IAI America ERC3 User Manual
Page 262
Chapter 4 Operation
4.3
O
per
at
io
n
in
P
ul
se
T
rai
n
Co
nt
ro
l M
od
e
(Ho
w
to
O
per
at
e
Pulse
Train Control
Type)
252
Time Constant
Motor Rotation
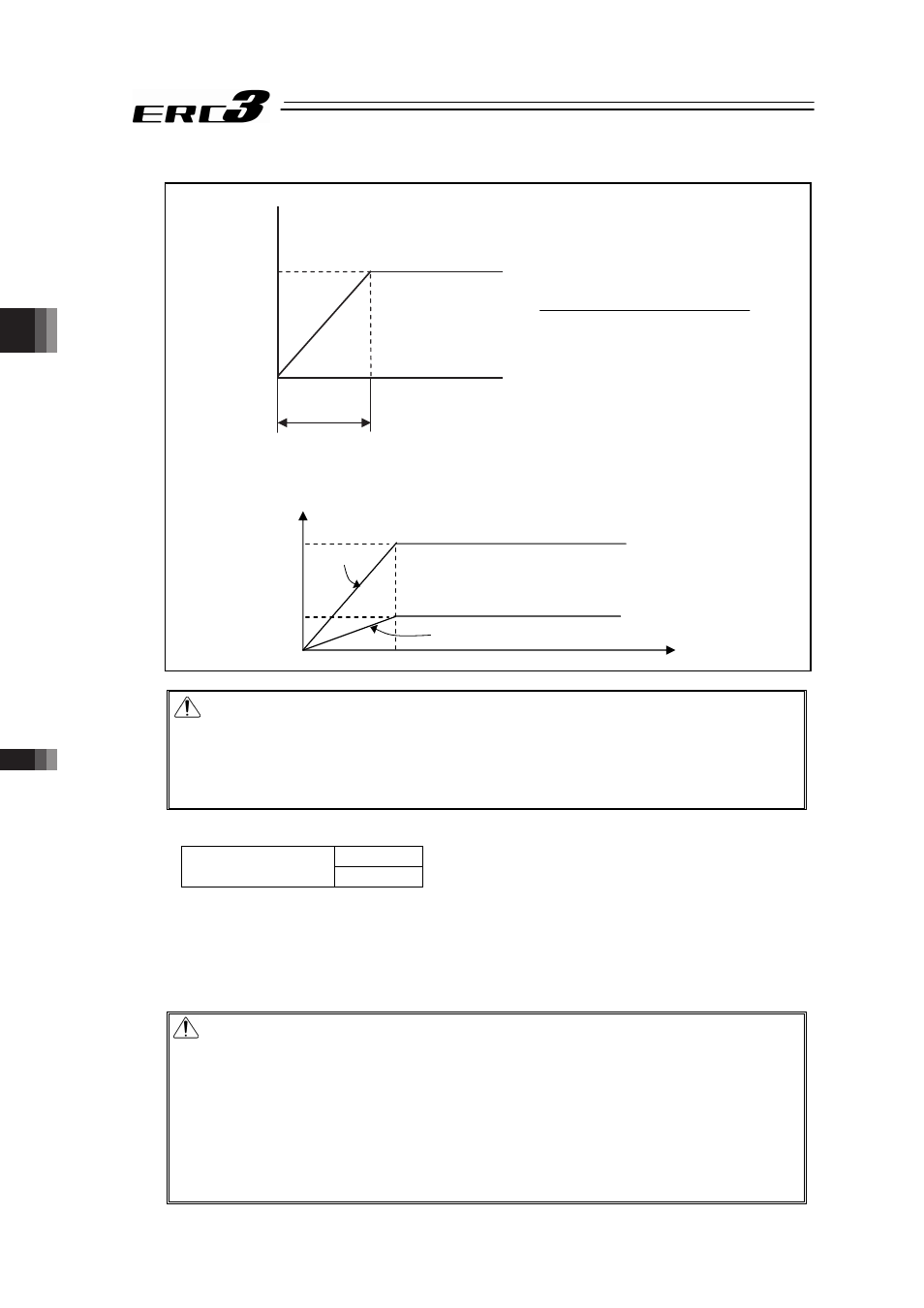
[Reference] Acceleration/deceleration settings of general positioning device
1G = 9800mm/s
2
: Acceleration capable to accelerate up to 9800mm/s per second
0.3G : Acceleration capable to accelerate up to 9800mm/s × 0.3 = 2940mm/s per
second
Caution:
• Set the acceleration/deceleration speed not to exceed the maximum
acceleration/deceleration speed of the actuator. An operation with exceeding condition
may cause a malfunction.
• Consider the electric gear ratio of the host side and that of the controller side via the
following calculation.
(2) Position complete INP
Output
PIO signal
INP
This signal will turn ON when the remaining travel pulses (accumulated pulses) on the
deviation counter enters the positioning width.
When the servo is ON, this signal turns ON when the accumulated pulses on the deviation
counter are within the number of pulses set in Parameter No.10 “Default positioning width”.
This signal is OFF while the servo is OFF.
Caution:
• This signal will turn ON when the servo turns ON (because positioning is executed at
the current position where the servo is ON).
• Since this signal turns ON only with the deviation (servo lag pulses), it could turn ON
even during an operation (even if positioning is not completed) when operating in low
speed and getting into the positioning width range if the setting of Parameter No.10
“Positioning width initial setting” is too wide. Also, even when the deviation is in this
range, the signal turns OFF when there is a change to the command pulse in 1ms.
Therefore, if operating with a command of 1kpps or less, INP may repeatedly turn ON
and OFF.
Motor Rotation [rpm] =
Velocity [mm/s]
Ball Screw • Lead Length [mm/rev]
u
60
Velocity
Time
9800mm/s
1s
1G
2940mm/s
0.3G
