Nortel Networks 8000 User Manual
Page 392
Attention! The text in this document has been recognized automatically. To view the original document, you can use the "Original mode".
10 Low-speed ATM configuration
Nortel Secure Router 8000 Series
Configuration -WAN Access
•
F4 flow is the OAM cell flow in the Virtual Path Connect (VPC) and provides the
operation management and maintenance of the VP layer.
•
F5 flow is the Virtual Channel Connect (VCC) and provides the operation management
and maintenance of the VC layer.
After the OAM is activated in the F4 and F5 layers, the specified OAM cells are inserted into
the user cells to occupy certain bandwidth and to be transmitted in the same physical channel
with the cells of the other users.
The F4 and F5 flows support four types of OAM cells: FM OAM cell, PM OAM cell,
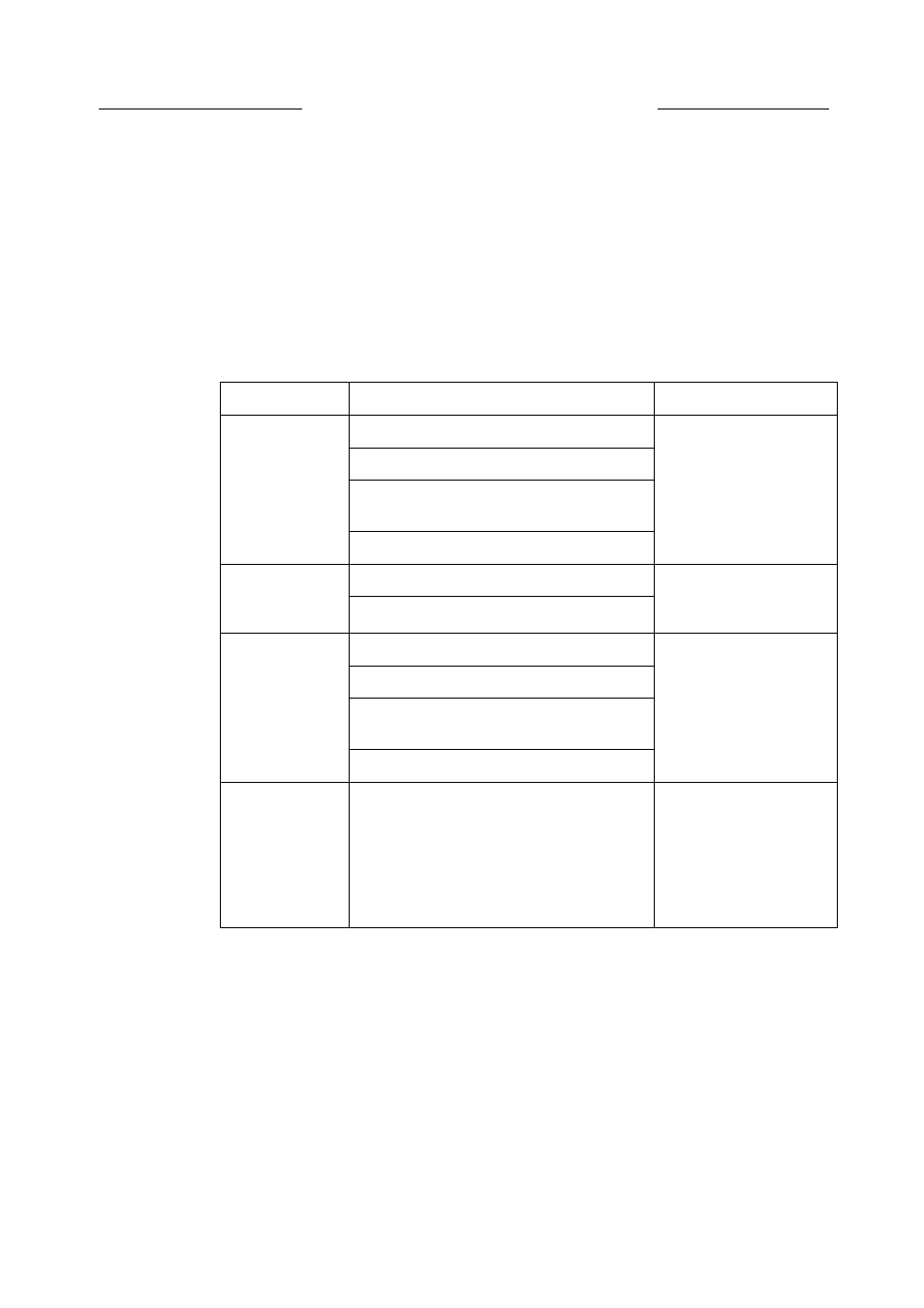
active/deactive OAM cell, and SM OAM cell, as shown in Table 10-2.
Table 10-2
OAM functions in the ATM layer
Cell Type
Content
Description
FM (Fault
Management)
AIS (reports the errors to downstream)
The FM OAM cell is
uses to detect and locate
the faults of in-service.
RDI (reports the errors to upstream)
Loopback (detects the make-bread and
locates the faults)
CC (continuity detection)
PM
(Performance
Management)
FM (forward performance monitoring)
The PM OAM cell is
used to monitor the
performance.
BM (backward performance monitoring)
Active/Deactive
Active PM (active performance monitoring)
The active/deactive
OAM cell is used to
activate/deactivate the
OAM cell.
Active CC (active continuity detection)
Deactive PM (deactive performance
monitoring)
Deactive CC (deactive continuity detection)
SM (System
Management)
Can only be used by the terminal system.
The SM OAM cell is
used to maintain and
control the different
functions among the
terminal devices and can
only exist in the
end-to-end F4/F5.
On the ATM network, the three types of the OAM functional nodes are as follows:
•
End point
The end point is defined as the point connecting the ATM network and usually refers to
the border of the ATM network. The end points are the termination points of all the
OAM cells and cannot send the OAM cells backwards. If the end points detect that the
link is faulty, they do not insert the OAM cells into the downstream node but insert the
end Remote Defect Indication (RDI) cells into the upstream nodes and notify the
upstream nodes that the upstream link is faulty.
•
Segment point
10-6
Nortel Networks Inc.
Issue 5.3 (30 March 2009)
