Viewing and configuring vlans by port – Brocade Mobility RFS7000-GR Controller System Reference Guide (Supporting software release 4.1.0.0-040GR and later) User Manual
Page 97
Brocade Mobility RFS7000-GR Controller System Reference Guide
83
53-1001944-01
Viewing and configuring Layer 2 virtual LANs
4
advantages of a VLAN, is when a computer is physically moved to another location, it can stay on
the same VLAN without reconfiguration. The switch can support multiple VLANs. Use the Layer 2
Virtual LANs screen to view and configure VLANs by Port and Ports by VLAN information. Refer to
the following VLAN configuration activities:
•
Viewing and configuring VLANs by port
•
Viewing and configuring ports by VLAN
Viewing and configuring VLANs by port
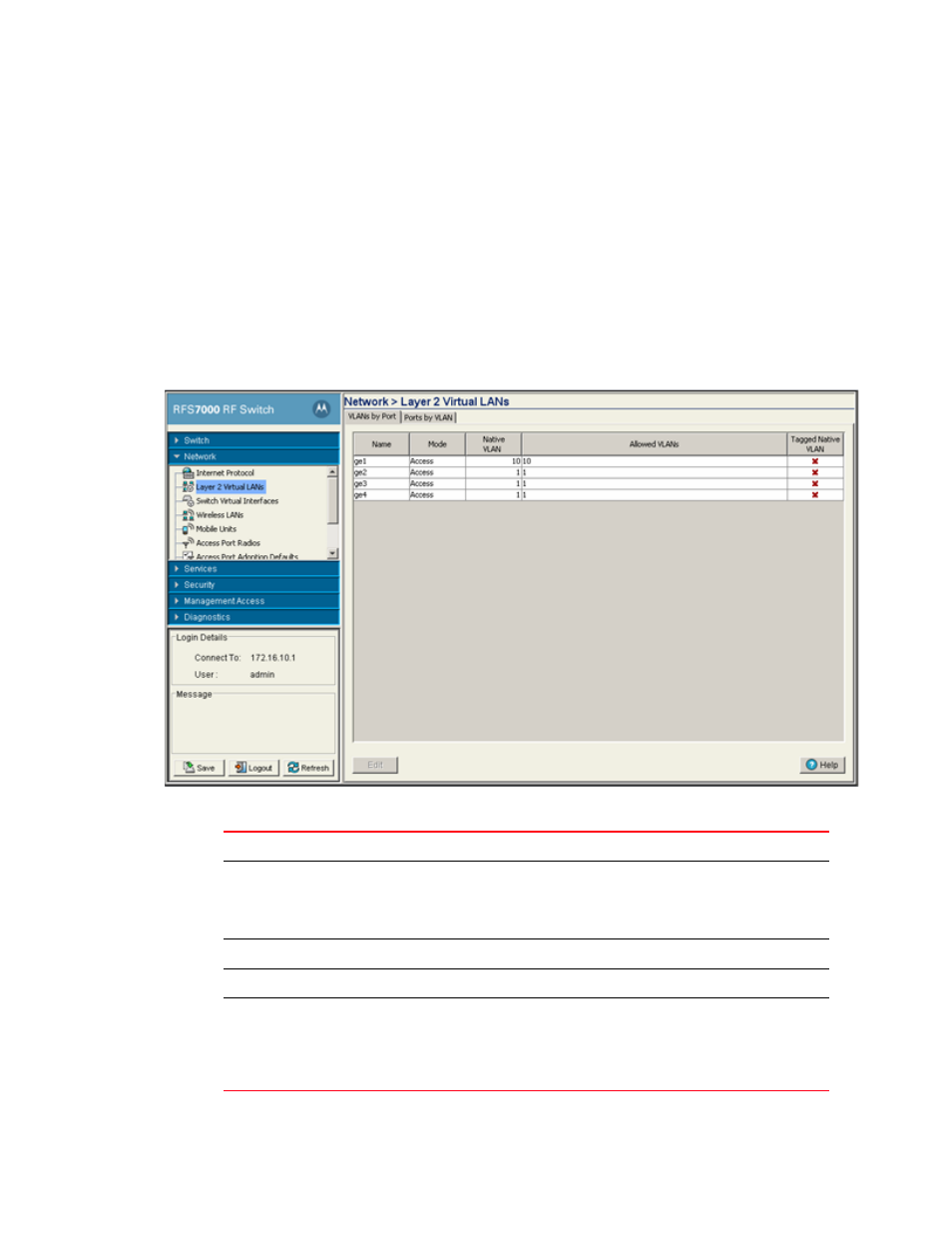
1. Select Network > Layer 2 Virtual LANs from the main menu tree. VLAN by Port details display
within the Virtual LANs screen.
2. Refer to following details within the table:
Name
Displays the name of the VLAN to which the switch is currently connected.
Mode
It can be either Access or Trunk.
•
Access– This ethernet interface accepts packets only form the native VLANs.
•
Trunk– The Ethernet interface allows packets from the given list of VLANs you
add to the trunk.
Native VLAN
Displays the tag assigned to the native VLAN.
Allowed VLANs
Displays VLAN tags allowed on this interface
Tagged Native VLAN
Displays if the Native VLAN for each port is tagged or not. The column displays a
green check mark if the Native VLAN is tagged. If the Native VLAN is not tagged the
column will display a red “x”.
A Native VLAN is the VLAN which untagged traffic will be directed over when using
a port in trunk mode.
