Write behavior, Overrun/underrun conditions, Overrun – Altera Embedded Peripherals IP User Manual
Page 94: Receive overrun behavior, Overrun/underrun conditions -8
Reads are expected to have 2 types of behavior:
• When status registers are being polled, Reads are expected to be done in singles
• When data needs to be read out from the Rx FIFO, Reads are expected as back-to-back cycles to the
same address (these back-to-back reads are likely generated as Fixed Bursts in AXI – but translated
into INCR with length of 1 by FPGA interconnect)
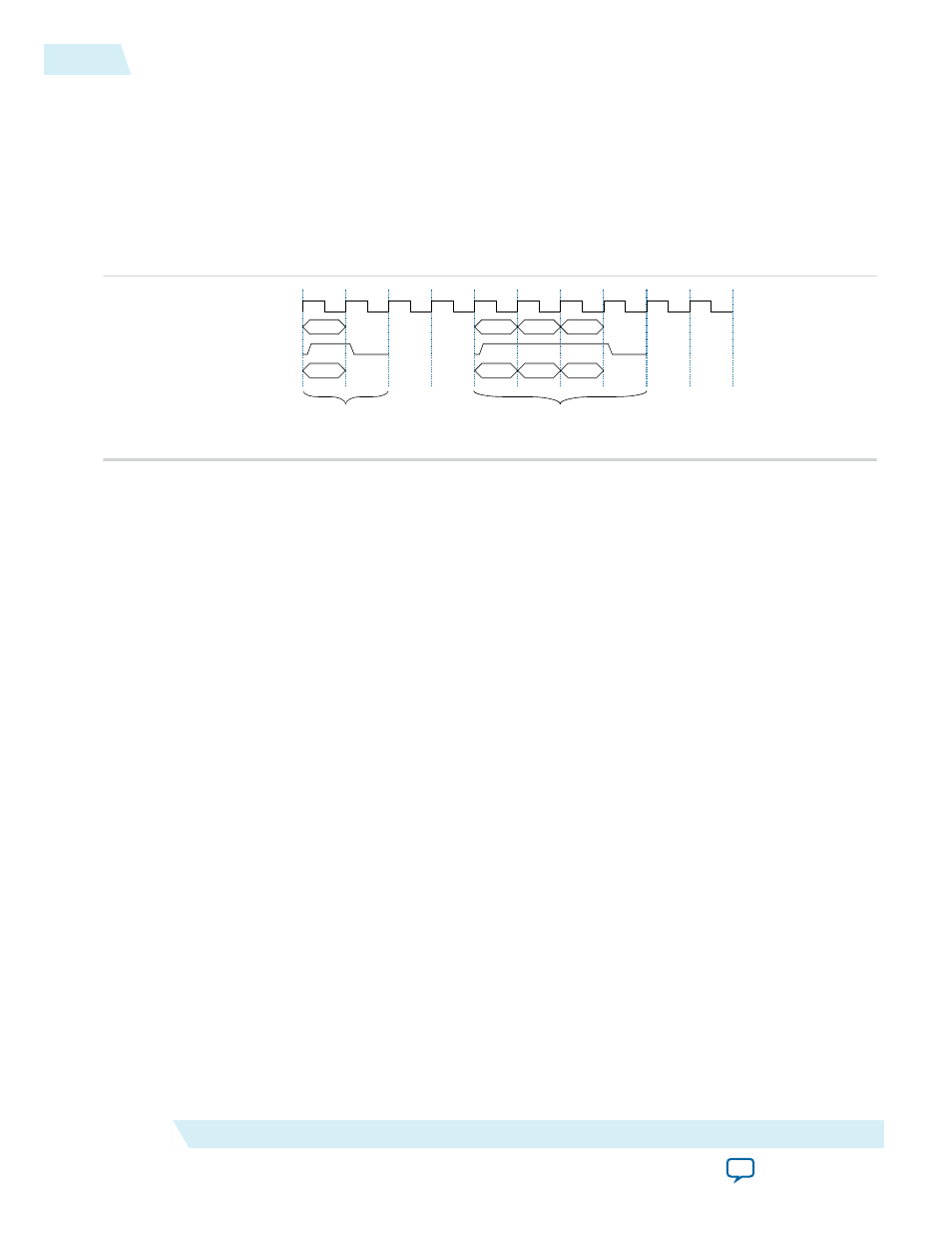
Write behavior
Figure 9-4: Writing to UART over Avalon-MM
addr1
addrF
addrF
addrF
data1
data2
data3
data4
addr
read
readdata
Configuration
Writing to
TX FIFO
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
Writes to the UART are expected as singles during setup phase of any transaction and as back-to-back
writes to the same address when the Tx FIFO needs to be filled.
Overrun/Underrun Conditions
Consistent with UART implementation in PC16550D, the soft UART will not implement overrun or
underrun prevention on the Avalon-MM interface.
Preventing overruns and underruns on the Avalon-MM interface by back-pressuring a pending transac‐
tion may cause more harm than good as the interconnect can be held up by the far slower UART.
Overrun
On receive path, interrupts can be triggered (when enabled) when overrun occurs. In FIFO-less mode,
overrun happens when an existing character in the receive buffer is overwritten by a new character before
it can be read. In FIFO mode, overrun happens when the FIFO is full and a complete character arrives at
the receive buffer.
On transmit path, software driver is expected to know the Tx FIFO depth and not overrun the UART.
Receive Overrun Behavior
When receive overrun does happen, the Soft-UART handles it differently depending on FIFO mode. With
FIFO enabled, the newly receive data at the shift register is lost. With FIFO disabled, the newly received
9-8
Write behavior
UG-01085
2014.24.07
Altera Corporation
16550 UART
