Avalon slave interface and registers, Read and write fifos, Jtag interface – Altera Embedded Peripherals IP User Manual
Page 59: Host-target connection, Avalon slave interface and registers -2, Read and write fifos -2, Jtag interface -2, Host-target connection -2, Figure 7-1: jtag uart core block diagram
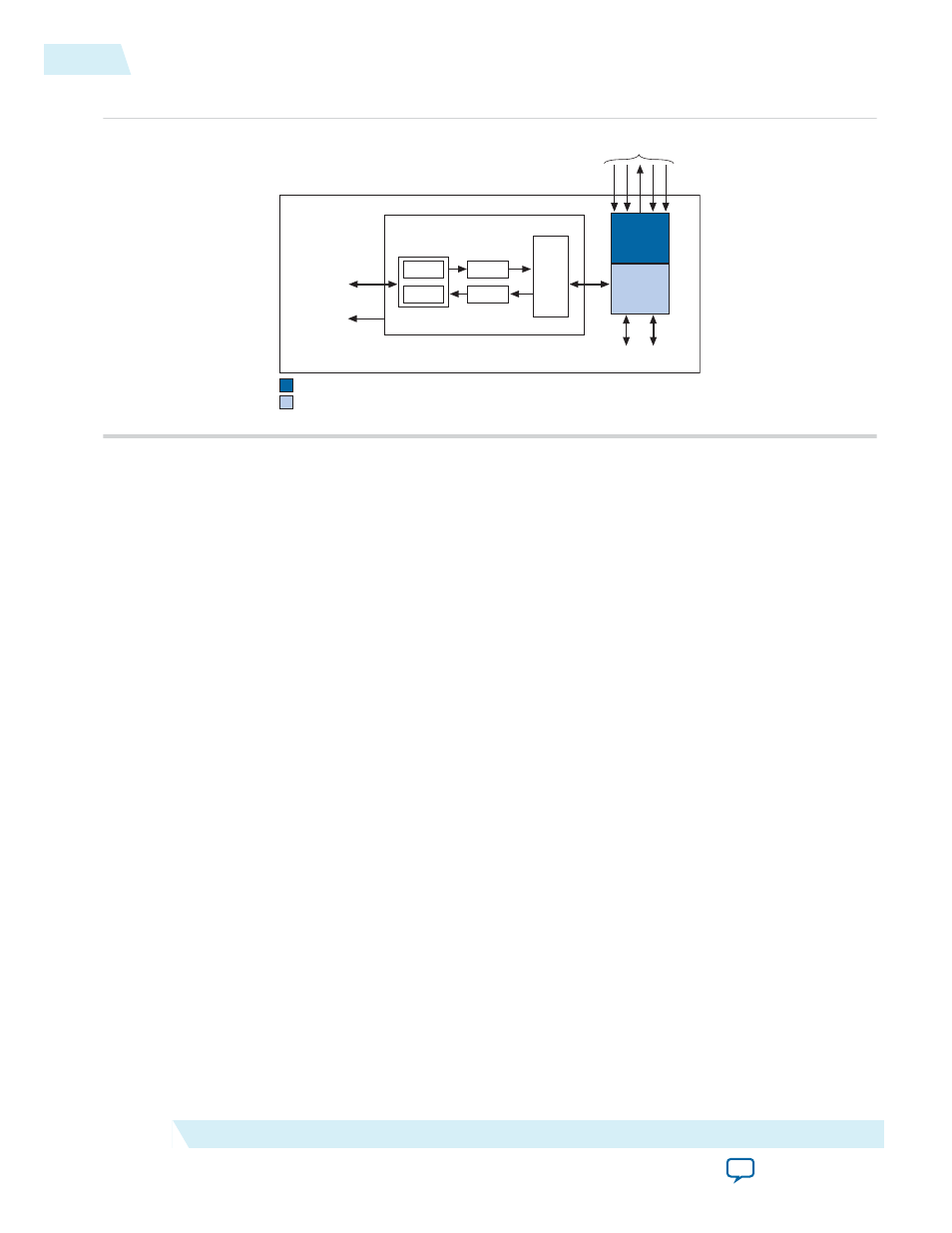
Figure 7-1: JTAG UART Core Block Diagram
Avalon-MM slave
interface
to on-chip
logic
JTAG UART Core
Registers
JTAG
Hub
Interface
IRQ
Built-In Feature of Altera FPGA
Write FIFO
Read FIFO
Data
Control
JTAG
Hub
JTAG Connection to Host PC
Altera FPGA
Other Nodes Using J
TAG Interface
(for example, another JTAG UART)
TCK
TDI
TDO
TMS
TRST
JTAG
Controller
Automatically Generated by Quartus II Software
Avalon Slave Interface and Registers
The JTAG UART core provides an Avalon slave interface to the JTAG circuitry on an Altera FPGA. The
user-visible interface to the JTAG UART core consists of two 32-bit registers,
data
and
control
, that are
accessed through an Avalon slave port. An Avalon master, such as a Nios II processor, accesses the
registers to control the core and transfer data over the JTAG connection. The core operates on 8-bit units
of data at a time; eight bits of the
data
register serve as a one-character payload.
The JTAG UART core provides an active-high interrupt output that can request an interrupt when read
data is available, or when the write FIFO is ready for data. For further details see the Interrupt Behavior
section.
Read and Write FIFOs
The JTAG UART core provides bidirectional FIFOs to improve bandwidth over the JTAG connection.
The FIFO depth is parameterizable to accommodate the available on-chip memory. The FIFOs can be
constructed out of memory blocks or registers, allowing you to trade off logic resources for memory
resources, if necessary.
JTAG Interface
Altera FPGAs contain built-in JTAG control circuitry between the device's JTAG pins and the logic inside
the device. The JTAG controller can connect to user-defined circuits called nodes implemented in the
FPGA. Because several nodes may need to communicate via the JTAG interface, a JTAG hub, which is a
multiplexer, is necessary. During logic synthesis and fitting, the Quartus
®
II software automatically
generates the JTAG hub logic. No manual design effort is required to connect the JTAG circuitry inside
the device; the process is presented here only for clarity.
Host-Target Connection
Below you can see the connection between a host PC and an Qsys-generated system containing a JTAG
UART core.
7-2
Avalon Slave Interface and Registers
UG-01085
2014.24.07
Altera Corporation
JTAG UART Core
