2] detail explanation of parameters, 2) servo gain number (parameter no.3), 3) torque filter time constant (parameter no.4) – IAI America ERC3 User Manual
Page 350
Chapter 6
Adjustment of Operation
6.3 I/O Parameter
6.3.2 MEC Mode 1, MEC Mode 2 and MEC Mode 3
340
[2] Detail Explanation of Parameters
(1) Default positioning width (in-position) (Parameter No.1)
No.
Name
Symbol
Unit
Input Range
Default factory setting
1
Default positioning width
INP
mm
0.01
(Note 1)
to 999.99
0.10
The positioning complete signal PEND/INP is output once the remaining movement amount
comes into this width.
Note 1 It is down to the minimum positioning width (L = Lead length/800).
(2) Servo gain number (Parameter No.3)
No.
Name
Symbol
Unit
Input Range
Default factory setting
3
Servo gain number
PLGO
–
0 to 31
In accordance with
actuator
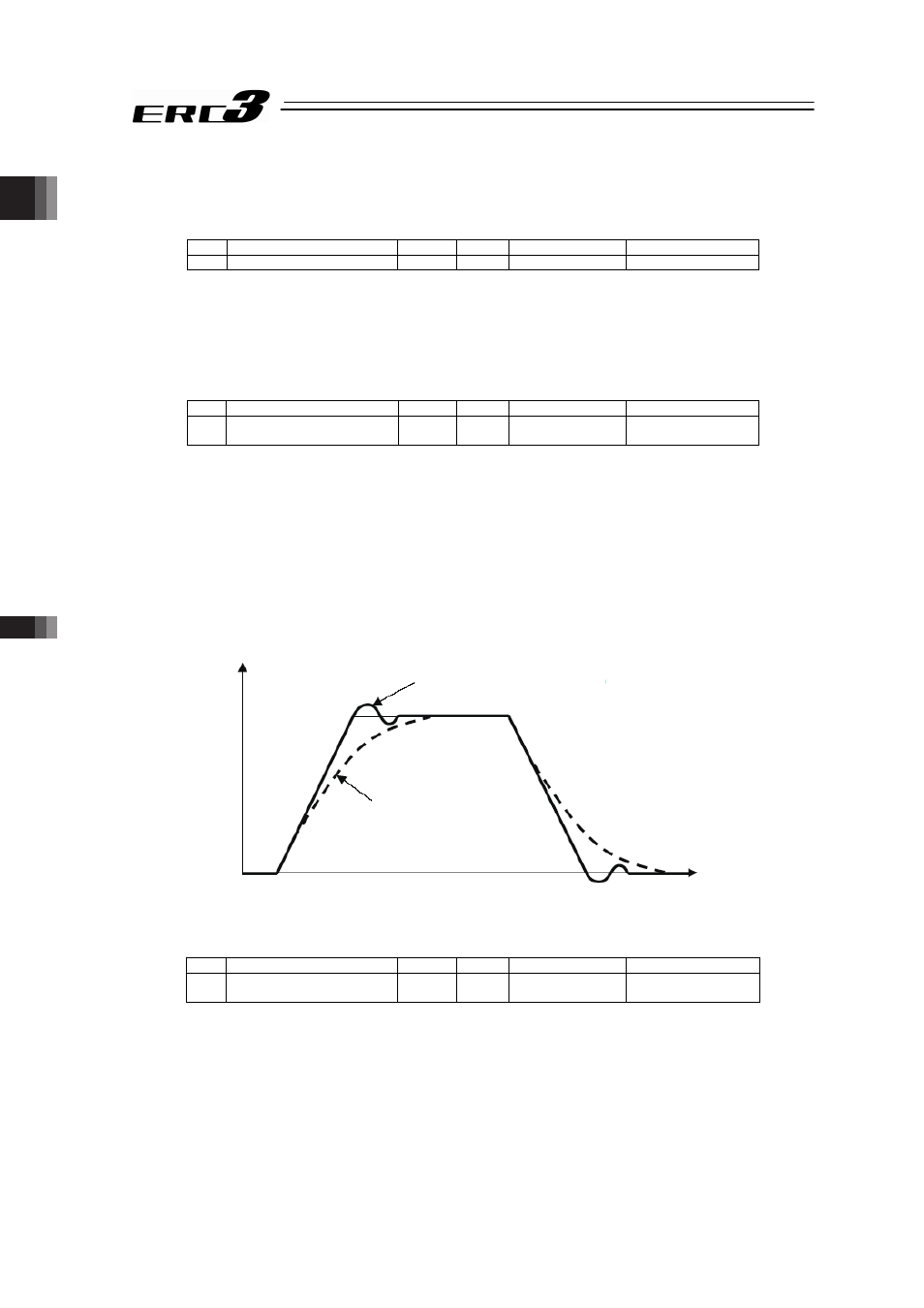
The servo gain is also called position loop gain or position control system proportion gain. The
parameter defines the response when a position control loop is used. Increasing the set value
improves the tracking performance with respect to the position command. However, increasing
the parameter value excessively increases the chances of overshooting.
When the set value is too low, the follow-up ability to the position command is degraded and it
takes longer time to complete the positioning.
For a system of low mechanical rigidity or low natural frequency (every object has its own
natural frequency), setting a large servo gain number may generate mechanical resonance,
which then cause not only vibrations and/or noises but also overload error to occur.
When the set value is high (over-shoot)
When the set value is low
Velocity
Time
(3) Torque filter time constant (Parameter No.4)
No.
Name
Symbol
Unit
Input Range
Default factory setting
4
Torque filter time constant
TRQF
–
0 to 2500
In accordance with
actuator
This parameter decides the filter time constant for the torque command. When vibrations and/or
noises occur due to mechanical resonance during operation, this parameter may be able to
suppress the mechanical resonance. This function is effective for torsion resonance of ball
screws (several hundreds Hz).
