Metrohm viva 1.0 (process analysis) User Manual
Page 631
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
5 Method
viva 1.0 (for Process analysis)
■■■■■■■■
619
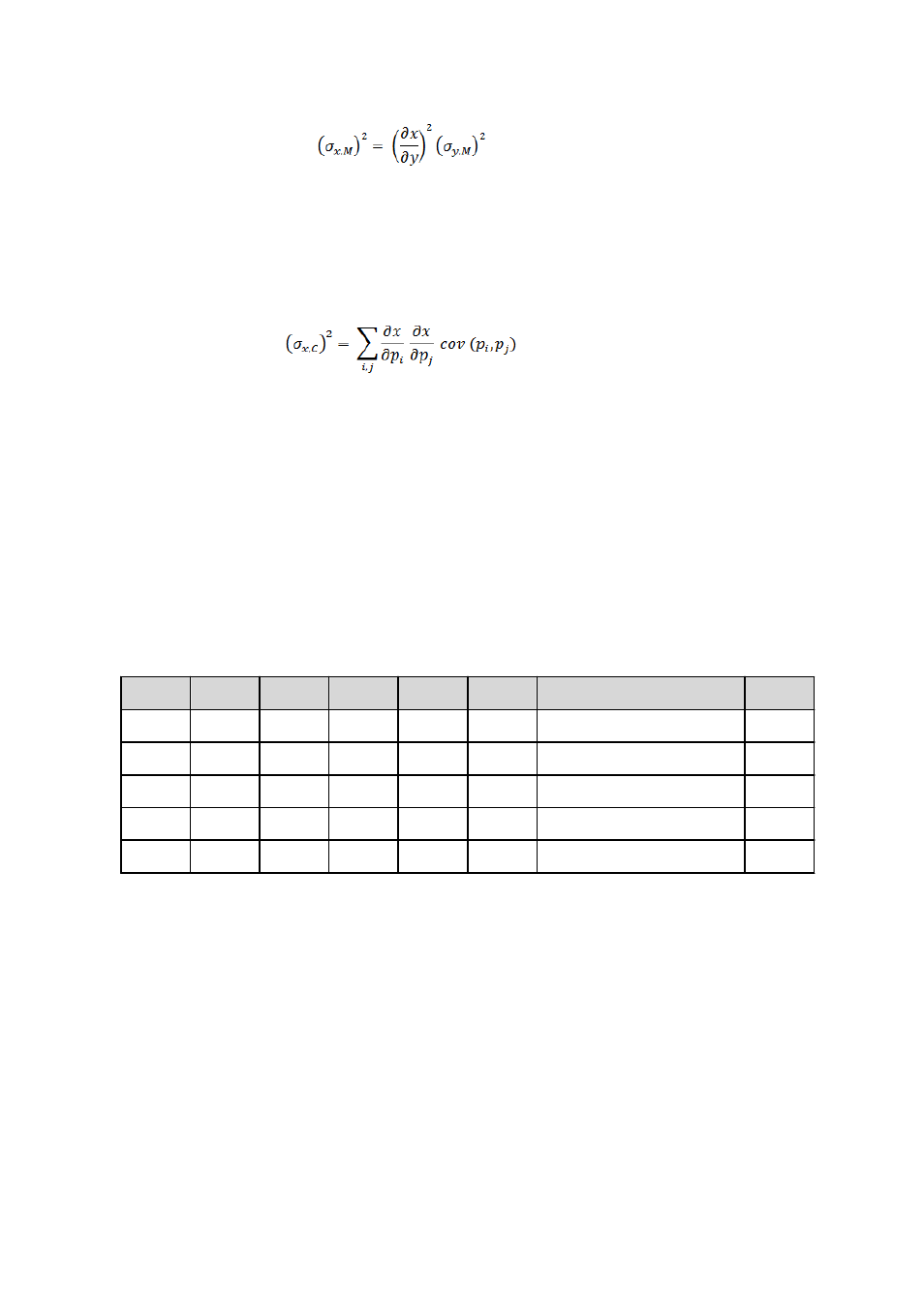
The errors of the individual parameters p
i
= a, b, c, d of the calibration
function used are determining for the calculation of the error amount
from the calibration. Because of the fact that these parameters are statisti-
cally dependent on one another, all covariances cov(p
i
, p
j
) must be taken
into account here:
Statistically speaking, only small random samples (<10) are determined for
voltammetric measurements from a population with Gaussian distribution.
These random samples indicate a student distribution that is taken into
account with the student factor t. If the variance is made up of a number
of partial variances, then the student factor is calculated by means of
Welch-Satterthwaite formula approximation. The variance acquired with
this procedure is multiplied by t
2
; the resulting square root yields the
standard deviation of the result.
The student factor t depends on the number of measurements n, or, to be
more precise, on the number of degrees of freedom n
− f, for which n is
the number of measuring points and f is the number of estimated parame-
ters. The student factor t is defined as follows for a probability of 68.3%:
n
− f
t
n
− f
t
n
− f
t
Curve type
f
1
1.837
6
1.091
15
1.035
y = a + bx
2
2
1.321
7
1.077
20
1.026
y = a + bx + cx
2
3
3
1.197
8
1.067
30
1.017
y = a + bx + dx
4
3
4
1.142
9
1.059
50
1.010
5
1.111
10
1.053
100
1.005
Even though probabilities of 90% and more are usual in statistics, we
select 68.3% in order to ensure compatibility with the conventional speci-
fication of normally distributed measured values Mean value
± Standard
deviation. With normally distributed values, a standard deviation corre-
sponds to a probability of 68.3%.
The total error CONCM.ASD of the result CONCM consequently indi-
cates the CONCM
± CONCM.ASD area in which the true value of
CONCM may be expected with a probability of 68.3%.
