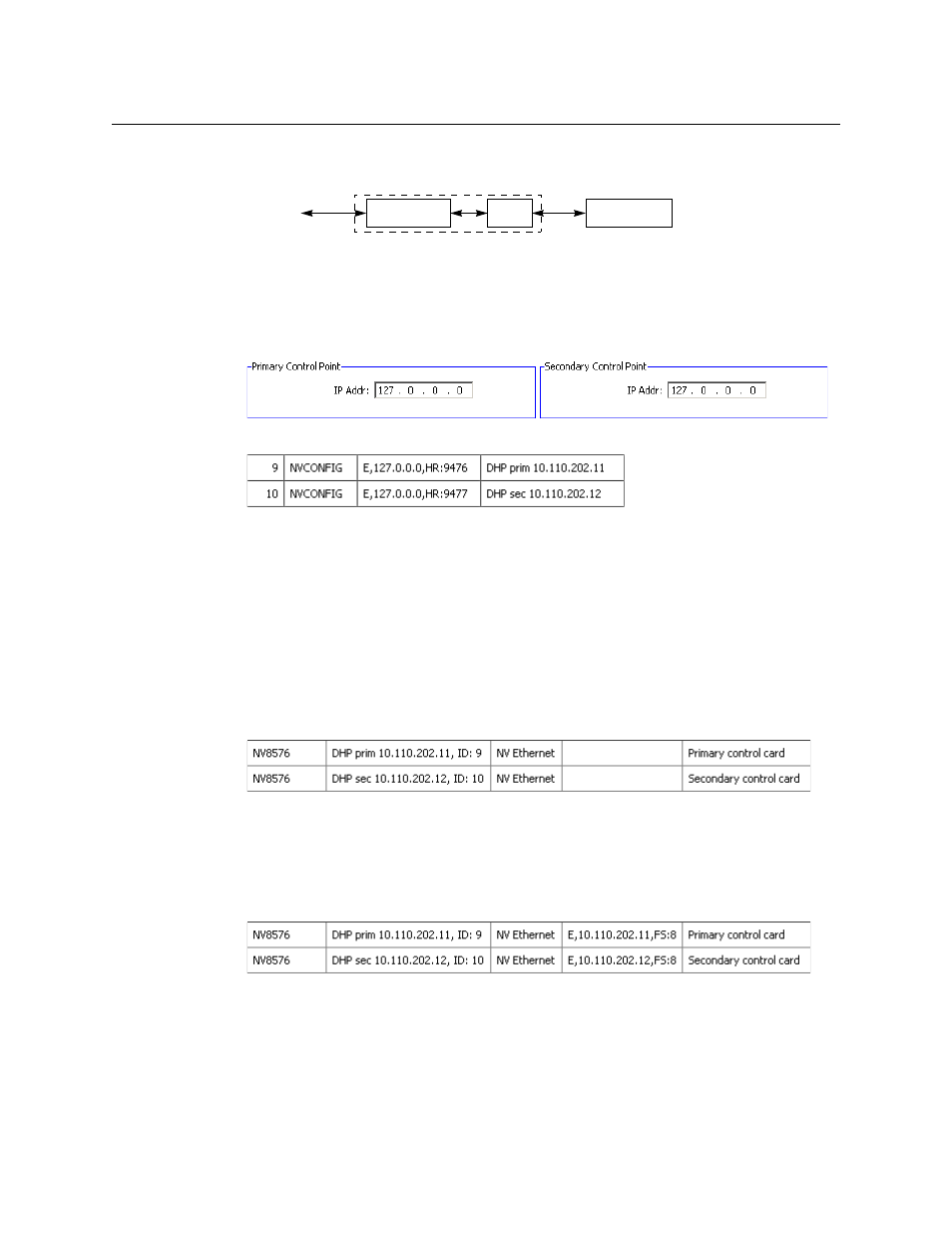
To set up DHP processing means “playing games” with the IP addresses involved. Thus . . .
1 In the router details page, define both control points for the NV8500 router as (Ethernet)
127.0.0.0:
2 In the control points table, create those two control points:
The host is the system controller in which DHP is to be active (i.e., the system controller con-
trolling the NV8500 router to which DHP applies). The default host name for most system
controllers is “NVCONFIG.”
NV9000-SE Utilities will have partially filled in the ‘Parameters’ field as “E” followed by a
comma, followed by the 127.0.0.0 IP address. For DHP, you must add a comma, “HR”, and a
4-digit port number. (Illustrated above are two suitable port numbers. Refer to the DHP
User’s Guide for a list of acceptable port numbers and to understand why you need these
port numbers.). The syntax of the ‘Parameter’ field must be exact.
Enter anything in the description field that is useful to you.
3 Go to the router controls table. It will list the two control points you created:
The ‘Parameters’ field will be empty. It is necessary to specify in that field (1) the actual IP
addresses of the router control cards and (2) the DHP free source.
In step 2, we noted the actual IP addresses of the router control cards in the control point
description. Also we choose a DHP free source (in our example here, that is 8).
This is the result in our example:
The syntax for the free source is comma, “FS”, colon, ‹source number›.
Refer to the DHP User’s Guide to learn what a DHP free source is and how to use one.
Router
NV9000 s/w
DHP
Operator
