HP Array Controller HSG V8.7 Software User Manual
Page 87
Creating Storagesets
3–9
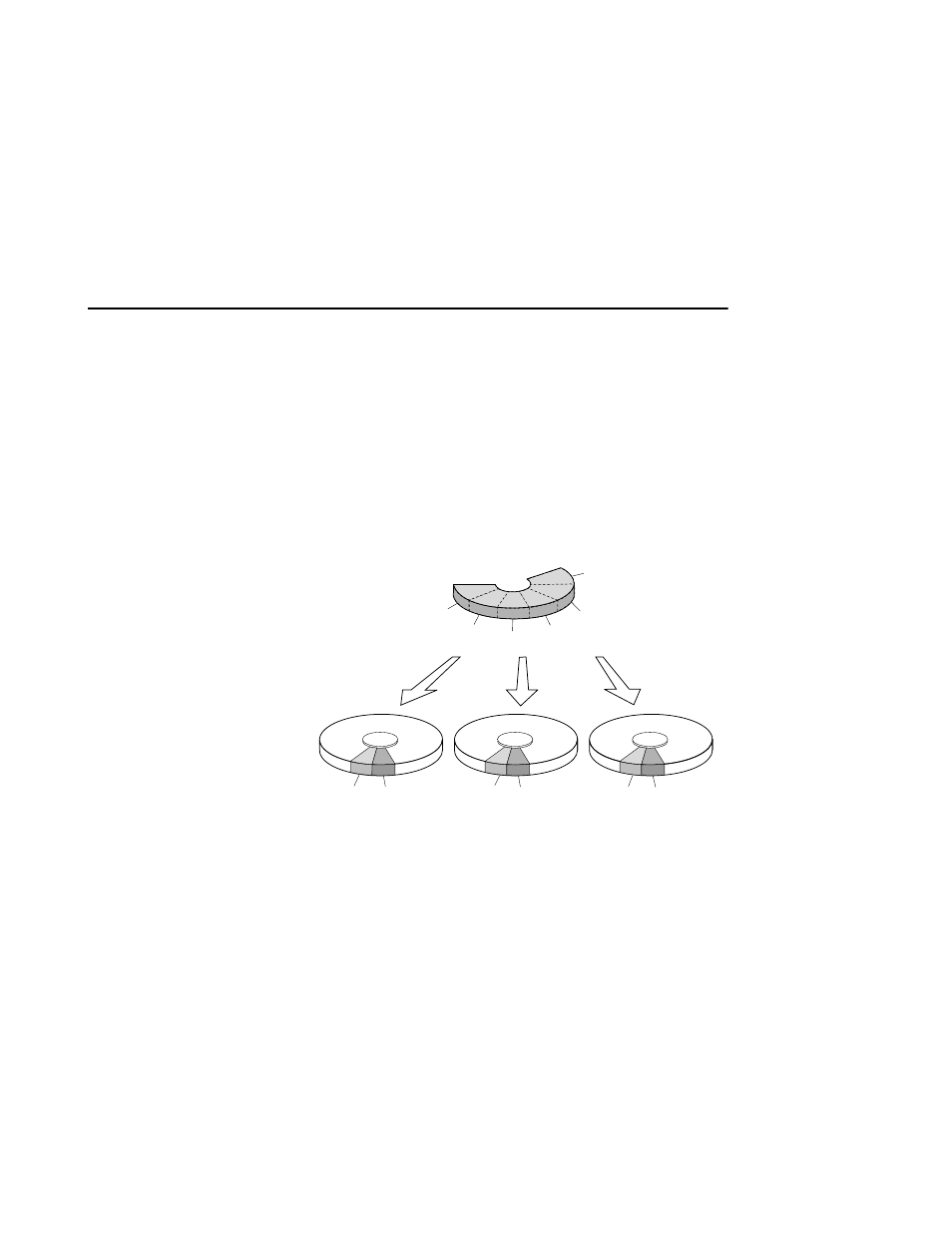
called “chunks.” These chunks are then “striped” across the disk drives
in the storageset, thereby allowing several disk drives to participate in
one I/O request to handle several I/O requests simultaneously.
For example, in a three-member stripeset that contains disk drives
10000, 20000, and 30000, the first chunk of an I/O request is written to
10000, the second to 20000, the third to 30000, the fourth to 10000, and
so forth until all of the data has been written to the drives.
Figure 3–3
Striping Lets Several Disk Drives Participate in Each
I/O Request
The relationship between the chunk size and the average request size
determines if striping maximizes the request rate or the data-transfer
rate. You can set the chunk size or let the controller set it automatically.
See “Chunk Size,” page 3–47, for information about setting the chunk
size.
A major benefit of striping is that it balances the I/O load across all of
the disk drives in the storageset. This can increase the subsystem’s
performance by eliminating the hot spots, or high localities of
reference, that occur when frequently-accessed data becomes
concentrated on a single disk drive.
Disk 10000
CXO5507A
Chunk
1
4
Disk 20000
2
5
Disk 30000
3
6
1
2
4
5
6
3
