5 lin slave, 1 lin slave setup example, 2 lin slave receiving – Maxim Integrated MAXQ7667 User Manual
Page 151: 5 lin slave -21, 1 lin slave setup example -21, Figure 8-5. lin bus slave communication -21, Maxq7667 user’s guide
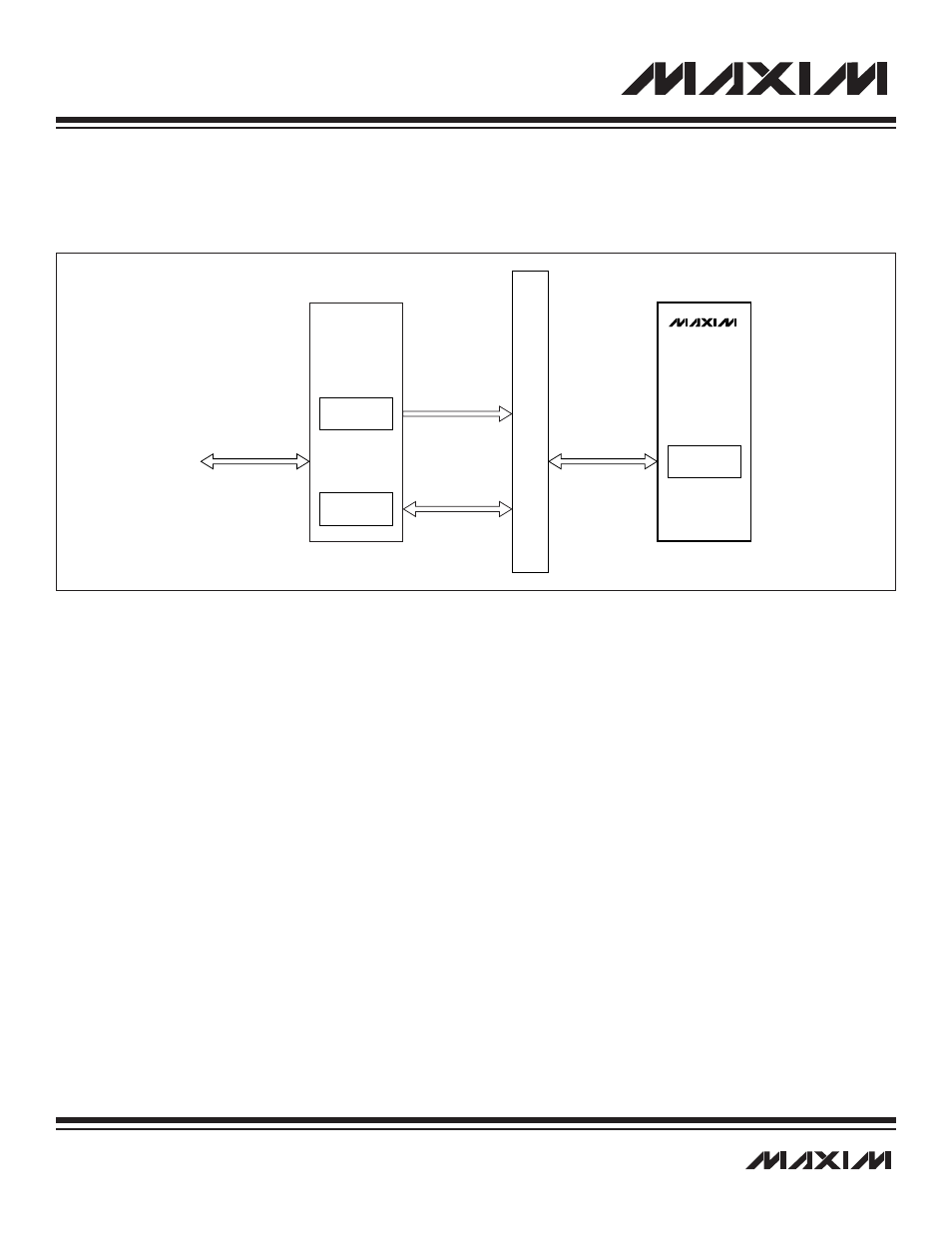
8.4.5 LIN Slave
The MAXQ7667 can be used as a LIN slave as shown in Figure 8-5. As the LIN slave, the bus master controls all traffic on the bus.
The slave must synchronize its baud rate to match the master and respond if the master’s identifier is within the slave’s address range.
8.4.5.1 LIN Slave Setup Example
To set the slave mode, the LIN or UART mode select (LUN[1:0]) bits in CNT0 are set for slave mode. To set up the slave mode, the fol-
lowing registers are set as shown.
•
Set INIT bit (CNT0.2) to 1 to force LIN into initialization state.
•
Set LUN[1:0] bits (CNT0.1:0) to 0x02 to set LIN slave mode.
•
Set AUT bit (CNT0.3) to 1 to enable automatic checksum.
•
Set INE bit (CNT0.4) to 1 to enable interrupts.
•
Set FP[1:0] bits (CNT0.6:5) to 0 to disable receive filter.
•
Set WU bit (CNT0.7) to 1 to set the peripheral to wake up.
•
Set CNT1 to 0x00.
•
Set CNT2 to 0x00.
•
Set SCON to 0x60, i.e., mode 1.
•
Clear the INIT bit (CNT0.2) by setting it to 0.
•
Set BT (0x0320 sets it for 20kBd).
8.4.5.2 LIN Slave Receiving Protected ID and Break/Sync Example
The LIN slave is now configured and ready to receive and send the break/sync sequence and identifier. The MAXQ processor must
wait until the break/sync sequence has been successfully received.
8-21
__________________________________________________________________________________________________________
MAXQ7667 User’s Guide
Figure 8-5. LIN Bus Slave Communication
LIN BUS MASTER
LIN
BUS
MASTER TASK
SLAVE TASK
WRITE
READ/WRITE
READ/WRITE
CAN BUS
LIN BUS SLAVE
SLAVE TASK
MAXQ7667
