Configuring the timer as a watchdog timer, Software programming model, Hal system library support – Altera Embedded Peripherals IP User Manual
Page 252: Configuring the timer as a watchdog timer -4, Software programming model -4, Hal system library support -4
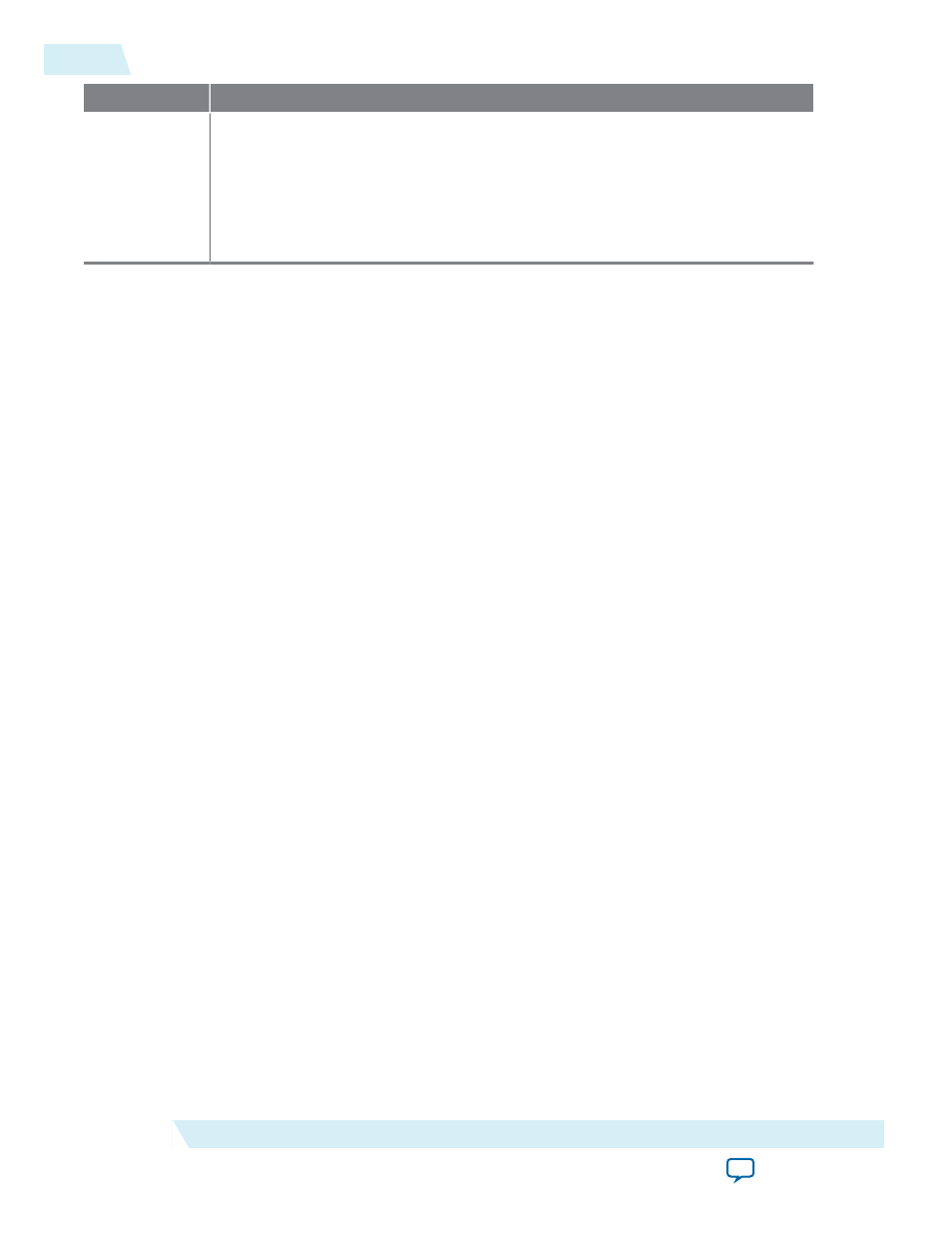
Option
Description
System reset
on timeout
(watchdog)
When this option is on, the core’s Avalon-MM slave port includes the
resetre-
quest
signal. This signal pulses high for one clock cycle whenever the timer
reaches zero resulting in a system-wide reset. The internal timer is stopped at reset.
Explicitly writing the START bit of the
control
register starts the timer.
When this option is off, the
resetrequest
signal does not exist.
Refer to the Configuring the Timer as a Watchdog Timer section.
Configuring the Timer as a Watchdog Timer
To configure the core for use as a watchdog, in the MegaWizard Interface select Watchdog in the Preset
Configurations list, or choose the following settings:
• Set the Timeout Period to the desired "watchdog" period.
• Turn off Writeable period.
• Turn off Readable snapshot.
• Turn off Start/Stop control bits.
• Turn off Timeout pulse.
• Turn on System reset on timeout (watchdog).
A watchdog timer wakes up (comes out of reset) stopped. A processor later starts the timer by writing
a 1 to the
control
register's
START
bit. Once started, the timer can never be stopped. If the internal
counter ever reaches zero, the watchdog timer resets the system by generating a pulse on its
resetre-
quest
output. The
resetrequest
pulse will last for two cycles before the incoming reset signal
deasserts the pulse. To prevent an indefinite
resetrequest
pulse, you are required to connect the
resetrequest
signal back to the reset input of the timer.
To prevent the system from resetting, the processor must periodically reset the timer's count-down
value by writing one of the period registers (the written value is ignored). If the processor fails to access
the timer because, for example, software stopped executing normally, the watchdog timer resets the
system and returns the system to a defined state.
Software Programming Model
The following sections describe the software programming model for the interval timer core, including
the register map and software declarations to access the hardware. For Nios II processor users, Altera
provides hardware abstraction layer (HAL) system library drivers that enable you to access the interval
timer core using the HAL application programming interface (API) functions.
HAL System Library Support
The Altera-provided drivers integrate into the HAL system library for Nios II systems. When possible,
HAL users should access the core via the HAL API, rather than accessing the core's registers directly.
Altera provides a driver for both the HAL timer device models: system clock timer, and timestamp timer.
System Clock Driver
When configured as the system clock, the interval timer core runs continuously in periodic mode, using
the default period set. The system clock services are then run as a part of the interrupt service routine for
25-4
Configuring the Timer as a Watchdog Timer
UG-01085
2014.24.07
Altera Corporation
Interval Timer Core
