Managing data links, Overview, Introduction to e1 and t1 – H3C Technologies H3C MSR 50 User Manual
Page 724: E1 and t1 voice functions
339
Managing data links
This section provides information about data link management and configuration.
Overview
Introduction to E1 and T1
Plesiochronous digital hierarchy (PDH) includes two major communications systems: ITU-T E1 system and
ANSI T1 system. The E1 system is dominant in European and some non-Europe countries. The T1 system
is dominant in USA, Canada and Japan.
E1 and T1 use the same sampling frequency (8 kHz), PCM frame length (125 μs), bits per code (8 bits)
and timeslot bit rate (64 kbps). They differ in these aspects:
•
E1 adopts A law coding/decoding of 13-segment but T1 adopts μ law coding/decoding of
15-segment.
•
Each PCM primary frame of E1 contains 32 timeslots but that of T1 contains 24 timeslots. Each
PCM primary frame of E1 contains 256 bits but that of T1 contains 193 bits. Therefore, E1 provides
2.048 Mbps bandwidth and T1 provides 1.544 Mbps bandwidth.
E1 and T1 voice functions
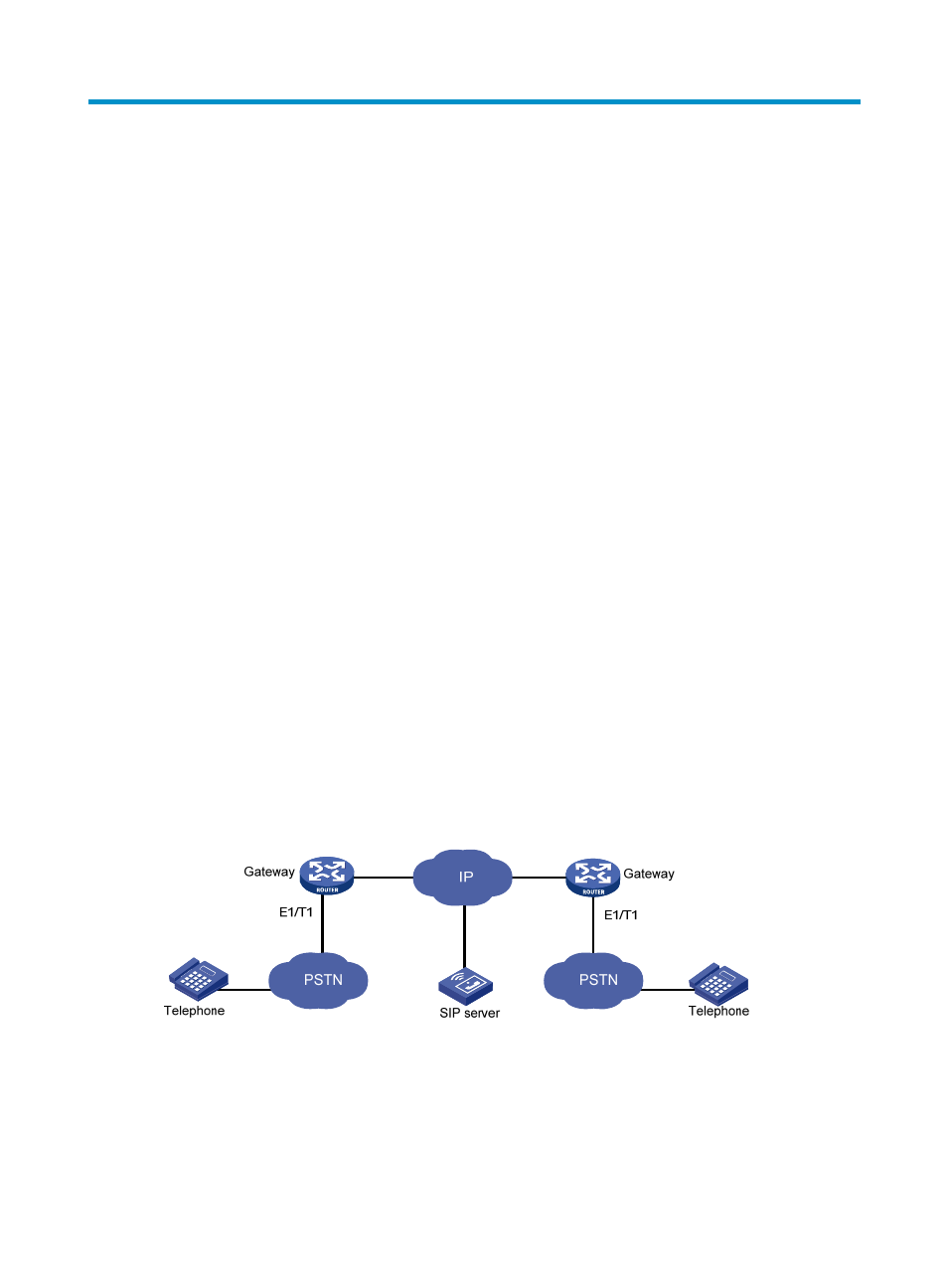
E1 and T1 mainly provide voice and signaling trunks to the PSTN. To realize this function, the router must
have E1 and T1 voice interfaces and be configured with functions required for transmitting voice over E1
and T1 lines.
The E1 and T1 voice physical interfaces are VE1 and VT1 interfaces, respectively.
PSTN and routers are connected through E1/T1 trunks, as shown in
.
Figure 733 Network diagram
E1/T1 voice transmission allows a router to provide more channels of voice communication, greatly
improving router use and broadening service range.
