Configuring wlan qos, Configuring wireless qos, Enabling wireless qos – H3C Technologies H3C MSR 50 User Manual
Page 144: Setting the svp service
123
Configuring WLAN QoS
An 802.11 network offers wireless access based on the carrier sense multiple access with collision
avoidance (CSMA/CA) channel contention. All clients accessing the WLAN have equal channel
contention opportunities, and all applications carried on the WLAN use the same channel contention
parameters. A live WLAN, however, is required to provide differentiated access services to address
diversified requirements of applications for bandwidth, delay, and jitter.
To provide applications with QoS services, IEEE developed 802.11e for the 802.11-based WLAN
architecture.
While IEEE 802.11e was being standardized, Wi-Fi Alliance defined the Wi-Fi Multimedia (WMM)
standard to allow QoS provision devices of different vendors to interoperate. WMM makes a WLAN
network capable of providing QoS services.
For more information about the WLAN QoS terminology and the WMM protocol, see WLAN
Configuration Guide in H3C MSR Series Routers Configuration Guides (V5).
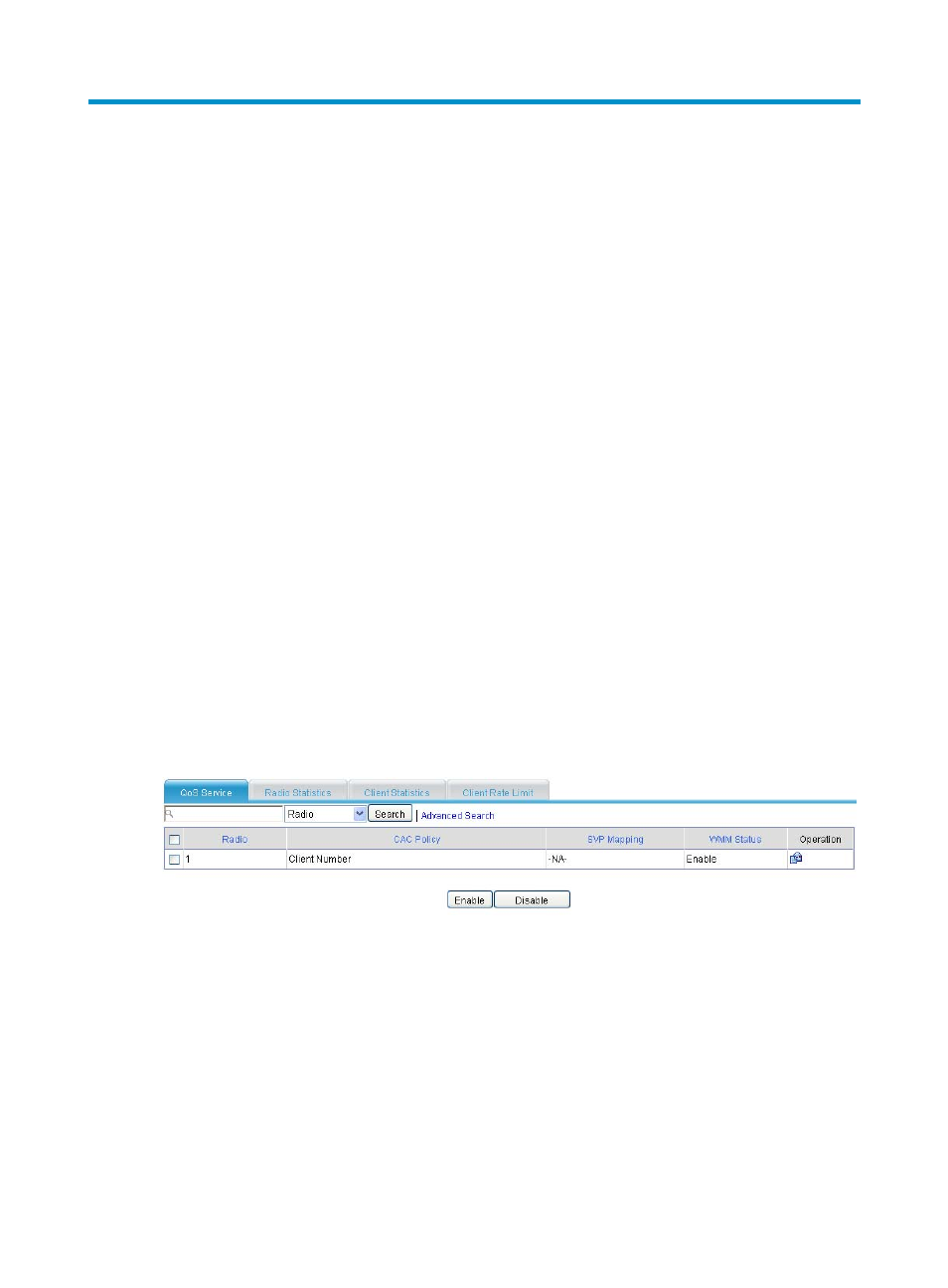
Configuring wireless QoS
Enabling wireless QoS
1.
Select Interface Setup > Wireless > Wireless QoS from the navigation tree.
2.
Click the QoS Service tab.
3.
Select the box in front of the radio unit to be configured, and click Enable.
By default, wireless QoS is enabled.
Figure 119 Enabling wireless QoS
The WMM protocol is the foundation of the 802.11n protocol. Therefore, when the radio operates in
802.11n (5 GHz) or 802.11n (2.4 GHz) radio mode, you must enable WMM. Otherwise, the associated
802.11n clients may fail to communicate.
Setting the SVP service
1.
Select Interface Setup > Wireless > Wireless QoS from the navigation tree.
2.
Click the QoS Service tab.
