9 raid 50 – Avago Technologies MegaRAID Fast Path Software User Manual
Page 38
Page 38
LSI Corporation Confidential
|
July 2011
MegaRAID SAS Software User Guide
Chapter 2: Introduction to RAID
|
RAID Levels
NOTE: Other factors, such as the type of controller, can restrict the number of drives
supported by RAID 10 virtual drives.
provides an overview of RAID 10.
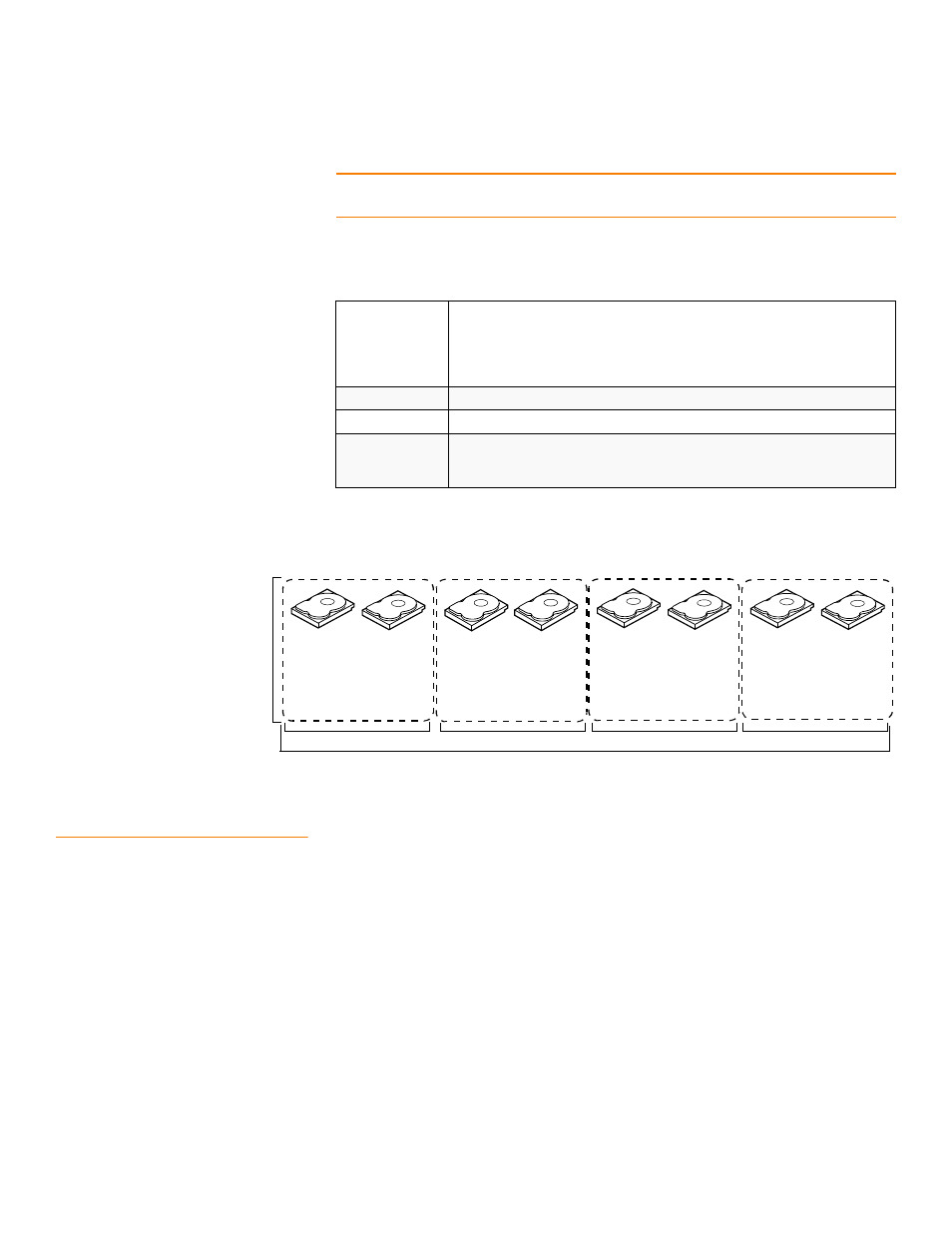
In
, virtual drive 0 is created by distributing data across four drive groups
(drive groups 0 through 3).
Figure 12:
RAID 10 Level Virtual Drive
2.5.9
RAID
50
RAID 50 provides the features of both RAID 0 and RAID 5. RAID 50 includes both parity
and disk striping across multiple drive groups. RAID 50 is best implemented on two
RAID 5 drive groups with data striped across both drive groups.
RAID 50 breaks up data into smaller blocks and then stripes the blocks of data to each
RAID 5 disk set. RAID 5 breaks up data into smaller blocks, calculates parity by
performing an exclusive-or on the blocks and then writes the blocks of data and parity
to each drive in the drive group. The size of each block is determined by the stripe size
parameter, which is set during the creation of the RAID set.
RAID level 50 can support up to 8 spans and tolerate up to 8 drive failures, though less
than total drive capacity is available. Though multiple drive failures can be tolerated,
only one drive failure can be tolerated in each RAID 5 level drive group.
Table 12: RAID 10 Overview
Uses
Appropriate when used with data storage that needs 100 percent
redundancy of mirrored drive groups and that also needs the enhanced I/O
performance of RAID 0 (striped drive groups.) RAID 10 works well for
medium-sized databases or any environment that requires a higher degree
of fault tolerance and moderate-to-medium capacity.
Strong Points
Provides both high data transfer rates and complete data redundancy.
Weak Points
Requires twice as many drives as all other RAID levels except RAID 1.
Drives
4 to 32 in multiples of 4 — The maximum number of drives supported by the
controller (using an even number of drives in each RAID 10 virtual drive in
the span).
Segment 1
Segment 1
Duplicate
Segment 2
Segment 3
Duplicate
Segment 4
Duplicate
Segment 3
Segment 4
Segment 5
Segment 6
Segment 7
Segment 8
Segment 5
Duplicate
Segment 6
Duplicate
Segment 7
Duplicate
Segment 8
Duplicate
Segment 2
Duplicate
...
...
...
...
RAID1
RAID1
RAID1
RAID1
RAID 10
RAID 0
- MegaRAID SAS 9240-4i MegaRAID SAS 9240-8i MegaRAID SAS 9260-16i MegaRAID SAS 9260-4i MegaRAID SAS 9260-8i MegaRAID SAS 9261-8i MegaRAID SAS 9280-16i4e MegaRAID SAS 9280-4i4e MegaRAID SAS 9280-8e MegaRAID SafeStore Software MegaRAID SAS 9361-4i MegaRAID SAS 9361-8i MegaRAID SAS 9266-4i MegaRAID SAS 9266-8i MegaRAID SAS 9270-8i MegaRAID SAS 9271-4i MegaRAID SAS 9271-8i MegaRAID SAS 9271-8iCC MegaRAID SAS 9286-8e MegaRAID SAS 9286CV-8e MegaRAID SAS 9286CV-8eCC MegaRAID CacheCade Pro 2.0 Software MegaRAID SAS 9341-4i MegaRAID SAS 9341-8i MegaRAID SAS 9380-8e MegaRAID SAS 9380-4i4e
