Static route, Default route, Configuring ipv4 routing – H3C Technologies H3C WX6000 Series Access Controllers User Manual
Page 188: Displaying the ipv4 active route table, Displaying the ipv4 active route table -2
25-2
Preference for the route: Routes to the same destination may be found by various routing protocols
or manually configured, and routing protocols and static routes have different priorities configured.
The route with the highest priority (the smallest value) will be selected as the optimal route.
Static Route
A static route is manually configured. If a network’s topology is simple, you only need to configure static
routes for the network to work normally. The proper configuration and usage of static routes can
improve network performance and ensure bandwidth for important network applications.
The disadvantage of using static routes is that they cannot adapt to network topology changes. If a fault
or a topological change occurs in the network, some routes will be unreachable. In this case, the
network administrator has to modify the static routes manually.
While configuring a static route, you can specify either the output interface or the next hop address as
needed. The next hop address cannot be a local interface’s IP address; otherwise, the route
configuration will not take effect.
Actually, it is necessary to identify next hop addresses for all route entries because the router needs to
use the next hop address of a matching entry to resolve the corresponding link layer address.
Default Route
A router selects the default route when it cannot find any matching entry in the routing table for a packet.
If there is no default route, the packet will be discarded and an ICMP packet will be sent to the source to
report that the destination is unreachable.
You can configure the default route, and some dynamic routing protocols can also generate the default
route.
An IPv4 static default route has both its destination IP address and mask configured as 0.0.0.0.
An IPv6 static default route has its destination IP address and prefix configured as ::/0.
Configuring IPv4 Routing
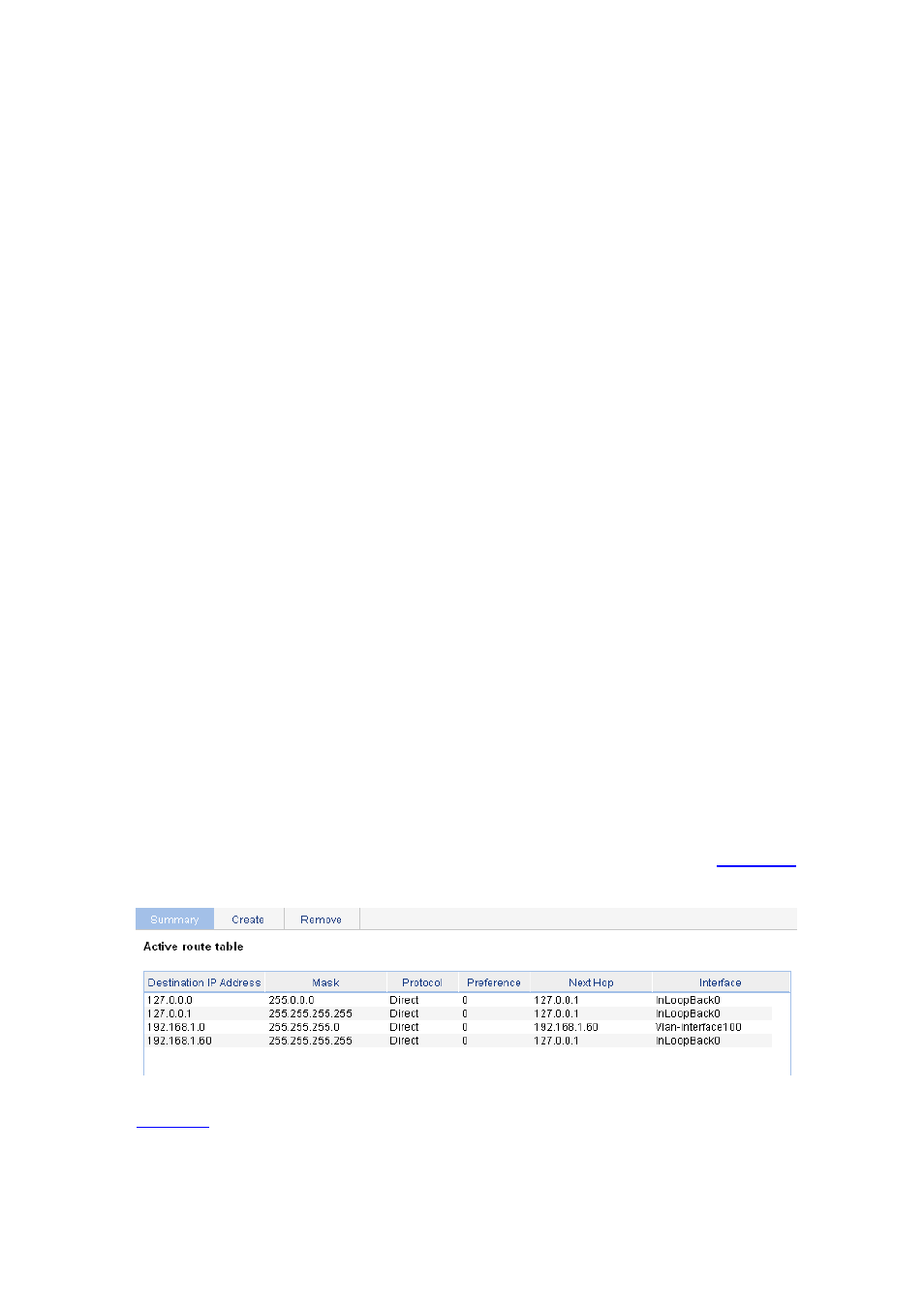
Displaying the IPv4 Active Route Table
Select Network > IPv4 Routing from the navigation tree to enter the page shown in
Figure 25-1 IPv4 active route table
describes the fields of the IPv4 active route table:
