Altera Embedded Peripherals IP User Manual
Page 305
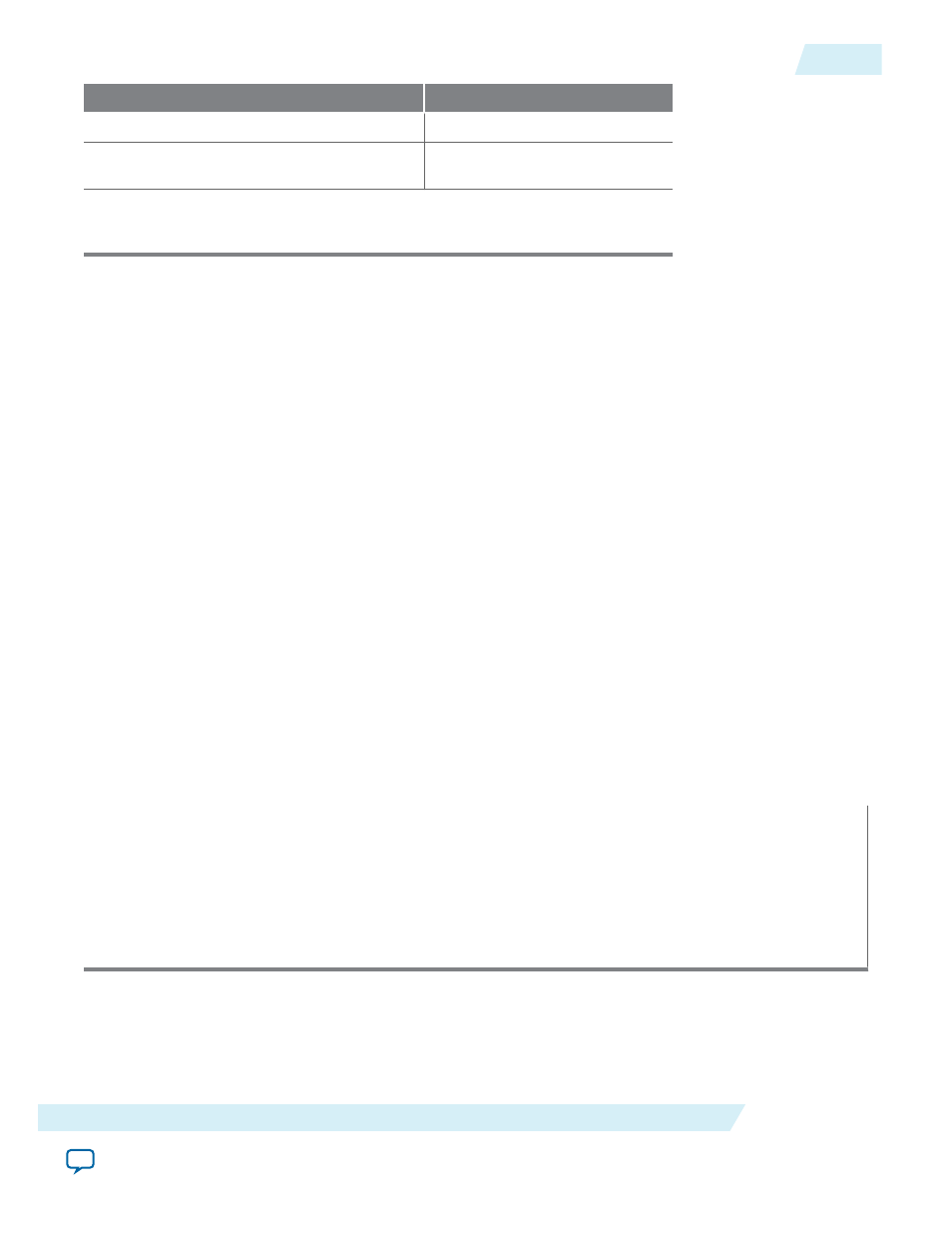
Name
Meaning
PERFORMANCE_COUNTER_SPAN
Number of hardware registers
PERFORMANCE_COUNTER_HOW_
MANY_SECTIONS
Number of section counters
1. Example based on instance name
performance_counter
.
Startup
Before using the performance counter core, invoke
PERF_RESET
to stop, disable and zero all counters.
Global Counter Usage
Use the global counter to enable and disable the entire performance counter core. For example, you might
choose to leave profiling disabled until your software has completed its initialization.
Section Counter Usage
To measure a section in your code, surround it with the macros
PERF_BEGIN()
and
PERF_END()
. These
macros consist of a single write to the performance counter core.
You can simultaneously measure as many code sections as you like, up to the number specified in Qsys.
See the Define Counters section for details. You can start and stop counters individually, or as a group.
Typically, you assign one counter to each section of code you intend to profile. However, in some
situations you may wish to group several sections of code in a single section counter. As an example, to
measure general interrupt overhead, you can measure all interrupt service routines (ISRs) with one
counter.
To avoid confusion, assign a mnemonic symbol for each section number.
Viewing Counter Values
Library routines allow you to retrieve and analyze the results. Use
perf_print_formatted_report()
to
list the results to
stdout
, as shown below.
Table 31-4: Example 1:
perf_print_formatted_report(
(void *)PERFORMANCE_COUNTER_BASE, // Peripheral's HW base address
alt_get_cpu_freq(), // defined in "system.h"
3, // How many sections to print
"1st checksum_test", // Display-names of sections
"pc_overhead",
"ts_overhead");
The example below creates a table similar to this result.
UG-01085
2014.24.07
Using the Performance Counter
31-5
Performance Counter Core
Altera Corporation
