Operation, Timing, Operation -2 – Altera Embedded Peripherals IP User Manual
Page 132: Timing -2
Feature
Property
Channel
Not supported.
Error
Not used.
Packet
Not supported.
For more information about Avalon-ST interfaces, refer to the
.
Operation
The Avalon-ST SPI core waits for the
nSS
signal to be asserted low, signifying that the SPI master is
initiating a transaction. The core then starts shifting in bits from the input signal
mosi
. The core packs the
bits received on the SPI to bytes and checks for the following special characters:
•
0x4a
—Idle character. The core drops the idle character.
•
0x4d
—Escape character. The core drops the escape character, and
XOR
s the following byte with
0x20
.
For each valid byte of data received, the core asserts the
valid
signal on its Avalon-ST source interface
and presents the byte on the interface for a clock cycle.
At the same time, the core shifts data out from the Avalon-ST sink to the output signal
miso
beginning
with from the most significant bit. If there is no data to shift out, the core shifts out idle characters
(
0x4a
). If the data is a special character, the core inserts an escape character (
0x4d
) and XORs the data
with
0x20
.
The data shifts into and out of the core in the direction of MSB first.
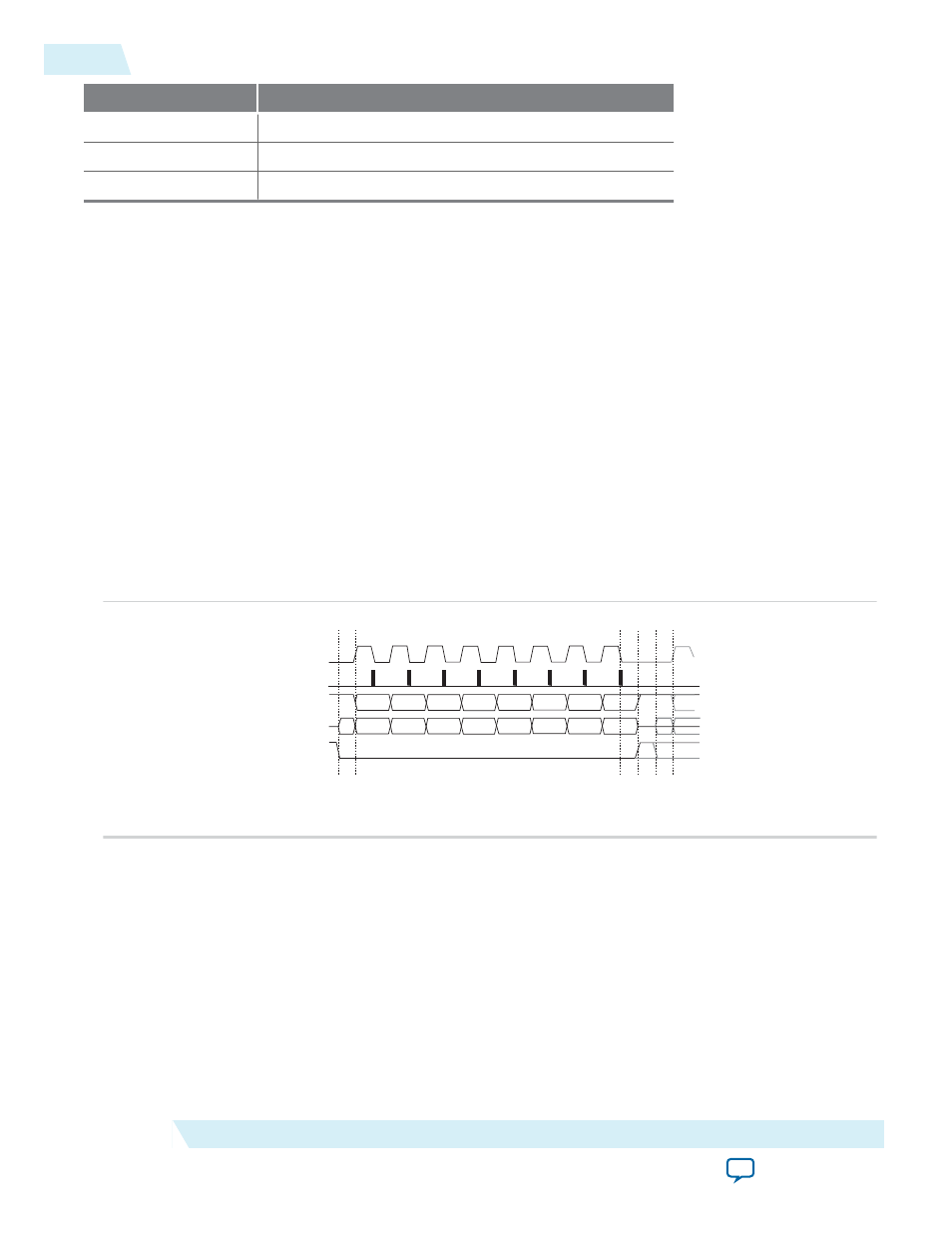
Figure 13-2: SPI Transfer Protocol
sclk
(CPOL = 0)
Sample I
MOSI/MISO
Change O
MISO pin
Change O
MOSI pin
nSS
TL
TT
TI
TL
SPI Transfer Protocol Notes:
• TL = The worst recovery time of
sclk
with respect with
nSS
.
• TT = The worst hold time for
MOSI
and
MISO
data.
• TI = The minimum width of a reset pulse required by Altera FPGA families.
Timing
The core requires a lead time (TL) between asserting the
nSS
signal and the SPI clock, and a lag time (TT)
between the last edge of the SPI clock and deasserting the
nSS
signal. The
nSS
signal must be deasserted
for a minimum idling time (TI) of one SPI clock between byte transfers. A TimeQuest SDC file (.sdc) is
13-2
Operation
UG-01085
2014.24.07
Altera Corporation
Avalon-ST Serial Peripheral Interface Core
