IAI America ERC3 User Manual
Page 337
Chapter 6
Adjustment of Operation
6.3 I/O Parameter
6.3.1 Positioner Mode 1, Positioner Mode 2 and Pulse
Train Control Mode
327
(51) Electronic gear denominator (Parameter No.66)
This parameter is exclusively used for the pulse-train control mode.ޕ
[Refer to Chapter 4, 4.3 Operation in Pulse Train Control Mode, [9] Parameter Settings
Required for Advanced Operations]
(52) Compulsory stop input (Parameter No.67)
This parameter is exclusively used for the pulse-train control mode.ޕ
[Refer to Chapter 4, 4.3 Operation in Pulse Train Control Mode, [9] Parameter Settings
Required for Advanced Operations]
(53) Position feed forward gain (Parameter No.71)
No.
Name
Symbol
Unit
Input Range
Default factory setting
71 Feed forward gain
PLFG
–
0 to 100
0
This parameter defines the level of feed forward gain to be applied to position control.
Setting this parameter allows the servo gain to be increased and the response of the position
control loop to be improved. This is the parameter to improve the takt time and traceability even
more after fine-tuning the settings for “Servo Gain Number (Parameter No.7)”, “Velocity Loop
Proportional Gain (Parameter No.31)”, “BU velocity loop proportional gain (Parameter No.153)”,
“GS velocity loop proportional gain (Parameter No.145)” etc. This can result in shorter
positioning time.
The gain adjustment of position, speed and current loop in feedback control can directly change
the response of the servo control system. Thus, improper adjustment may cause the control
system to be unstable and further vibrations and/or noises to occur. On the other hand, since
this parameter only changes the speed command value and does not relate with the servo loop,
it neither makes the control system unstable nor generate continuous vibrations and/or noises.
However, excessive setting may generate vibrations and/or noises until the machine can follow
command values in every operation.
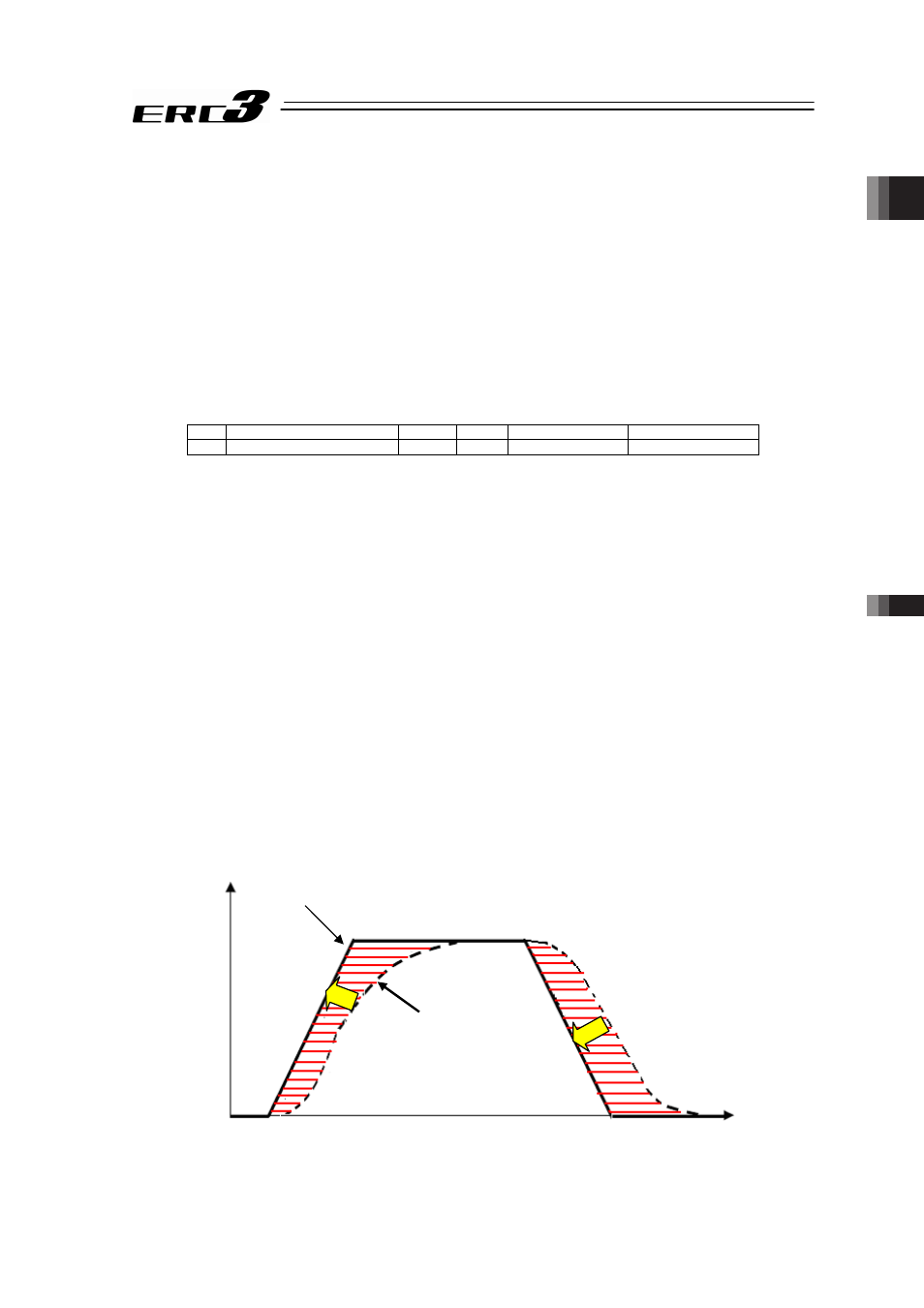
In the trapezoidal pattern, adding the value resulting from multiplying the speed command by
the feed forward gain to the speed command can reduce the delay of speed follow-up and the
position deviation.
The feedback control providing control in accordance with the result causes control delay to
occur. In contrast, compensative control is available that is not dependent on control delay.
Actual velocity
Velocity command value (trapezoidal pattern)
Velocity
Time
