7 managing protocol-based vlan – Fortinet 548B User Manual
Page 715
- 715 -
Non-Configurable Data
Group ID - The protected ports can be combined into a logical group. Traffic can flow between
protected ports belonging to different groups, but not within the same group. The valid range of the
Group ID is (0 to 2) .
Group Name - Displays the alphanumeric string associated with a Group ID.
Protected Ports - The display list consists of all the protected ports. It is to be noted that no traffic
forwarding is possible between two protected ports of a same group, but traffic can flow between
protected ports of different groups.
Command Buttons
Refresh - Refresh the data on the screen to obtain data on current state of the ports.
11.3.7
Managing Protocol-based VLAN
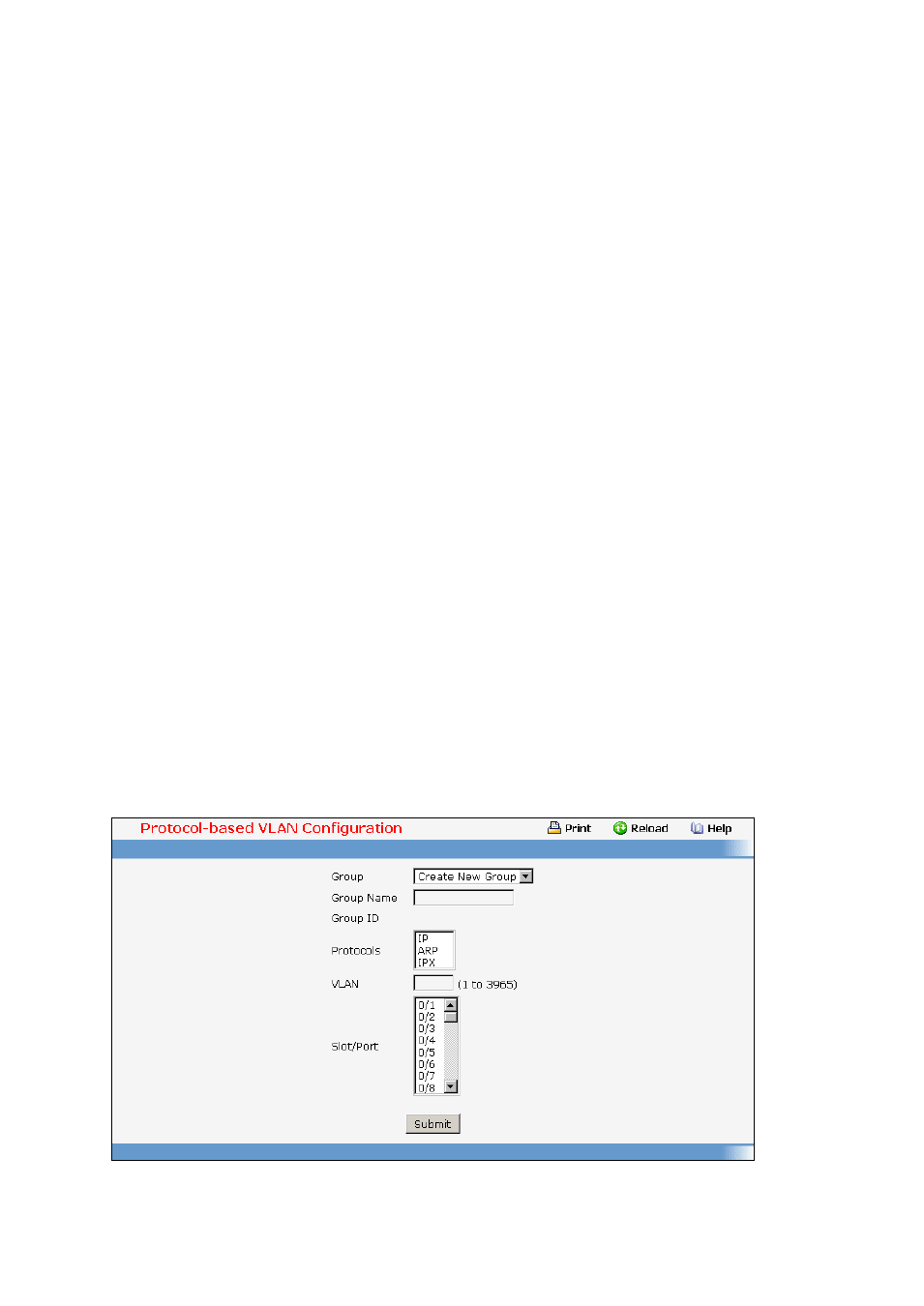
11.3.7.1 Protocol-based VLAN Configuration Page
You can use a protocol-based VLAN to define filtering criteria for untagged packets. By default, if you do
not configure any port- (IEEE 802.1Q) or protocol-based VLANs, untagged packets will be assigned to
VLAN 1. You can override this behavior by defining either port-based VLANs or protocol-based VLANs,
or both. Tagged packets are always handled according to the IEEE 802.1Q standard, and are not
included in protocol-based VLANs.
If you assign a port to a protocol-based VLAN for a specific protocol, untagged frames received on that
port for that protocol will be assigned the protocol-based VLAN ID. Untagged frames received on the
port for other protocols will be assigned the Port VLAN ID - either the default PVID (1) or a PVID you
have specifically assigned to the port using the Port VLAN Configuration screen.
You define a protocol-based VLAN by creating a group. Each group has a one-to-one relationship with a
VLAN ID, can include one to three protocol definitions, and can include multiple ports. When you create
a group you will choose a name and a Group ID will be assigned automatically.
