Ieee standards, Spanning tree configurations, Ieee802.1d spanning tree – Avaya 580 User Manual
Page 202: Spanning tree configurations -4
7-4
User Guide for the Avaya P580 and P882 Multiservice Switches, v6.1
Chapter 7
IEEE Standards
For more detailed information about the STP and RSTP, see the IEEE
802.1D standard for Media Access Control (MAC) bridges and
IEEE802.1w amendment for rapid reconfiguration.
Spanning Tree Configurations
The Avaya Multiservice switches support the following Spanning Tree
configurations:
■
IEEE 802.1D Spanning Tree
■
Per-VLAN Spanning Tree
■
Dual-Layer Spanning Tree (
■
Global Disable
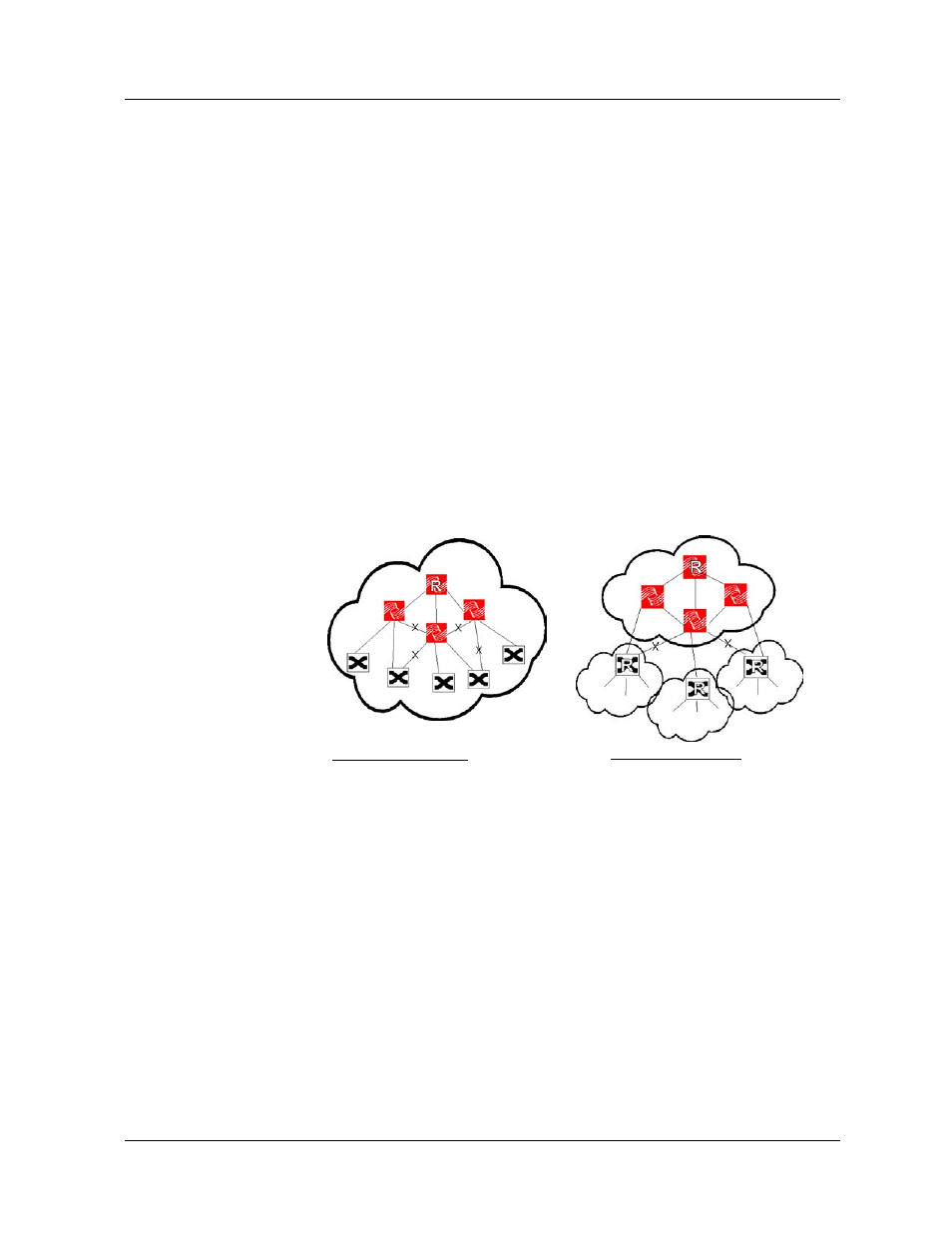
Figure 7-1. Spanning Tree Models
IEEE802.1D
Spanning Tree
All Avaya Multiservice switches participate in a Single Spanning Tree
domain in the IEEE802.1D STP mode. All ports with STP configured
belong to the same spanning tree domain and rules are as defined in
IEEE802.1D. BPDUs are as defined by 802.1D and are sent out Clear on
each link regardless of whether or not the link has a tagging method
defined. As documented in the IEEE specification, 802.1 D Spanning Tree
is intended for environments where only one VLAN is used in the network.
If you are using 802.1 D Spanning Tree in the network and have multiple
VLANs, you should set the P580 or P882 switches to run Dual-Layer
Spanning Tree.
Single 802.1D Spanning Tree
One Spanning Tree
Longer convergence
One path to and from root for all VLANs
Improper configuration
can shut down Trunk Links
Multi-Level Spanning Tree
Backbone terminates 802.1D STP
Smaller STP Domains
Quicker Convergence
VLAN Load Balancing
Interoperates w/ existing Bridge/Routers
