Avalon-st sink to avalon-mm read slave, Avalon-st sink to avalon-mm read slave -4 – Altera Embedded Peripherals IP User Manual
Page 159
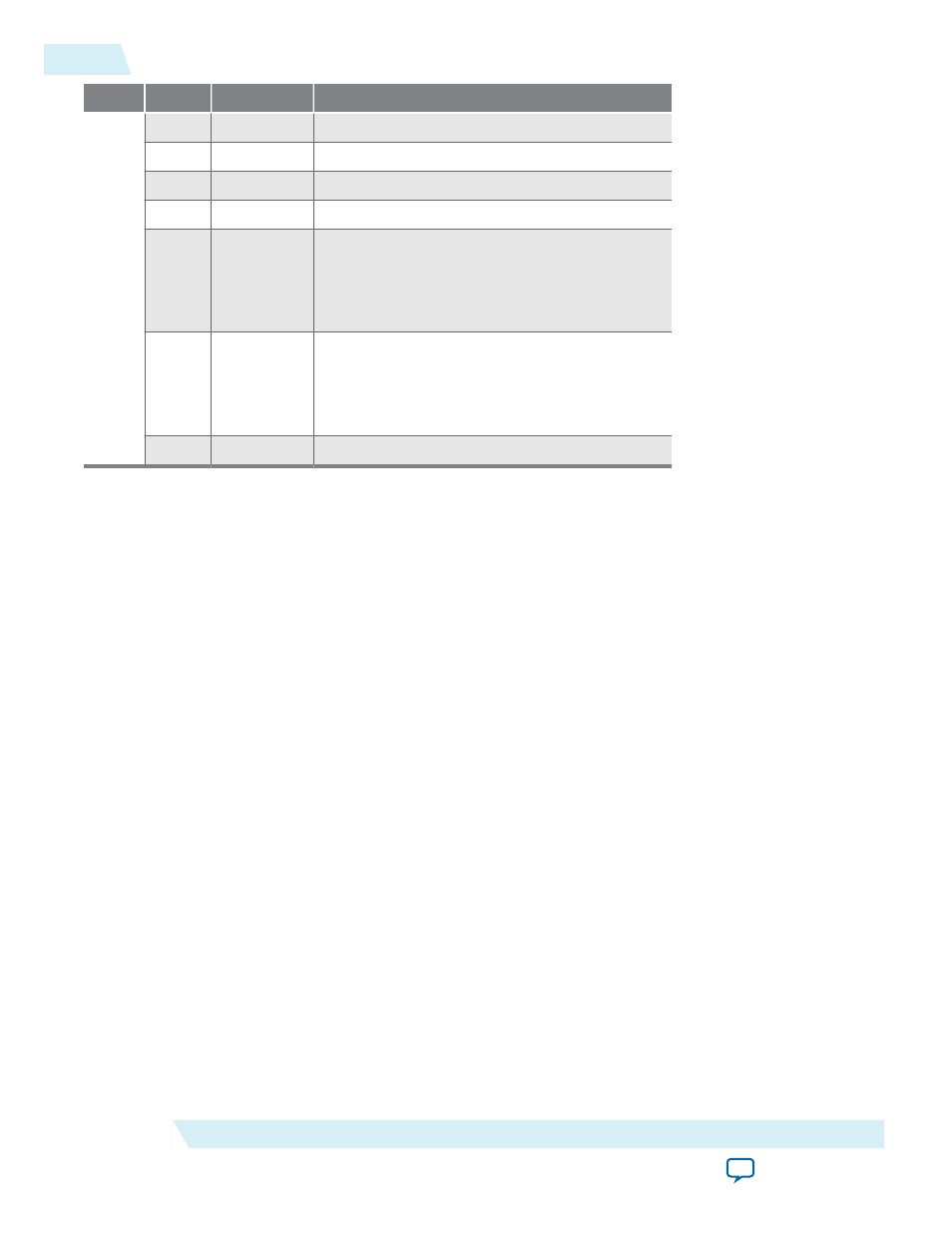
Offset
Bits
Field
Description
1
0
SOP
The value of the
startofpacket
signal.
1
EOP
The value of the
endofpacket
signal.
6:2
EMPTY
The value of the
empty
signal.
7
—
Reserved.
15:8
CHANNEL The value of the
channel
signal. The number
of bits occupied corresponds to the width of
the signal. For example, if the width of the
channel signal is 5, bits 8 to 12 are occupied
and bits 13 to 15 are unused.
23:16
ERROR
The value of the
error
signal. The number of
bits occupied corresponds to the width of the
signal. For example, if the width of the error
signal is 3, bits 16 to 18 are occupied and bits
19 to 23 are unused.
31:24
—
Reserved.
If Enable packet data is turned off, the Avalon-MM write master writes all data at address offset 0
repeatedly to push data into the FIFO core.
If Enable packet data is turned on, the Avalon-MM write master starts by writing the
SOP
,
ERROR
(optional),
CHANNEL
(optional),
EOP
, and
EMPTY
packet status information at address offset 1. Writing to
address offset 1 does not push data into the FIFO core. The Avalon-MM master then writes packet data to
address offset 0 repeatedly, pushing 8-bit symbols into the FIFO core. Whenever a valid write occurs at
address offset 0, the data and its respective packet information is pushed into the FIFO core. Subsequent
data is written at address offset 0 without the need to clear the
SOP
field. Rewriting to address offset 1 is
not required each time if the subsequent data to be pushed into the FIFO core is not the end-of-packet
data, as long as
ERROR
and
CHANNEL
do not change.
At the end of each packet, the Avalon-MM master writes to the address at offset 1 to set the
EOP
bit to 1,
before writing the last symbol of the packet at offset 0. The write master uses the empty field to indicate
the number of unused symbols at the end of the transfer. If the last packet data is not aligned with the
symbols per beat, the
EMPTY
field indicates the number of empty symbols in the last packet data. For
example, if the Avalon-ST interface has symbols per beat of 4, and the last packet only has 3 symbols, the
empty field will be 1, indicating that one symbol (the least significant symbol in the memory map) is
empty.
Avalon-ST Sink to Avalon-MM Read Slave
In this configuration seen in the figure below, the input is an Avalon-ST sink and the output is an Avalon-
MM read slave with a width of 32 bits. The Avalon-ST input (sink) data width must also be 32 bits. You
can configure input interface parameters, including: bits per symbol, symbols per beat, and the width of
the
channel
and
error
signals. The FIFO core performs the endian conversion to conform to the output
interface protocol.
An Avalon-MM master reads the data from the FIFO core. The signals are mapped into bits in the Avalon
address space. If Allow backpressure is turned on, the input (sink) interface uses the
ready
and
valid
signals to indicate when space is available in the FIFO core and when valid data is available. For the
output interface,
waitrequest
is asserted for read operations when there is no data to be read from the
FIFO core. It is deasserted when the FIFO core has data to send. The memory map for this configuration
16-4
Avalon-ST Sink to Avalon-MM Read Slave
UG-01085
2014.24.07
Altera Corporation
On-Chip FIFO Memory Core
