Multi-hop tielines – Grass Valley NV9000-SE v.5.0 User Manual
Page 465
447
NV9000-SE Utilities
User’s Guide
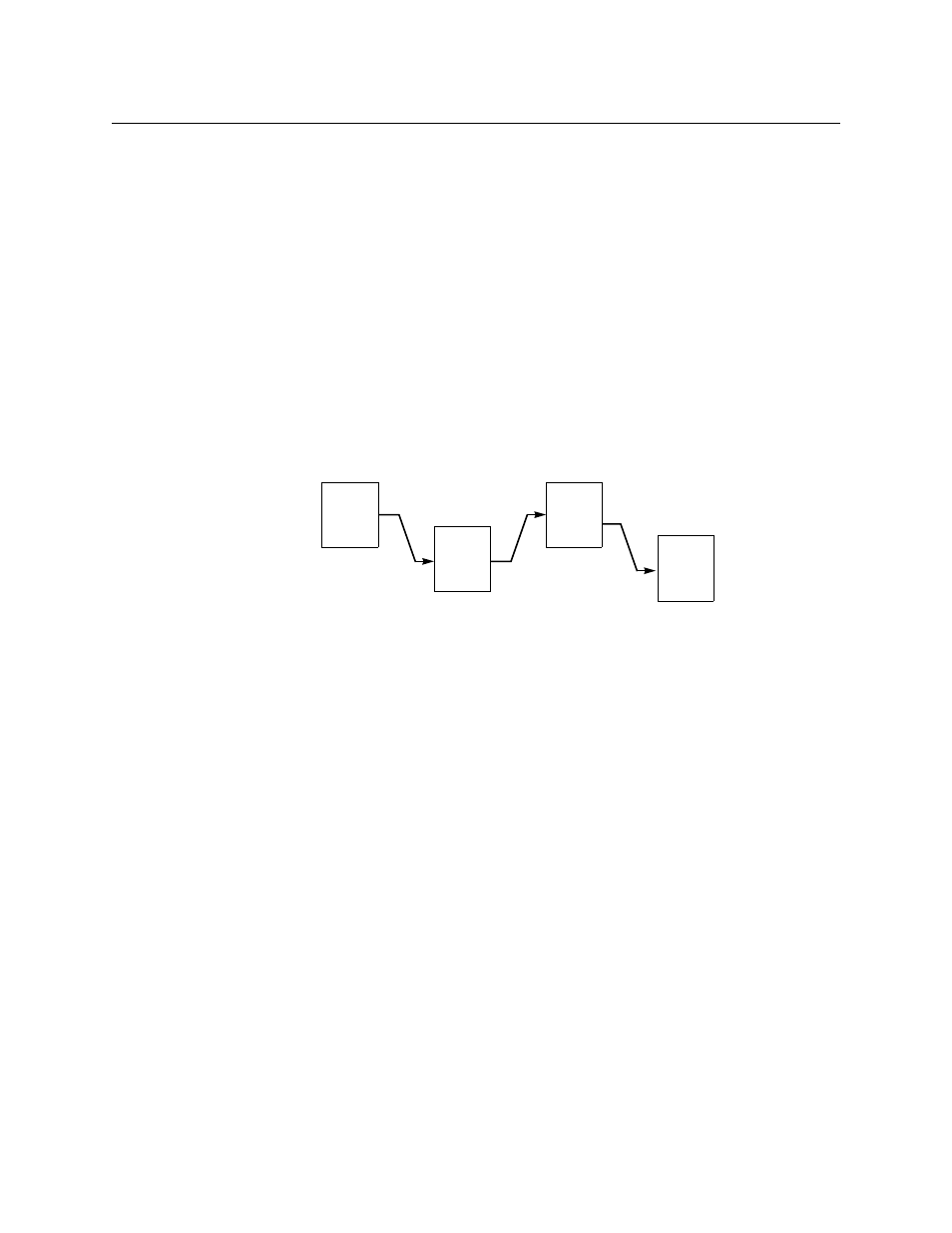
Multi-Hop Tielines
For the sake of path calculations, a multi-hop tieline consists of a starting partition, A, and an
ending partition, Z, and one or more intervening partitions (B, C, D, . . . X, Y) through which
signals are routed from A to Z.)
Each partition, A, B, C, and so on to Z, has degree d
A
, d
B
, d
C
, d
D
, . . . d
X
, d
Y
, d
Z
.
Let N
AB
, N
BC
, N
CD
, . . . N
YZ
be the number of connections between adjacent partitions.
The path count for the multi-hop tieline is
AZ = [ AB × BC × CD × . . . × YZ ] / (d
B
× d
C
× d
D
× . . . d
Y
)
that is, the product of path count for all simple tielines in the route divided by the product of
degrees of all intermediate partitions.
(The result is a maximum; if you have declined to use certain signal types for certain tielines,
the result will be less. The calculations for that situation are extremely complex and not at all
useful.)
Example:
A supports 1080i/59.94, 720p/29.97, 1080i/50, 720p/50, 1080p/23.98. The degree of A is 5.
B supports 525i/59.94 and 625i/50. The degree of B is 2.
C supports 1080i/59.94, 720p/29.97, 1080i/50, 720p/50, 1080p/23.98. The degree of C is 5.
D supports 525i/59.94 and 625i/50. The degree of D is 2.
There are 3 tielines defined between A and B, and also between B and C and between C and D.
The path count is
AD = [ (AB)(BC)(CD) ] / (d
B
× d
C
)
Where
AB = d
A
× d
B
× 3 = 5 × 2 × 3 = 30
BC = d
B
× d
C
× 3 = 2 × 5 × 3 = 30
CD = d
C
× d
D
× 3 = 5 × 2 × 3 = 30
Then
AD = [ (30)(30)(30) ] / (2 × 5)
AD = 27,000 / 10 = 2700.
A
(HD)
d = 5
1080i/59.94,
720p/29.97,
1080i/50,
720p/50,
1080p/23.98
C
(HD)
d = 5
B
(SD)
d = 2
D
(SD)
d = 2
525i/59.94,
625i/50
1080i/59.94, 720p/29.97, 1080i/50,
720p/50, 1080p/23.98
525i/59.94,
625i/50
