Rockwell Automation 1757-SWKIT4000 ProcessLogix R400.0 Installation and Upgrade Guide User Manual
Page 280
Publication 1757-IN040B-EN-P - March 2002
11-28 Performance and Capacity Specifications
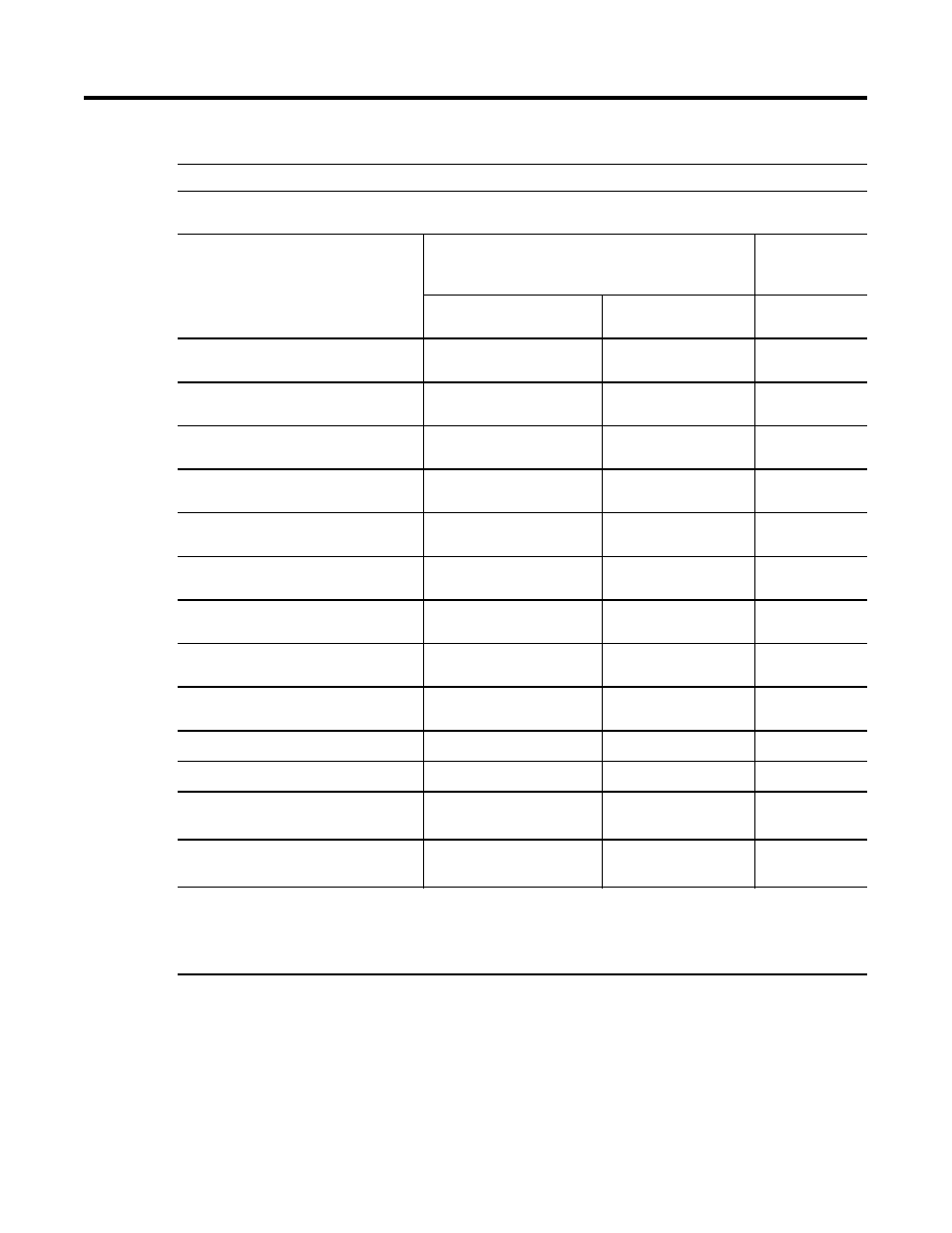
Table 11.V Typical IOM/CM/SCM Processing and Memory Resource Requirements
Typical IOM/CM/SCM Processing and Memory Resource Requirements
Total Processing Resources (PU/sec) per module are computed as = Processing Resource Consumption (PU/module
execution) / Execution Period (sec/module execution).
Typical Module Types
(FB Content in Parenthesis)
Processing Resource Consumption
(Per Module)
Memory
Resource
Usage
50/5 ms CEE Non-Redundant
(PU/Module Execution)
50 ms CEE Redundant
(PU/Module Execution)
50/5 ms CEE
(MU/Mod)
Typical I/O Module
(Average consumption of available IOMs)
0.3
0.19
0.6
Analog Digital Acquisition Module
(10 AI, 10 DataAcq FBs)
2.9
3.8
7.4
Small Analog Data Acquisition Module
(1 AI, 1 DataAcq FB)
0.47
0.43
1.0
Regulatory Control Module
(1 AI, 1 DataAcq, 1 PID, 1 AO, 6 Logic FBs)
2.8
2.8
3.9
Auxiliary Function Module
(10 Aux. FBs, such as AuxCalc, Totalizer)
4.2
5.1
13.1
Digital Data Acquisition Module
(10 DI, 10 Flag FBs)
1.2
1.2
3.1
Small Digital Data Acquisition Module
(1 DI, 1 Flag FBs)
0.22
0.14
0.6
Device Control Module
(2 DI, 2 DO, 1 DevCtl, 5 Logic FBs)
1.3
1.3
3.1
Logic Control Module
(20 Logic FBs)
1.0
1.0
3.5
Sequence Control Module A
(1)
2.0
3.0
50.4
Sequence Control Module B
(2)
2.0
3.0
63.1
Sequence Control Module with an alias
table of size 45 rows by 100 columns
(3)
2.0
3.0
150
Sequence Control Module with an alias
table of size 500 rows by 9 columns
(4)
2.0
3.0
146
These Block Libraries will consume the following extra memory when the first block is loaded to the 1757-PLX52
Controller:
•
EXCHANGE – 70 MUs
•
1757-PIM – 100 MUs
•
1797-FLEX EX + 1794- FLEX I/O – 125 MUs
•
FBUSIF – 90 MUs
(1)
1 each of Main, Hold, Stop and Abort Handlers, 10 Steps with 8 Outputs each, 10 Transitions with 5 Conditions each interspersed in all handles, 10
Recipe items, 5 History items. SCM has a total of 10 Steps and 10 Transitions among the 4 Handlers.
(2)
1 each of Main Handler, no other Handlers, 20 Steps with 4 Outputs each, 20 Transitions with 3 Conditions each interspersed in all handles, 10 Recipe
items, 5 History items. SCM has a total of 20 Steps and 20 Transitions.
(3)
1 each of Main, Hold, Stop and Abort Handlers, 10 Steps with 8 Outputs each, 10 Transitions with 5 Conditions each interspersed in all handles, 10
Recipe items, 5 History items. SCM has a total of 10 Steps and 10 Transitions among the 4 Handlers.
(4)
1 each of Main, Hold, Stop and Abort Handlers, 10 Steps with 8 Outputs each, 10 Transitions with 5 Conditions each interspersed in all handles, 10
Recipe items, 5 History items. SCM has a total of 10 Steps and 10 Transitions among the 4 Handlers.
