Metrohm viva 1.0 (process analysis) User Manual
Page 630
5.6 Evaluation subwindow
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
618
■■■■■■■■
viva 1.0 (for Process analysis)
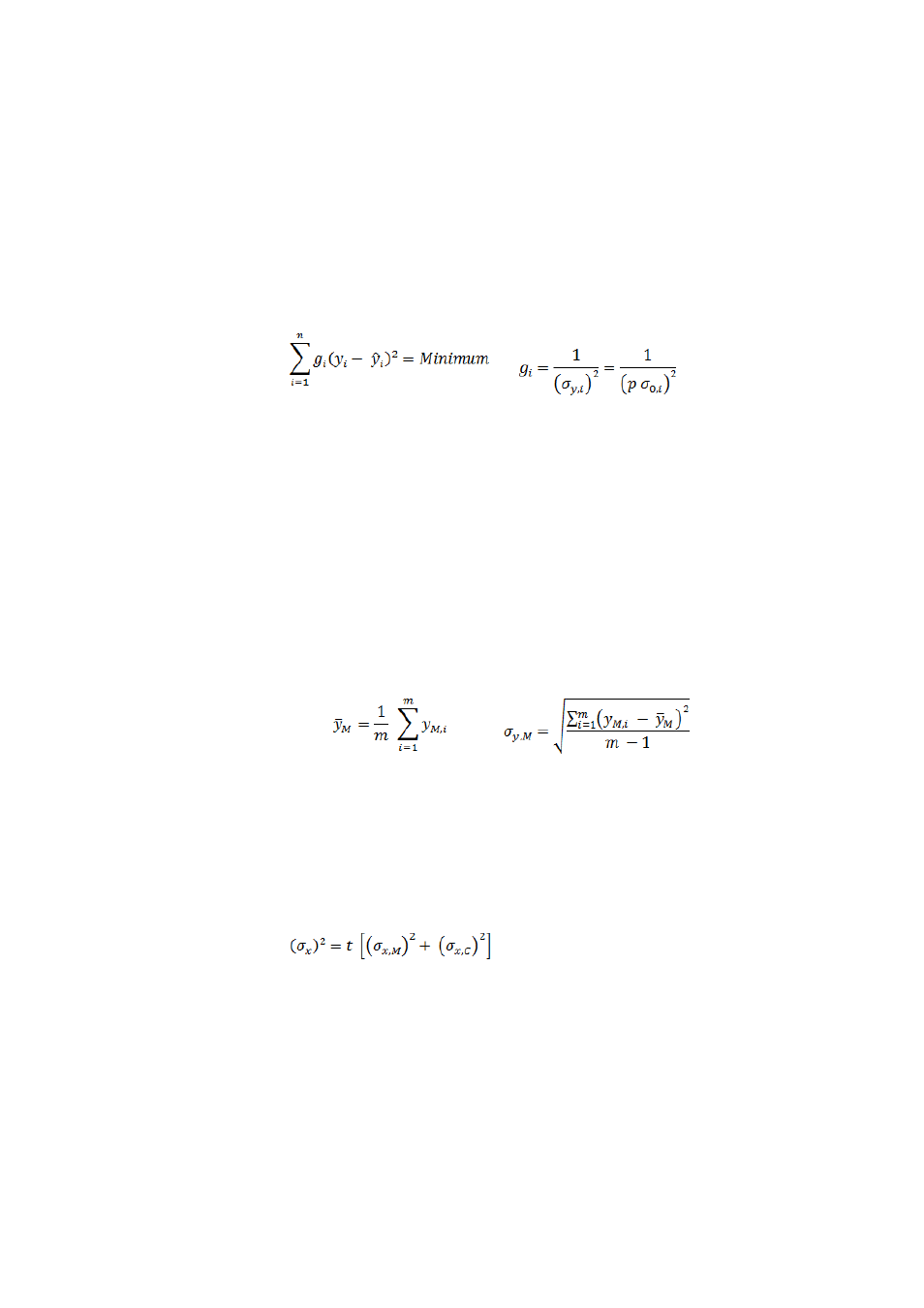
In the case of most measuring instruments, the scatter is comprised of a
constant basic part and of a part proportional to the measured quantity.
Influences that change over time also exist, however, e.g. the electrode
status or the temperature. These usually change only slowly, which is why
they can be regarded as constant during the measurement. One can
therefore take their influence into account by means of an (unknown) fac-
tor p, which is multiplied against the basic scatter. Because of the fact that
a constant factor has no influence over curve fitting, however, it can be
ignored.
with
The weighting must adopt a constant value for small measured values in
the vicinity of the instrument noise in order to exclude the possibility that
small measured values are over-weighted.
The weighting is then also appropriate if a calibration curve is acquired
across a wide concentration range. Without weighting the wide scatter of
the values with a high concentration would falsify the calibration curve for
the small values.
The calculated calibration curve is used with subsequent measurements to
determine the associated result x
M
from the mean value y
̅
M
. The mean
value y
̅
M
and the scattering
σ
y,M
of the individual values are defined
thereby as follows:
The estimation of the total error
σ
x
of the result x
M
is carried out with a
linear error calculation that takes into account not only the error
amount from the measurement but also that from the calibration.
Because of the fact that the two amounts are statistically independent of
one another, it is not the individual errors
σ that are added but rather
their variances
σ
2
(with t = student factor):
The error amount from the measurement itself is calculated from the
derivative of the calibration function resolved in accordance with x in
accordance with y and the measured scattering
σ
y,M
as follows:
