Fax and modem, Protocols and standards for foip, Fax flow – H3C Technologies H3C MSR 50 User Manual
Page 589
204
Fax and modem
Traditional fax machines transmit and receive faxes over PSTN. As time passes, fax has gained wide
applications owing to its advantages such as various information, high transmission speed, and simple
operations. By far, G3 fax machines are dominant in the fax communications. A G3 fax machine adopts
the signal digitizing technology. Image signals are digitized and compressed internally, converted into
analog signals through a modem, and finally transmitted into the PSTN switch through common
subscriber lines.
FoIP means sending and receiving faxes over the Internet. Devices can provide the FoIP function after the
FoIP feature is added on the basis of the VoIP function. Because the FoIP is the Internet-based fax service,
users spend low cost for sending national and international faxes.
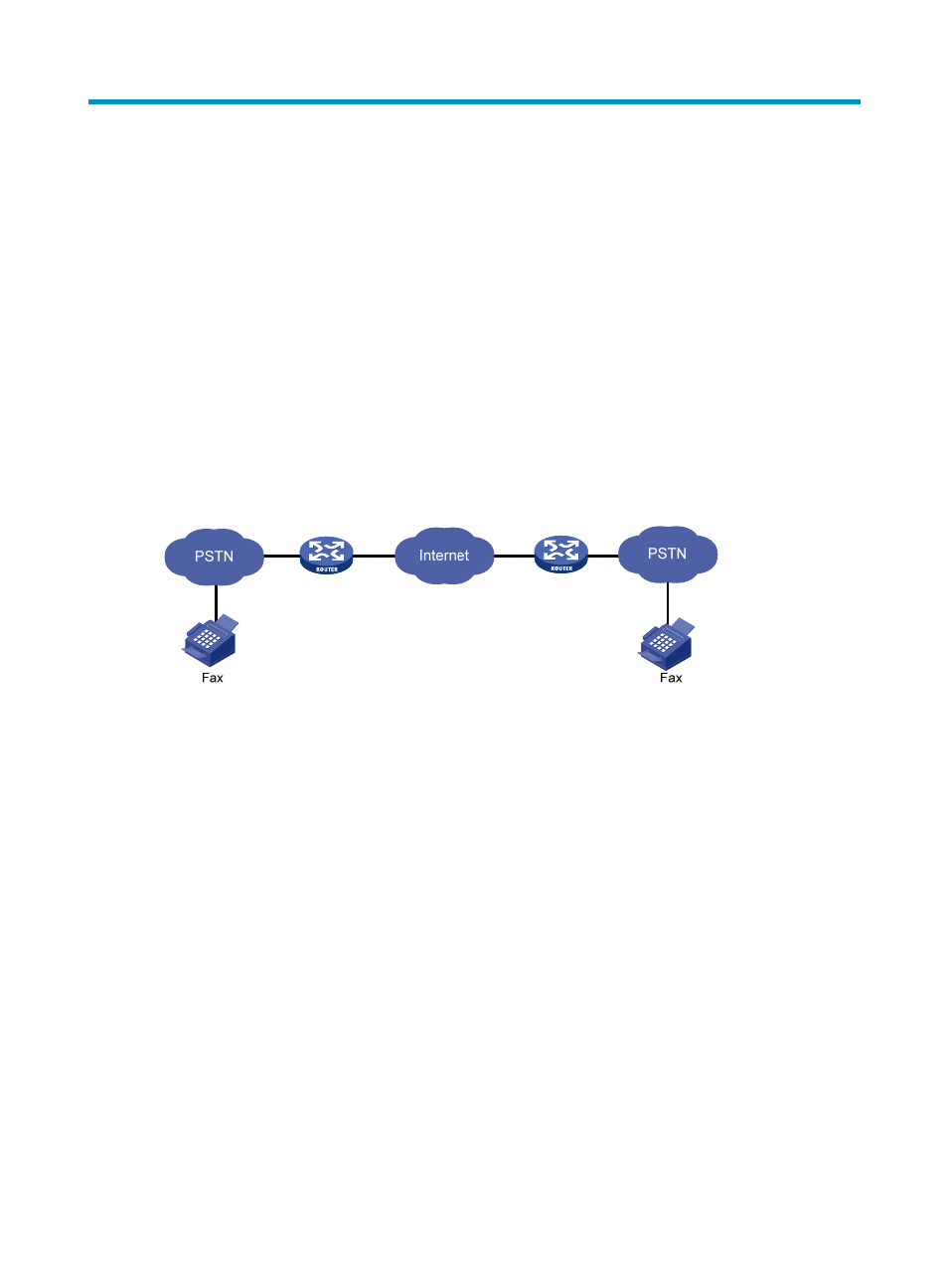
The network diagram for FoIP is similar to that for VoIP. You just replace the IP phone with a fax machine
to implement the fax function. As long as you can use IP phones, you can use the fax function. Therefore,
the fax function is very simple. The following figure shows the FoIP system structure.
Figure 598 FoIP system structure
Protocols and standards for FoIP
IP real-time fax complies with the ITU-T T.30 and T.4 protocols on the PSTN side and the H.323 and T.38
protocols on the IP network side.
•
T.30 protocol is about file and fax transmission over PSTN. It describes and regulates the
communication traffic of G3 fax machines over common telephone networks, signal format, control
signaling, and error correction to the full extent.
•
T.4 protocol is a standard protocol involving the G3 fax terminals for file transmission. It provides
a standard regulation for the G3 fax terminals on image encoding/decoding scheme, signal
modulation and speed, transmission duration, error correction, and file transmission mode.
•
T.38 protocol is about the real-time G3 fax over IP networks. It describes and regulates the
communication mode, packet format, error correction and some communication flows of real-time
G3 fax over IP networks.
Fax flow
In FoIP, the call setup, handshake, rate training, packet transfer, and call release are always in real time.
From the perspective of users, FoIP has no difference from faxing over PSTN.
