2 lin frame, 3 lin peripheral, 2 lin frame -18 – Maxim Integrated MAXQ7667 User Manual
Page 148: 3 lin peripheral -18, Figure 8-2. lin frame format -18, Figure 8-3. lin block diagram -18, Maxq7667 user’s guide
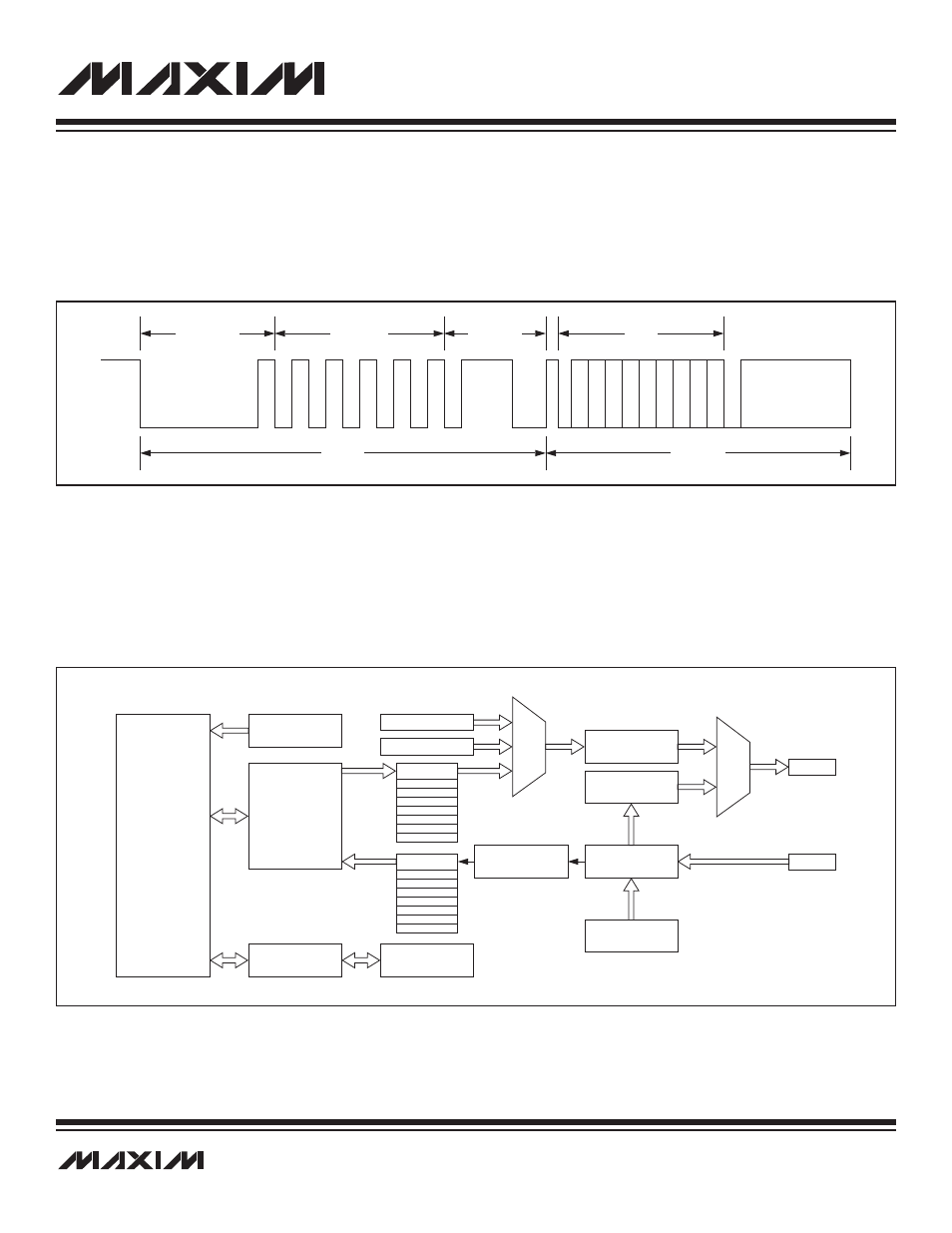
8.4.2 LIN Frame
The LIN protocol uses a single message frame to synchronize and address the nodes and to exchange data between them. The mas-
ter sets the transmission speed and sends the message header shown in Figure 8-2. The header starts with the sync/break sequence
followed by the sync field. The slave recognizes the sync/break and sets up to receive the sync field. Once the slave receives the sync
field, it adjusts its internal baud rate to match the master. The slave then examines the identifier field and acknowledges the message
if the identifier field is within the slave’s identifier range. The slave then sends data to the master.
8.4.3 LIN Peripheral
Figure 8-2 shows the dedicated LIN hardware. The MAXQ core interfaces with the LIN peripheral through the registers in Module 3.
The application software configures the LIN controller for master or slave operation and monitors the LIN interrupts for status. The appli-
cation software writes and reads the SBUF register for sending data over the LIN bus. The checksum and parity calculations are done
in hardware and require no software intervention.
The LIN control registers and bit descriptions are detailed in Module 3 of the MAXQ7667 register specification.
__________________________________________________________________________________________________________
8-18
MAXQ7667 User’s Guide
Figure 8-3. LIN Block Diagram
MAXQ
CORE
INTERRUPTS
SBUF
REGISTER
TRANSMIT REGISTER
BREAK/SYNC
GENERATOR
LIN PROTOCOL
STATE MACHINES
LIN CONTROL
REGISTERS
CHECKSUM
PARITY
Tx FIFO
FILTER/RECEIVE
REGISTER
ID BOUNDARY
REGISTER
BAUD-RATE
GENERATOR
Tx PIN
Rx PIN
Rx FIFO
Figure 8-2. LIN Frame Format
SYNC/BREAK
SYNC FIELD
IDENTIFIER
DATA
RESPONSE
HEADER
DATA n
